Economic & Commercial Laws Practice Paper
advertisement

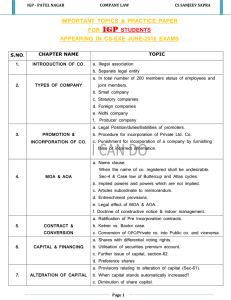
IGP Patel CS SANJEEV SAPRA Nagar ECONOMIC & COMMERCIAL LAWS Important Topics & Practice Paper For IGP STUDENTS Appearing In CS-EXE JUNE-2016 Exams FEMA 1. List the transactions which require prior approval of RBI. 2. Prohibition on drawl of foreign exchange for certain transactions. 3. Limits on amount of foreign exchange facility for individual. 4. Limits on amount of foreign exchange facility for other than individual. 5. Liberalized Remittance Scheme (LRS). FDI 1. FPI and QFI meaning. 2. What are the forms in which business can be conducted by a foreign company in India? 3. Remittance reporting. 4. Overseas Investment outside India. 5. Limits on Overseas Investment outside India. 6. Permission for purchase/acquisition of foreign securities. 7. Establishment in India of branch/liaison/project office and permitted activities. 8. Time limit for surrender of realised foreign exchange. 9. Write short note on the following: (i) Compounding of Contraventions (ii) Directorate of Enforcement (iii) Appellate Tribunal FOREIGN CONTRIBUTION (REGULATION) ACT, 2010 1. State the provisions of Prohibition to accept foreign contribution. 2. Foreign hospitality. 3. Organizations/individuals specifically debarred from receiving foreign contribution? 4. Discuss the provisions of FCRA relevant to exemptions from acceptance of foreign contribution. IGP Patel CS SANJEEV SAPRA Nagar FTP 1. What are the objectives of foreign trade policy? 2. State the general provisions regarding imports and exports. 3. Explain Importer-Exporter Code (IEC) Number and procedure for application for Grant of IEC Number. 4. Write short note on (a) Towns of Export Excellence (TEE) (b) Board of Trade SEZ 1. What is Special Economic Zone and its salient features? Who can set up SEZs? 2. What is the procedure for Setting up of Unit in SEZ. 3. What do you mean by Offshore Banking Unit? 4. Special Economic Zones are growth engines. Discuss. COMPETITION ACT 1. What is competition in the market? and why do we need it? 2. Write short note on (a) Monopolistic trade practice (b) Restrictive trade practices (c) Unfair trade practices 3. Define and discuss the Relevant Market, Relevant Geographic Market, and Relevant Product Market. 4. What do you mean by Cartel state the conditions that are conducive to cartelization. 5. What is an anti-competitive agreement? 6. What is dominant position? What constitutes abuse of dominance? 7. What is combination? 8 Write short note on: (a) tie-in agreement; (b) exclusive supply agreement; (c) exclusive distribution agreement; (d) refusal to deal; (e) resale price maintenance (f) Competition advocacy IGP Patel CS SANJEEV SAPRA Nagar 9. While determining whether an agreement has appreciable adverse effect on competition, which are the factors are taken in consideration by the Commission? 10. Power of Commission to regulate its procedure. 11. Power of Director General to regulate its procedure. CONSUMER PROTECTION ACT 1. Which are the basic rights of consumers that are sought to be promoted and protected ? 2. Contract of Service and Contract for Service. 3. Write a note on the following: (i) Complaint and Complainant (ii) Deficiency in service (iii) Consumer 4. Explain consumer protection councils under the consumer Act in India. 5. Explain the redressal machinery under the Consumer Protection Act and their juridiction. 6. What is Limitation Period for Filing of Complaint and appeal under the Consumer Protection Act. 7. What are the Nature and Scope of Remedies under the Consumer Protection Act? INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS (IPR) 1. Intellectual and Industrial property. PATENTS 1. Which are not inventions within the meaning of the Patent Act. 2. Does a Patent obtained in India give protection worldwide? 3. Discuss in detail the provisions of the Patents Act in relation to compulsory licences. 4. Write short note on the following: (i) Invention and Inventive step. (ii) Patent agent. (iii) Deceptive Similarity (iv) Opposition of patent 5. Mention the cases that do not qualify to be called as inventions, within the meaning of the Patents Act, 1970? 