PHYSICS STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 13: ELECTRIC CIRCUITS TOPICS: 1. ELECTRIC CURRENT
advertisement

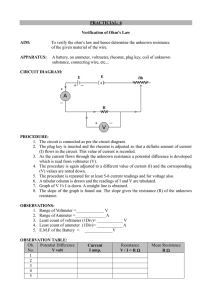
PHYSICS STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 13: ELECTRIC CIRCUITS TOPICS: Electric current Resistance Ohm’s Law Circuits in series Circuits in parallel 1. ELECTRIC CURRENT PHYSICAL QUANTITY Electric Current ( I ) DEFINITION Amount of electric charge (q) per unit of time (t). MATH MODEL I= UNITS Ampere ( A ) q t 2. RESISTANCE PHYSICAL QUANTITY Resistance ( R ) DEFINITION Property that determines how much current will flow. UNITS Ohms ( ) 3. OHM’S LAW MATH MODEL I= Electric current (A) DEFINITION Electric current ( I ) is directly prportional to voltage (v). Electric current ( I ) is indirectly prportional to Resistance (R). v R 0.50 0.45 0.40 0.35 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 Electric current vs. voltage graph: 0 5 10 15 voltage (v) 20 25 30 Shape: diagonal straight line As voltage increases, so does the electric current. The slope of the graph is: slope = 1 R 4. ELECTRIC CIRCUITS PHYSICAL QUANTITY CIRCUITS IN SERIES CIRCUITS IN PARALLEL Stays the same IT = I1 + I2 + I3 +. . . VT = V1 + V2 + V3 +. . . Stays the same RT = R 1 + R 2 + R 3 + . . . 1 1 1 1 = + + + ... RT R1 R 2 R3 PT = P1 + P2 + P3 +. . . PT = P1 + P2 + P3 +. . . ELECTRIC CURRENT VOLTAGE RESISTANCE POWER 5. CIRCUITS IN SERIES R1 R2 R3 VT I (A) V (v) R () P (w ) LIGHT BULB 1 0.34 A LIGHT BULB 2 0.34 A LIGHT BULB 3 0.34 A Measured with ammeter Measured with ammeter Measured with ammeter TOTAL 0.34 A 56 v 40 v 24 v 120 v Measured with voltmeter Measured with voltmeter Measured with voltmeter Measured with voltmeter 164.7 117.6 70.6 352.9 Calculated using Ohm’s law Calculated using Ohm’s law Calculated using Ohm’s law Calculated using Ohm’s law 19 w 13.6 w 8.2 w 40.8 w Calculated using P = I · V Calculated using P = I · V Calculated using P = I · V Calculated using P = I · V Stays the same in electric circuits connected in SERIES VT = V1 + V2 + V3 Sum of the individual voltages VT = 56 v + 40 v + 24 v VT = 120 v RT = R 1 + R 2 + R 3 Sum of the individual resistances RT = 164.7 + 117.6 + 70.6 RT = 352.9 PT = P 1 + P 2 + P 3 Sum of the individual powers PT = 19 W + 13.6 W +8.2 W Brighter bulb: Light bulb 1 Greater power, brighter bulb P=I2·R (Electric current is constant, greater resistance, brighter bulb) PT = 40.8 W 6. CIRCUITS IN PARALLEL LIGHT BULB 1 I (A) V (v) R () P (w ) LIGHT BULB 2 LIGHT BULB 3 TOTAL IT = I1 + I2 + I3 Sum of the individual electric currents 0.500 A 0.625 A 0.750 A Measured with ammeter Measured with ammeter Measured with ammeter 120 v 120 v 120 v 120 v Measured with voltmeter 240 Measured with voltmeter 192 Measured with voltmeter 160 Measured with voltmeter 64 Calculated using Ohm’s law Calculated using Ohm’s law Calculated using Ohm’s law Calculated using Ohm’s law 60 w 75 w 120 w 225 w Calculated using P = I · V Calculated using P = I · V Calculated using P = I · V Calculated using P = I · V 1. Mathematical model 1 1 1 1 = + + RT R1 R2 R3 1.875 A IT = 0.500A + 0.625A + 0.750A RT = 1.875 A Stays the same in electric circuits connected in PARALLEL See below PT = P 1 + P 2 + P 3 Sum of the individual powers PT = 60 W + 75 W + 120 W PT = 225 W 4. Add the fractions 1 15 = RT 960 2. Substitutions 1 1 1 1 = + + RT 240 192 160 5. Cross multiply 960 = 15 · RT 3. Find the common denominator 1 4 5 6 = + + RT 960 960 960 6. Solve for RT RT = 64 (this number must match RT in the chart above). Brighter bulb: Light bulb 3 Greater power, brighter bulb P=V2 / R (voltage is constant, greater resistance, dimmer bulb)