ONLINE HELPDESK FOR MAYBANK ACCOUNT PAYABLE SYSTEM (MAPS) SHOBINI D/ RAMAN NAIR
advertisement

ONLINE HELPDESK FOR MAYBANK ACCOUNT PAYABLE SYSTEM
(MAPS)
SHOBINI D/ RAMAN NAIR
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
PSZ19:16(Pind.1/97)
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA
BORANG PENGESAHAN STATUS TESIS◆
JUDUL
:
ONLINE HELPDESK FOR MAYBANK ACCOUNT PAYABLE
SYSTEM (MAPS)
SESI PENGAJIAN: 2005
Saya SHOBINI A/P RAMAN NAIR
Mengaku membenarkan tesis (Sarjana) ini disimpan di Perpustakaan Universiti Teknologi
Malaysia dengan syarat-syarat kegunaan seperti berikut :1.
2.
3.
4.
Tesis adalah hakmilik Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
Perpustakaan Universiti Teknologi Malaysia dibenarkan membuat salinan untuk tujuan
pengajian sahaja.
Perpustakaan dibenarkan membuat salinan tesis ini sebagai bahan pertukaran antara institusi
pengajian tinggi.
**Sila tandakan ( 9 )
SULIT
TERHAD
TIDAK TERHAD
Disahkan oleh
(TANDATANGAN PENULIS)
(TANDATANGAN PENYELIA)
Alamat Tetap :
No 29 Jalan Asa 2,
Taman Asa Jaya,
43000 Kajang
Selangor Darul Ehsan.
Tarikh : 20 November 2005
Prof Madya Wardah Zainal Abidin
Nama Penyelia
Tarikh :
SUPERVISOR DECLARATION
“We hereby declare that we have read this thesis and in our opinion this thesis is
sufficient in terms of scope and quality for the award of the degree of Master of Science
– Information Technology Management”
Signature
Name of Supervisor I
Date
: ....................................................
: ....................................................
: ....................................................
Signature
: ....................................................
Name of Supervisor II : ....................................................
Date
: ....................................................
ONLINE HELPDESK FOR MAYBANK ACCOUNT PAYABLE SYSTEM
(MAPS)
SHOBINI D/O RAMAN NAIR
A thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of
Masters of Science (Information Technology – Management)
Faculty of Computer Science & Information Systems
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
NOVEMBER 2005
ii
DECLARATION
I declare that this thesis entitled ‘ONLINE HELPDESK FOR MAYBANK ACCOUNT
PAYABLE SYSTEM’ is the result of my own research except as cited in the references.
The thesis has not been accepted for any degree and is not concurrently submitted in
candidature of any other degree.
Signature
: ....................................................
Name
: ....................................................
Date
: ....................................................
iii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I would like to thank Prof.Wardah, my project supervisor from bottom of my
heart for being the first person to recognize my interest in taking up this project. She is
knowledgeable and is always willing to give a helping hand for me. She allocates time
for me to meet her for my project updates and also shares idea and view in spite of her
hectic schedule. I would also like to thank Dr.Rosalinda for her kind advice and support
in this project.
It is also my pleasure to dedicate thanks to my encouraging parents, fiancée,
friends and AITI staffs. My sincere appreciation also extends to all my colleagues and
others who have provided assistance at various occasions.
iv
ABSTRACT
The aim of this project is to develop a web-based Online Helpdesk for Maybank
Account Payable System. Maybank Account Payable System (MAPS) is a system
currently used in Maybank to make payments to third party vendors on product and
services obtained by Maybank. The users of the system will be users from Property and
ISD Department in Maybank. Currently when the system users face a problem with
MAPS system, there is no tool or system used to log the problem to the IT Technical
Supports. The users will log the problem in a manual method by making a phone call to
the IT Technical Support. Besides that, the management is also facing difficulties
because there is no proper tracking to problems raised by users. The management is also
facing difficulties to gauge the performance of the IT Technical Support, because the
support provided is not documented within the organization. Thus, Online Helpdesk for
Maybank Account Payable System is designed specifically to address the problems
mentioned above. The system will automate the manual process of logging a problem to
the IT Technical Support via the web-based system. With the system, there will be a
proper control over the problem logged because there is an escalation process. The
system will be able to determine whether a problem is resolved within the time frame
allocated or better known as SLA (Service Level Agreement) timing. When the IT
Technical Support closes a case, a PDF format report will be generated for the view of
the IT Manager. The report will log the time the case is opened and closed. The report
will also indicate whether the case has been closed within the agreed time. With this
report, the IT Manager will be able to gauge the performance of the IT Technical
Support and will be able to make fair decision during the KPI review.