6. Discuss the grounds on which the registration of a patent can be refused? 7. Elaborate the provisions relating to infringement of patent. IGP Patel CS SANJEEV SAPRA Nagar TRADE MARK 1. What is a trade mark and its functions? Which are Prerequisites for a trade mark to be registered? 2. Grounds for refusal to register trademark. 3. Infringement of trademark. 4. State “Registered user” under the Trade Marks Act, 1999. 5. Who are the beneficiaries from a trade mark? 6. Trademark is decided by the date of usage of the mark by a person in business transactions. Comment with decided case of Uniply Industries. 7. Explain the 'Assignment of a trade mark' and 'transmission of a trade mark' under the Trade Marks Act, 1999. COPYRIGHT 1. What is Assignment of copyright and Mode of assignment. 2. Which are the common copyright infringements? Certain acts do not constitute infringement of copyright under Copyright Act, 1957. Discus 3. Discuss in detail the Copyright Board. 4. Elaborate the provisions relating to certain exception to infringement have been stipulated by the Copyright Act 5. Compulsory licensing of copy rights. GEOGRAPHICAL INDICATION 1. How a geographical indication is different from a trade mark? 2. How long the registration of Geographical Indication is valid? 3. When is a registered Geographical Indication said to be infringement? DESIGN ACT 1. What is meant by ‘Design’ under the Designs Act, 2000? 2. What is the object of registration of Designs? and the effect of registration of design? 3. What is piracy of a Design? IGP Patel CS SANJEEV SAPRA Nagar ARBITRATION AND CONCILIATION ACT, 1996 1. State form and contents of an arbitral award. 2. What are the grounds to challenge the appointment of an Arbitrator under the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996? Discuss. 3. What are the grounds for setting aside of an arbitral award under the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996? 4. Alternative dispute resolution (ADR) TRANSFER OF PROPERTY ACT, 1882 1. Write short note on: (a) Absolute Interest (b) Reversion and Remainder (c) Vested and Contingent Interest (d) Transfer by ostensible owner or doctrine of holding out (e) Doctrine of feeding the grant by estoppels (f) Doctrine of fraudulent transfer (g) Doctrine of part-performance (h) Rule against perpetuity (i) Doctrine of Lis pendens. 2. Restraint on transfers or rule against inalienability 3. What is the subject matter of transfer under the T.P. Act? Discuss properties which cannot be transferred. 4. Give definition and nature, essentials and types of a mortgage. 5. Give Distinction between (a) Mortgage and Charge. (b) English mortgage and mortgage by conditional sale. 6. What is the rule against perpetuity? 7. State ‘Actionable claim’ under the Transfer of Property Act, 1882. LAW RELATING TO STAMPS 1. Write short notes on (a) Conveyance (b) Instrumeny (c) Bill of Exchange (d) Denoting duty 2. State the instruments chargeable with duty and Time of stamping of instruments. IGP Patel CS SANJEEV SAPRA Nagar 3. Are securities dealt in depository not liable to stamp Duty, comment. 4. Can Parliament reduce the stamp duty on an agreement? 5. What are the modes of cancellation of adhesive stamps? LAW RELATING TO CONTRACT 1. A minor’s contract is void ab initio, yet he enjoys special status under the Indian Contract Act, 1872. Explain. 2. Explain considerations to be taken collaboration/multinational Agreement. for contracts under Joint venture/foreign 3. The essence of every agreement is that there ought be free consent on both the sides. Discuss. 4. The law does not compel the impossible, comment. 5. How does a binding contract differ from other agreements? THE PREVENTION OF MONEY-LAUNDERING ACT, 2002 1. What influence does money laundering have on economic development? And role of The Financial Action Task Force (FATF). 2. What are the obligation of Banking Companies, Financial Institutions and Intermediaries? 3. What are the objectives of KYC guidelines and when does KYC norms apply? 4. Define the term money laundering and explain the process of money laundering. ESSENTIAL COMMODITIES ACT, 1955 1. Explain the Powers of Central Government to control production, supply and distribution etc., of essential commodities. 