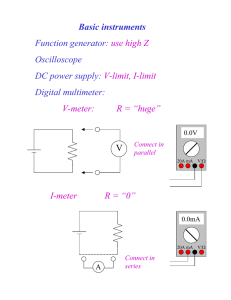
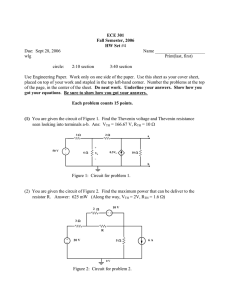
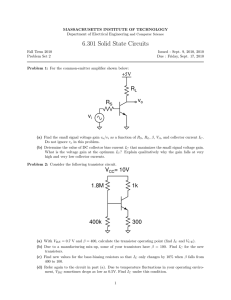
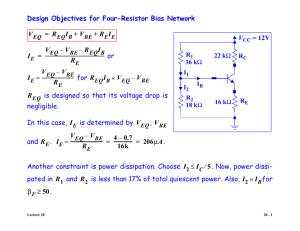
ECE 332 BJT Bias Circuits Previous
advertisement

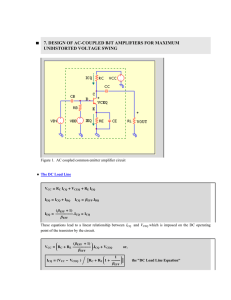
Previous Common-Emitter Configuration Problem — Two Sources ECE 332 BJT Bias Circuits iC iB + RC VCE + RB + VBE VCC VBB iE Single-Power-Source BJT Biasing l Linear amplifier — Q-point should be near the center of the load line VCEQ VCC 2 Single Base-Resistor Biasing Base bias resistor VCC l Biasing — establishing the Q point — the dc operating “reference.” Types: Coupling Capacitor: acts as open circuit to dc & very low impedance to ac RB Single-Resistor Circuit Relationships I CQ Base bias resistor = VCC –VCEQ RC VCC I CQ RC I BQ + VBE VCEQ VCEQ VBE vs u Voltage divider biasing, also termed “stabilized bias.” + + CC2 + Direct-Current Equivalent Circuit I CQ VO CC1 u Single base-resistor biasing RB RC RB = = ICQ VCC –VBE(on) I BQ VCEQ = VCC – R C I CQ Voltage-Divider Biasing Direct-Current Equivalent VCC VCC Voltage divider R1 Voltage divider I CQ RC R1 I CQ RC VO + CC2 CC1 CC1 + VCEQ VCEQ vs R2 R2 RE RE Stabilizing resistor Stabilizing resistor BJT Bias Stability Thévenin Equivalent of Base VTh = RTh IBQ + VBE(on) + IEQ RE VCC VCC I CQ RC RTh RTh + + VCEQ VCEQ + IBQ + VTh VTh I EQ I CQ RC RE VTh = RTh IBQ + VBE(on) + ( + 1)IB RE I BQ = VTh VBE(on) RTh + ( + 1) RE ICQ = (VTh VBE(on) ) RTh + ( + 1) RE IBQ I EQ RE For Bias Stability: RTh << (1 + ) RE For Bias Stability: RTh << (1 + ) RE ICQ If Then (VTh VBE(on) ) ≈ ( + 1)RE >> 1, then /(1 + ) ≈ 1 Therefore, ICQ BJT Bias Stability General Rule ≈ VTh VBE(on) RE ICQ not a significant function of For Bias Stable Circuit RTh ≈ 0.1 (1 + ) RE BJT Biasing — Resistor Tolerances l Typical resistor tolerances: u ± 5 % for carbon film or metal-oxide film u ± 1 % for metal film (also ± 0.1 %) l The Q-point is a function of resistor values l Therefore u IB(min) @ R1(max), R2(min), R E(max) u IB(max) @ R1(min), R 2(max), RE(min) BJT Thermal Runaway l Without RE u Expect junction current increase to cause temperature increase (I 2R) u This T can cause further current increase thereby further increasing temperature. u Phenomenon -- thermal runaway. u Result BJT Thermal Runaway l Without RE u Expect junction current increase to cause temperature increase (I 2R) u This T can cause further current increase thereby further increasing temperature. u Phenomenon -- thermal runaway. u Result -- device destruction: Pfffft BJT Thermal Runaway l RE stabilizes Q-point with respect to temperature. u T causes ground) I which results in u RTh independent of u Therefore, u VE (to T VE reduces VBE (junction) VBE tends to stabilize transistor current