v
ABSTRAK
Tujuan projek ini adalah untuk membangunkan “Online Helpdesk for Maybank
Account Payable System (MAPS)”. “Maybank Account Payable System” kini
digunakan di Maybank untuk membuat bayaran kepada vendor di atas perkhidmatan dan
servis yang diberikan kepada Maybank. Pengguna sistem terdiri daripada dua unit iaitu
Unit Informasi & Sistem Maklumat dan Unit Hartabenda. Apabila penguna sistem
menghadapi masalah dengan MAPS, mereka tidak mempunyai sistem yang boleh
digunakan untuk membuat aduan mengenai masalah yang dihadapi kepada pegawai
teknikal. Pengguna sistem hanya boleh membuat aduan dengan menghantar email atau
membuat panggilan telefon kepada pegawai teknikal. Selain itu, pihak pengurusan juga
menghadapi masalah kerana aduan yang dibuat oleh pengguna sistem tidak dapat
direkod. Oleh yang demikian, “Online Helpdesk for Maybank Account Payable System
(MAPS)” dibangunkan dengan tujuan untuk mengatasi masalah yang dihadapi oleh
pengguna sistem and juga pihak pengurusan. Sistem ini dibangunkan dalam persekitaran
yang fleksibel dan interaktif berasaskan permukaan “web”. Sistem ini juga akan
menghasilkan laporan untuk pihak pengurusan apabila setiap aduan yang dibuat oleh
pengguna telah disiapkan oleh pegawai IT. Setelah lengkap implementasi sistem ini,
tahap efisyen keseluruhan proses membuat aduan akan dapat dipertingkatkan.
vi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter
Chapter
1
Title
Page
Project Title
i
Declaration
ii
Acknowledgements
iii
Abstract
iv
Abstrak
v
Table of Contents
vi
List of Tables
xii
List of Figures
xiv
List of Acronyms
xvi
List of Appendices
xvii
Title
Page
Project Background
1.1 Introduction
1
1.2 Background of Problem
2
1.3 Problem Statement
5
1.4 Project Objective
6
1.5 Project Scope
6
1.6 Project Importance
7
1.7 IS / IT Solution
7
1.8 Chapter Summary
8
vii
Chapter
2
Title
Page
Literature Review
2.1 Introduction
9
2.2 Definition of Online Helpdesk
9
2.3 Background of Online Helpdesk
10
2.4 Incidents & Problems
11
2.4.1 Incidents
11
2.4.2 Problems
11
2.5 Benefit of Online Helpdesk
2.5.1 For Business in Particular
12
2.5.2 For Organization in Particular
12
2.6 Characteristic of Online Helpdesk
13
2.7 Importance of Online Helpdesk in Banking Industry
14
2.8 Importance of Online Helpdesk for Maybank
16
2.8.1 KPI ( Key Performance Indicator)
16
2.8.1.1 Current KPI Structure in Maybank
2.8.2 Helpdesk Statistic
2.9 Chapter Summary
3
12
17
18
18
Research Methodology
3.1 Introduction
19
3.2 Waterfall Model
19
3.3 Phase in Waterfall Model
21
3.3.1 Requirement Analysis and Definition
3.3.1.1 Requirement Engineering
21
21
viii
3.3.1.2 Requirement Collection & Analysis
3.3.2 System and Software Design
22
3.3.3 Implementation and Unit Testing
22
3.3.4 Integration and System Testing
22
3.3.5 Operations and Maintenance
23
3.4 Chapter Summary
4
21
23
System Design
4.1 Introduction
25
4.2 Organizational Analysis
26
4.2.1 Organizational Background
26
4.2.2 IT Organization Structure
27
4.3 Current IS / IT Application
4.3.1 Problem Statement in the Organizational
28
28
Context
4.4 As – Is Process
29
4.4.1 Phone Call
29
4.4.2 Email
29
4.5 Use Case Description
31
4.6 Online Helpdesk Modules
35
4.6.1 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
35
4.6.2 Glossary
35
4.6.3 Tutorial
36
4.6.3.1 Getting Started with MAPS
36
4.6.3.2 Process for Payment
36
4.6.4 Email
36
4.6.5 Statistic
37
4.6.5.1 Statistic of Problems
37
4.6.6 Incidents / Cases
39
4.6.7 Management Report
39
ix
4.6.7.1 Problem Status Report
39
4.6.7.2 IT Support Status Report
41
4.6.7.3 AMD & ISD Statistic Report
42
4.7 System Design
44
4.8 System Interface Chart
46
4.8.1 User Interface Chart
46
4.8.2 Admin Interface Chart
46
4.8.3 IT Manager Interface Chart
47
4.8.4 IT Technical Support Interface Chart
47
4.9 Design Techniques – UML Diagram
4.9.1 To – Be Process
51
52
4.9.1.1 IT Technical Support
55
4.9.1.2 Manager
56