2. Explain the seizure and confiscation of essential commodities under the Essential Commodities Act, 1955. 3. Explain Mens rea with decided case under Essential Commodities Act, 1955. THE LEGAL METEOROLOGY ACT, 2009 1. Meaning of Legal Metrology. 2. Power of inspection, seizure 3. Declarations on pre-packaged commodities. IGP Patel CS SANJEEV SAPRA Nagar 4. Write short note on Counterfeit. 5. Every non-standard weight and measure used in the course of trade is liable to be forfeited. Comment. SOCIETIES REGISTRATION ACT, 1860 1. Explain the Procedure for Registration of Society. 2. State the status of a society registered under Societies Registration Act, 1860 3. Provisions for vesting of property of the Society 4. Dissolution of Society and distribution of properties. LAW RELATING TO TRUST 1. Classification of trust. 2. How a trust is created and by whom it is created? 3. Briefly discuss the provisions relating to rights and duties of trustees. 4. Who is a beneficiary? What are his rights and liabilities? 5. Discuss about the classification of Trusts. 6. Write short notes on (i) Extinction of a trust (ii) Revocation of a trust (iii) Doctrine of Cy Pres INDUSTRIES DEVELOPMENTAND REGULATION 1. What are the objectives of Industrial Policy of the government? 2. What do you mean by ’New Article’ under the Act? 3. Role of Central Advisory Council and development council. 4. What is an industrial license? Under what circumstances an industrial license can be revoked? 5. What do you mean by the term “Substantial Expansion”? and License for Effecting Substantial Expansion. 6. When can Central Government order Investigation into Industrial Undertakings?. 7. List out any five industries specified in First Schedule of the Act. IGP Patel CS SANJEEV SAPRA Nagar THE MICRO, SMALL AND MEDIUMENTERPRISES DEVELOPMENT ACT, 2006 1. The role of micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in the economic and social development of the country. 2. Classification of enterprises under MSME 3. Explain Memorandum of micro, small and medium enterprise. 4. Measures for promotion, development and enhancement of competitiveness 5. Delayed payments to micro and small enterprises. 6. What do you mean by the day of acceptance and ay of deemed acceptance?? LAW RELATING TO POLLUTION CONTROL AND ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION 1. Briefly explain the Concept of Sustainable Development. 2. Mention the powers of the central government to protect and improve the quality of environment under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986. 3. Write short notes on (a) Carbon credit (b) Environmental Audit 4. Environmental clearance and location of industries. 5. Briefly explain the objective of Environment Protection Act, 1986? 6. Explain no fault liability and compulsory insurance. 7. Explain Substantial question relating to environment. 8. Enumerate the powers and functions of National Green Tribunal? 9. List out the heads under which compensation or relief for damaged may be claimed under the National Green Tribunal Act. 10. Explain the composition, powers and Functions of the State Board under Air Pollution Act. 11. Briefly explain the objective of Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981. 12. Write short notes on IGP Patel Nagar CS SANJEEV SAPRA (i) Air Pollution (ii) State Air Laboratory (iii) Noise Pollution in Environment. 13. Discuss briefly the restriction on new outlets and new discharges under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act. 14. What are the powers of State Boards in taking samples? 15. Prohibition on Use of Stream or Well for Disposal of Polluting Matter. LAW RELATING TO REGISTRATIONOF DOCUMENTS 1. What is the object of the law of Registration? 2. Documents whose registration is compulsory and optional. 3. State the time limit for presentation of documents for registration. 4. State the places where documents relating to immovable property may be presented for registration under the Registration Act, 1908. 5. Effect of non-registration of documents required to be registered.