4.9.1.3 User
57
4.9.1.4 Administrator
58
4.10 Use Case Description
59
4.11 Sequence Diagram
72
4.11.1 IT Technical Support
72
4.11.2 Manager
73
4.11.3 User
74
4.11.4 Administrator
75
4.12 Activity Diagram
76
4.12.1 User Activity Diagram
76
4.12.2 Manager Activity Diagram
77
4.12.3 IT Technical Support Activity Diagram
78
4.12.4 Administrator Activity Diagram
79
4.13 Activity Diagram – Sub Module
80
4.13.1 Lookup FAQ, Glossary, Tutorial
80
4.13.2 Open Case
81
4.13.3 View Case
82
4.13.4 View Statistic
83
x
4.13.5 View Management Report
84
4.13.6 Update Case
85
4.13.7 Close Case
86
4.13.8 Delete Case
87
4.13.9 Add User
88
4.13.10 Maintain User
89
4.13.11 Delete User
91
4.14 Problem Categorization
91
4.15 Physical Design
92
4.15.1 Database Design
4.16 Software Requirement
94
4.17 Hardware Requirement
95
4.18 Test Plan
95
4.19 Testing Method
96
4.19.1 Unit Testing
96
4.19.2 Integration Testing
97
4.19.3 System Testing
97
4.19.4 User and Acceptance Testing
97
4.20 Chapter Summary
5
92
97
Design Implementation & Testing
5.1 Introduction
98
5.2 Coding Structure
99
5.3 Test Cases & Test Result
100
5.3.1 Login
100
5.3.2 Open Case
100
5.3.3 View Case
101
5.3.4.Update Case
101
5.3.5 Delete Case
101
5.3.6 Add User
101
5.3.7 Maintain User
101
xi
5.3.8 Delete User
102
5.3.9 Display Statistic
102
5.3.10 Display Management Report
102
5.3.11 View FAQ, Glossary, Tutorial
102
5.4 User Manual for Administrator
5.4.1 Hardware Configuration & Setup
103
5.4.2 Installation Procedure
103
5.4.2.1 Install Apache
103
5.4.2.2 Install PHP
104
5.4.2.3 Install Apache to Run PHP
104
5.4.2.4 Install MySQL
104
5.5 Chapter Summary
6
103
105
Organizational Strategy
6.1 Introduction
106
6.2 Roll-out Strategy
106
6.2.1 Pilot Strategy
106
6.3 Change Management
107
6.4 Business Continuity Plan ( BCP)
108
6.5 Expected Organizational Benefit
108
6.6 Chapter Summary
109
xii
7
Discussion & Conclusion
7.1 Achievements
110
7.2 Constraint and Challenges
111
7.3 Aspiration
111
7.4 Chapter Summary
112
References
113
xiii
LIST OF TABLES
TABLE NO
TITLE
PAGE
4.14
Problem Categorization
91
4.15.1
Caselog Table Details
92
4.15.2
UserDetail Table Details
93
xiv
LIST OF FIGURES
FIGURE NO
TITLE
PAGE
3.3
Waterfall Model
24
4.2.2
IT Organization Structure
27
4.4
Current Process to Log a Problem
30
4.6.5.1
Statistic of Problem
38
4.6.7.1
Problem Status Report
40
4.6.7.2
IT Status Support Report
41
4.6.7.3
AMD & ISD Status Report
43
4.7
Main Page for MAPS Online Helpdesk
44
4.9.1
System Use Case Diagram
53
4.9.1.1
IT Technical Support Use Case Diagram
55
4.9.1.2
Manager Use Case Diagram
56
4.9.1.3
User Use Case Diagram
57
4.9.1.4
Administrator Use Case Diagram
58
4.11.1
Sequence Diagram - IT Technical Support
72
4.11.2
Sequence Diagram –Manager
73
4.11.3
Sequence Diagram – User
74
4.11.4
Sequence Diagram – Administrator
75
4.12.1
Activity Diagram – User
76
4.12.2
Activity Diagram – Manager
77
4.12.3
Activity Diagram – IT Technical Support
78
4.12.4
Activity Diagram – Administrator
79
4.13.1
Lookup FAQ, Glossary, Tutorial
80
4.13.2
Open Case
81
4.13.3
View Case
82
xv
4.13.4
View Statistic
83
4.13.5
View Management Report
84
4.13.6
Update Case
85
4.13.7
Close Case
86
4.13.8
Delete Case
87
4.13.9
Add User
88
4.13.10
Maintain User
89
4.13.11
Delete User
90
xvi
LIST OF ACRONYMS
MAPS
- Maybank Account Payable System
FAQ
- Frequently Asked Question
UML
- Unified Modeling Language
MDTB
- Maybank Desktop Banking
SLA
- Service Level Agreement
KPI
- Key Performance Indicator
PO
- Purchase Order
DO
- Delivery Order
ISD
- Information System Department
AMD
- Property Department
xvii
LIST OF APPENDICES
APPENDIX
TITLE
A
Example of System Snapshots
B
Project Timeline – Gantt Chart
1
CHAPTER 1
1.0
PROJECT BACKGROUND
1.1 Introduction
The aim of this document is to develop an Online Helpdesk System for Maybank
Account Payable System (MAPS) for Information Technology Department of
Maybank.
This chapter will give a basic overview and glimpse of the system. The background of
this system will be described in this chapter. By reviewing this chapter, one will
understand the functionality of the system. Chapter one will be divided into few
categories as follows:
9Background of problem
9Problem Statement
9Project Objectives
9Project Scope
9Project Limitation
9Project Importance/ Significance
9Description of Solutions
IS / IT Solution
i.
Hardware Solution
ii.
Software Solution
2
1.2 Background of Problem
The system is mainly developed for Maybank Account Payable System or better known as
MAPS System. MAPS System is a payable system used by Maybank to pay vendors for their
goods purchased and services used. MAPS system is a vendor-based system introduced in
Maybank for the past two years.
The main users of this system is divided into two categories from two different departments,
which is the Property Department and ISD (Information System Department) or better known as
IT Management Department. The Property Department user does all the processing for goods or
services incurred by the bank while ISD Department does all the processing incurred by
Information Services Division. Once all the processing has been done via the system, the
property manager within the specified time frame will make the payment to the vendors or the
banks.
The processing that takes place includes processing of invoices, purchase orders and delivery
order in the system. All of the information will be fed into the system to enable the processing.
Besides that, invoices, purchase order and delivery order will also be uploaded to the MAPS
server by third party vendors. The invoices, purchase order and delivery order will be
automatically picked up by the system by time-triggered jobs to continue the processing within
the system. Once all of the processing is complete, the Property Department manager will
perform the MDTB process. The MDTB process is a process performed to pay the entire amount
due to the vendors within a specific time frame allocated via the system.
The main problematic situation identified in this context is, the unclear processes of task
involved. Many of the clerks are not clear of each processing which takes place within the
system. There isn’t any existing documentation, which documents the usability and the processes
3
of the system. Often the system users require assistance from the IT technical support to
complete the daily task and chores.
Besides that, the automated uploading of invoices, purchase order and delivery order by the
vendor very often fails due to network failure. When the automated job is not successful, the
processing for the day cannot be continued and this will impact the MDTB process.
In a daily situation when the documents are not uploaded automatically, users will have to
inform IT technical support about the problem faced. Then the IT technical support will have to
request for the data (invoice, purchase order, delivery order) from the third party vendor. Once
the vendor has emailed the required files, then the IT technical support will have to upload the
files manually to the server and complete certain encryption processes before the users can use
those files.
Users always face problems when they require assistance from IT technical support. Most of the
time the technical support cannot be contacted and there is no tool to log the problem
automatically for the technical support to attend to the problem later. The users have to keep on
trying to contact the technical support until they manage to log the problem.
Upon receiving the complaint, the IT technical support will have to raise this matter to the third
party vendor for data. All of these processes take a few hours or sometimes even a day to
complete. This will affect the performance of the users because until the data is available no
processing can be done.
Besides that, when this processes is not completed as scheduled, the MDTB (Maybank Desktop
Banking) process which involves payment made to vendors will also be delayed. This delay is a
significant delay to the management because when the payment is delayed, vendors will not
proceed with the services or goods to be delivered until the payment has been made.
4
The MDTB process itself often incurs a lot of problem whereby those processes cannot be
continued without IT technical supports guide and assistance. This process is a crucial process in
Maybank and can only be done by the Property Manager. This process is really crucial as it
involves millions of ringgits to be paid to the vendors on a weekly basic. When the manager hits
problem with the MDTB process, technical support has to reinterface the files manually to
continue with the processing. Besides that the manager also often faces problem such as network
failure during the MDTB process as the process takes a long duration to interface the files to
make the payment. This is the biggest challenge for the management because the delay to get in
touch with the technical support and there is no system or tool to log the problem even though
the technical support cannot be reachable. With a tool to log the problem, the technical support
can take quicker action to solve the users problem.
Inline with the problems faced by the users as mentioned, the technical support themselves are
facing problem. One of the most significant problem faced is that there is no proper tracking of
problems attended to by the technical staff. Most of the technical staff finds it difficult to justify
the support provided during review of KPI (Key Performance Indicator). The reason is because
there is no system to track the problems logged by the users and to track the support provided by
the technical support. During the review of KPI, it is difficult to gauge the performance of the
technical support since there is lack of tracking done.
5
1.3 Problem Statement
The delays in solving the technical problems are due to improper reporting of the problems.
The time taken by the IT technical support is significantly long because of few reasons as
follows:
Currently there no such system, which can be used by the users to log a problem.
In most cases, when users face a problem and wishes to log a problem, the IT
Technical support is not available and reachable. So the problem will be unknown
and unsolved until the user calls the technical support again to log the problem.
This gap of time taken for the technical support to receive the problem log and to
solve the problem is significantly long.
Due to this delay, the time taken by the users to complete their daily task is longer
than allocated hence reducing the productivity of the users.
Besides all of the problems mentioned above, users are also facing problem currently to obtain
information about the MAPS system. Any information in relations to the system has to be
obtained from the technical support itself. There is no any procedures or guidelines provided to
use the system and many of the functionalities of the system are unused.
With the statistics generated by the system, the IT Technical staff and the manager will be able to
further analyze the problem faced by the system users. The statistics generated will be able to
highlight the area within the system, which needs fine tuning to further improve the system.
6
1.4 Project Objective
The objectives of this project are as follows:
To develop a web based Online Helpdesk for MAPS (Maybank Account Payable
System). This system will be able to help users to automate the process of problem
logging to IT technical support via the web-based system.
To enable users to obtain information regarding the MAPS system via the Online
Helpdesk
To enable management to measure problems resolved by IT technical support to give
them a fair rating during KPI review.
To reduce turnaround time to complete problems logged by users.
1.5 Project Scope
The scopes of the online helpdesk are such as:
The online helpdesk is developed mainly to support MAPS (Maybank Account Payable
System) will be used by two departments namely Property Department and the ISD
Department users.
The system will be able to provide information about the processes within the MAPS
system
To log technical problem such as request for installation, and unlock of password.
To monitor and track all problems reported to the IT Technical Support.
To produce statistical and summarize information for the management. The data provided
will be used during KPI review.
7
1.6 Project Importance
The system will provide some significant importance to the management as well as the users of
the system. With the online helpdesk:
Time taken to complete users daily task will be shorten since the system will be able to
alert the technical staff in case of problem. Thus, it will be able to reduce delays.
Information and knowledge sharing among users will become more effective since users
will be able to gather information from the online helpdesk.
Management will be able to keep track of support provided by the IT Technical support.
Avoid unnecessary escalation and inappropriate resource allocation.
Online Helpdesk is expected to automate the process of problem logging and also to provide
statistical information for problem analysis. Hopefully with the Online Helpdesk System, all
technical problems are monitored, and escalated to the proper channel. In addition, with the
system the flow or process of handling problems will become more systematic and documented.
1.7 IS/IT Solution
All the problems mentioned in the problem statement and backgrounds of statement section are
the problems faced by the management and users currently in Maybank. In order to overcome
this problem in the future and have less impact on the productivity, an IS/IT solution has to be
introduced. The IS/IT solution identified is to develop the Online Helpdesk for MAPS System.
Without the IS/IT solution, the problems faced cannot be solved because it is interconnected with
IT and the resolvers of the problem are the technical support itself. The IS/IT solution will be
categorized under the software and hardware requirements section.
8
1.8 Chapter Summary
As a conclusion, this chapter describes the background of the project and the background of
problems faced by system users and IT Technical Support in Maybank. This chapter also
illustrates the importance of having an online helpdesk system to address the problems and
constraint faced as mentioned above. By developing the online helpdesk system, it is hoped that
to a certain extend the problems will be eliminated and the daily task can be carried out
smoothly.
9
CHAPTER 2
2.0
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Introduction
This chapter will describe the literature reviews done pertaining to developing the Online
Helpdesk System. This chapter will mainly contain information pertaining to definition of
online helpdesk, characteristics and importance of online helpdesk and some information on
importance of online helpdesk in the banking industry.
2.2 Definition of Online Helpdesk System
Online Helpdesk as defined by Donna Knapp in a Guide to Customer Service Skill and
Helpdesk Professional is a ‘single point of contact within a company for managing customers
problem and request and providing solution oriented support services’. Online help desk is
also defined as a problem-solving tool designed to provide technical support concerning a
specific product or service. Helpdesk is usually known as a department within a company
that responds to user's technical questions. Most large software companies have helpdesk
systems to answer user questions. There is even helpdesk software that makes it easier for the
people running the helpdesk to quickly find answers to common question.
10
2.3 Background of Online Helpdesk
Often the term Helpdesk is used for internal support within the company or for external
support groups. Many companies are turning to Helpdesk to automate a variety of tasks and,
at the same time, reduce costs by cutting staff and providing more user support with the
existing staff. Companies need to provide high quality of customer service and support to
survive in today’s business environment. Having the right helpdesk would ensure high
customer satisfaction. Customer support includes services that help a customer or user
understand and benefit from products capabilities by answering questions, solving problem
and providing online information. The advantages of automated Helpdesk are critical in that
they allow fewer people to deal with higher volume.
The Helpdesk is increasing in importance as companies move to client/server architectures.
Users who interface with the Helpdesk often form a general perception of the information
system group. Information systems helpdesks have an important role within an organization.
The helpdesk is responsible for bringing an organization's resources together in order to
provide its customers with quality support and service.
Helpdesk is designed and customized to provide businesses with an internal support system
as well as a link for providing support to its customers. Helpdesk applications host a number
of benefits that include:
11
Providing existing users or customers with knowledge and FAQ's (Frequently Asked
Questions) concerning the company’s products and systems.
24-hour availability thus catering to the trend of office personnel working late and to
those overseas or in different time zones.
Troubleshooting features gives users or customers the ability to solve many support
problems on their own. This tool provides the users or customer with quick and easy
solutions as well as saving the company money.
Serves as a tool for tracking and recording helpdesk inquiries, which provides a
knowledge base of resolutions to previous calls concerning similar issues.
Supplies information concerning trends and other issues, which aid in the continuing
improvement of products and services.
2.4 Incidents & Problems
Incidents and problems are two major players that can impact services of business
especially in the world of IT. Both of the definitions are as follows:
2.4.1 Incidents
An incident is an event that is not part of the standard operation of a service, which may
cause an interruption to the service or system. Examples of incident are such as:
i.
Network line may be down
ii.
Files are not transferred automatically
2.4.2 Problems
A problem is an unknown incident. A problem is usually bigger than an incident and
has more impact. Example of problem is:
i.
Failure of the system
ii.
Failure of the server
12
2.5 Benefits of Online Helpdesk System
Implementing Online Helpdesk System, management can have a single point of contact
to log and resolve an incident. The major benefits of implementing Online Helpdesk
Systems are as follows:
2.5.1
For the business in particular:
9Reduced business impact of incidents by timely resolution, thereby
increasing effectiveness.
9The proactive identification of beneficial system enhancements and
amendments.
9The availability of business-focussed management information related
to the SLA (Service Level Agreement)
2.5.2
For the organisation in particular:
9Improved monitoring, allowing performance against SLA’s to be
accurately measured.
9Improved IT service quality as all incidents or problems are
immediately taken action
9Timely identification, diagnosis and resolution of problem
9Improved user or customer satisfaction.
9Extra support during mergers, acquisitions and other
organizational transitions
13
2.6
Characteristic of Online Helpdesk
Throughout the Incident lifecycle, nearly all IT groups will handle an Incident or Case at
some stage of a Helpdesk System. To do this efficiently and effectively requires a formal
approach that facilitates the timely identification of problems.
A way of tracking back is required. It is recommended that the Helpdesk System records
should be held as the Problem, Known Error and Change records, or at least linked without
the need for re-keying, to improve the interfaces and ease interrogation and reporting.
The helpdesk system should record the status of an incident or case that reflects it current
position in its life cycle, sometimes known as its ‘workflow position’. Some examples of
status categories that a helpdesk system might include:
9New
9Scheduled
9Assigned to Vendor
9Work in Progress (WIP)
9On hold
9Resolved
9Closed
14
Throughout an Incident or Case life cycle, it is important that the Incident records are
maintained. This allows any member of the service team to provide a users or customer
with an up-to-date progress report. Example of update activities includes:
9Update history details
9Modify status (e.g. ‘new’ to ‘work-in-progress’ or ‘on hold’)
9Modify business impact / priority
9Monitor escalation status
2.7
Importance of Online Helpdesk in Banking Industry
This information was taken from a case study that proved that deploying a helpdesk
system has increased the revenue of the banking industry. Founded in 1871, Danske Bank
is the largest bank in Denmark and a leading player in the Scandinavian financial
markets, offering a wide range of financial services, including insurance, mortgage
finance, asset management, brokerage, credit card, real estate, and leasing services. In
2000, Danske Bank’s IT organization designed Business PC to provide its customers
throughout Europe with a reliable, easy way to perform financial transactions securely
and cost-effectively. While business PC would provide new levels of service and cost
efficiency, application problems constituted a major risk. A single lost or delayed
transaction could prove both expensive, and damaging to the bank’s reputation.
To address the problem faced, Ebbe Larsen the Chief Architect at Danske Bank,
recognized the need for a better infrastructure for application problem resolution
throughout Business PC. An inhouse helpdesk system was initiated to address the
problem. After initiating an in-house project to build a comprehensive system helpdesk
support solution, the support team can easily pinpoint the root cause of application
failures, such as performance bottlenecks, configuration problems, and functional errors,
without having to recreate the problems, saving them significant time and costs. With the
15
helpdesk system, the banks support operation work more effectively, streamlining the
process of capturing and communicating problems, and providing rapid root cause
analysis for problem resolution. The helpdesk system is able to pinpoint single
application error, recreate the problem, and resolve the issue. It also enabled the support
staff to identify the cause of problems in a few hours, rather than a few days.
Danske Bank is able to save more than $900,000 over a period of five years. A year after
implementation, Larsen calculated that return on investment for the first year of operation
alone amounted to more than $1,000,000.
The case study discussed above clearly illustrates the benefit of a helpdesk system in the
banking industry. The case study is able to illustrate the savings by the bank after
deploying the helpdesk system to overcome the problems faced with online banking.
16
2.8
Importance of Online Helpdesk for Maybank
As mentioned and illustrated in Chapter 1, Online Helpdesk for Maybank Account Payable
System will benefit the users and the organization to a certain extend. Besides all those
benefit, the most important aspect will be to judge process performance, clearly defined
objectives with measurable targets, which is often referred to as Key Performance
Indicators (KPI’s).
2.8.1
KPI (Key Performance Indicator)
The following metrics are examples for the effectiveness and efficiency of
the Online Helpdesk process:
Total numbers of incidents or cases solved
Mean elapsed time to achieve incident or cases resolution.
Percentage of incidents or cases handled within agreed response time
(Incident response-time targets may be specified in SLA)
Percentage of incidents or cases closed by the Helpdesk without reference
to other levels of support (vendors)
Reports that will be produced will be automatically escalated to the Unit Manager
for monitoring purposes. With the reports generated after each incidents or cases are
resolved will provide information of the resolver and particular issue or problem
faced by users. The reports will be useful to the management during the KPI (Key
Performance Indicator) review.
17
2.8.1.1 Current KPI Structure in Maybank
As illustrated in Appendix A, the current KPI (Key Performance Indicator)
used in Maybank does not cater for support work done by the staffs. As
mentioned previously, the core job scope for an IT Technical Support is
programming and developing new softwares. 90% of the ratings will
emphasis on the programming area and only 10% will be given for the
support task. In appendix A, only 10% of weight is given for problems
resolved on time, which is used to rate the support task done. Since the
weight of score given does not match the amount of support given by the
technical support, this model will be revised in future by the upper
management to provide new weight scale to suit the job scope of the
technical support employee.
In order for the management to revise the weight scale from the next
financial year, the upper management must be able to view all the
problems or incidents resolved by the IT Technical support. When the
management is able to keep track of all the problems faced by system
users, there will be stronger justification on why the current weight of
score has to be changed. So by developing the Online Helpdesk System
and the management report module, the management will be able to gauge
the amount of problems resolved and adjust the weight score of the current
KPI model for the next financial year. With the revised model of KPI, the
IT Technical staff will be able to obtain better rating during KPI
assessment.
18
2.8.2
Helpdesk Statistic
Besides KPI, the reports produced to the management will include statistical data
for analysing purposes. Helpdesk statistics plays a very important role in success of
any organization. A critical analysis of these helpdesk statistics is required to make
some strategic actions or strategies. Statistic will contain information problem logs
(referred to as cases) that were handled by the helpdesk over the past six months or
one year, and breakdown of the most common problems for which users request
help from IT technical support.
Helpdesk statistics shows the number of cases for each category of problem raised
within the system. Helpdesk statistics not only constitutes the current or past events
but also Helpdesk goals for the next year, such as follows:
Reduce number of work orders by training users.
Reduce backlog by increasing the number of completed work orders.
Develop procedures that will allow helpdesk technical support staff to
close a majority of calls over the phone instead of visiting users
workstations.
2.9 Chapter Summary
The analysis of literature review had broadened the scope of Online Helpdesk issues. The
information and findings collected form this chapter is used as a guidance to develop the Online
Helpdesk system. By reviewing the Danske Bank case study, we can conclude that helpdesk
system plays an important role in the financial or banking institution. This chapter has also
demonstrated the importance of helpdesk system in the context of Maybank. The KPI and
helpdesk statistic will further realize the organizations goal by helping to eliminate and smoothen
processes within the MAPS System.
19
CHAPTER 3
3.0 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1
Introduction
In this chapter, the researcher will describe the methodology used to develop the Online
Helpdesk System. The project methodology for this project starts from defining the project goals
until the closure of the project. This chapter will also describe each phase in the Waterfall model
and describes the importance in deploying this methodology. A methodology formally defines
the process that is used to gather requirements, analyze, and design an application that meets the
objective.
3.2 Waterfall Model
The waterfall model is a popular version of the systems development life cycle model for
software engineering. Waterfall model is considered the classic approach to the systems
development life cycle; the waterfall model describes a development method that is linear and
sequential. Waterfall model abstracts the essential activity of software development and lists
them in the most primitive sequence of dependency. Waterfall development has distinct goals for
each phase of development. This model is called a waterfall model because development process
moves forward from one phase to another same as the waterfall. Once a phase of development is
completed, the development proceeds to the next phase and there is no turning back. A new
phase can only begin when the previous phase has been completed.
20
The advantage of waterfall development is that it allows for departmentalization and managerial
control. Development moves from concept, through design, implementation, testing, installation,
troubleshooting, and ends up at operation and maintenance. Each phase of development proceeds
in strict order, without any overlapping or iterative steps. Waterfall model identifies the system
requirements long before the implementation begins and also minimizes the changes to the
requirement.
On the other hand, there are some disadvantages of waterfall development. It does not allow for
much reflection or revision and once an application is in the testing stage, it is very difficult to go
back and change something that was not well thought out in the concept stage.
In Waterfall model, there are few common steps practiced:
The existing system is evaluated and deficiencies are identified. This can be done by
interviewing users of the system and consulting with IT support personnel.
The new system requirements are defined. In particular, the deficiencies in the existing
system must be addressed with specific proposals for improvement.
The system is designed and plans are laid out concerning the physical construction,
hardware, operating systems, programming, communications, and security issues.
The new system is developed. The new components and programs must be obtained and
installed.
Users of the system must be trained in its use, and all aspects of performance must be
tested.
The system is put into use and this can be done in various ways. The new system can phase
in, according to application or location, and the old system gradually replaced. In some
21
cases, it may be more cost-effective to shut down the old system and implement the new
system all at once.
Maintenance must be kept up rigorously at all times. Users of the system should be kept
up-to-date concerning the latest modifications and procedures.
3.3 Phases in Waterfall Model
3.3.1
Requirement Analysis and Definition
This phase seeks to identify the systems services, constraint, and goals. They are defined in detail
and serves as the basic for system specification. This phase is used to gather information about
the current system, which is called the ‘as-is system’ identifying it’s strength and weaknesses,
then analyzing a new concept or the new system called the ’to-be system’. The goal for this
phase is truly to understand the requirement for the online helpdesk system.
3.3.1.1
Requirement Engineering
This is the process of discovering, documenting and maintaining a set of requirements for
this project. The requirement for this project is collected from the MAPS system users.
After collecting the requirement, it is documented for the use of this project.
3.3.1.2
Requirement Collections and Analysis
The requirement collection was done by interviewing Property Department and ISD
Department users regarding the problems faced with the current system. After conducting
the interview with the users of MAPS system, the need for an Online Helpdesk for MAPS
system is clearly understood and identified. During the interview, the drawbacks of the
MAPS system was discussed and evaluated, thus enabling to propose a suitable system.
After conducting the interview with the users, their needs and problems were clearly
understood and hopefully by developing the system, the users problem will be solved.
22
3.3.2
System and Software Design
This phase partitions the requirement to two sections, which is the hardware and software
section. In this phase the system design is developed to have a prototype of the future
system. Figure 4.1 illustrates the system design for the Online Helpdesk System. The
system design should include the GUI (Graphical User Interface) for the system users to
have a comfortable use with the system. The system will be designed with proper GUI to
enable users use the system without any problem. This phase will include coding to transfer
the system design into executable codes.
3.3.3
Implementation and Unit Testing
Software design is realized as a set of programs or programs unit. Each module from the
entire system is tested during this stage. The modules will be a combination, which makes
up to the Online Helpdesk System. This phase will ensure that all modules, which will be,
developed for the online helpdesk system meets the system specifications. In this phase unit
testing will also be conducted to ensure the modules developed is functioning as planned.
3.3.4
Integration and System Testing
In this phase, each individual module that are developed for the online helpdesk system
will be tested as a complete system to ensure that the system meets the software
requirement. After the testing is done, the product, which is the online helpdesk is delivered
to the user.
23
3.3.5
Operation and Maintenance
In this phase the online helpdesk system is installed and put into use. This stage involves
monitoring and maintaining the system at an acceptable level of performance. The support
and maintenance provided for this system will also be in this phase.
3.4 Chapter Summary
As a conclusion, this chapter has discussed the project methodology used to develop the
Online Helpdesk for Maybank Account Payable System. This chapter also has described in
depth the processes involved in the waterfall model and illustrates the benefit of deploying
waterfall methodology in developing the system.
24
Requirement Analysis
And Definition
System and Software
Design
Implementation and
Unit Testing
Integration and System
Testing
Operations and
Maintenance
Figure 3.3: Waterfall Model
25
CHAPTER 4
4.0
SYSTEM DESIGN
4.1 Introduction
This chapter will describe the initial finding for the development of the system. The initial
finding that has been gathered includes the following:
i.
The organizational analysis
ii.
As – Is process
iii.
To – Be process
This chapter will also include the use case diagram, which illustrates the interaction of IT
technical support, user, manager and administrator with the online helpdesk system. This chapter
will provide some information about the system to have a clear picture of the systems
functionality. The collected information is analyzed to identify the required information as well
as the actors who will be involved in the system. Systems design also explains the data flow of
the prototype of the system and the roles of each actor involved in the new system.
System design emphasizes on the basic processes of inquiry. Identifying the research problems;
determining and describing procedures for conducting research; designing data collecting
procedures; formulating testable hypotheses; interpreting and drawing conclusions from data
analysis, and reporting research findings and implications.
26
4.2 Organizational Analysis
This section provides information in the organization context .The information will provide the
organizational structure.
4.2.1 Organizational Background
Maybank was established on 12/9/1963. Maybank has many branches located in other
ASEAN countries namely Singapore, Brunei and Philippines. The objective of the bank is
such as:
To promote and mobilize banking activities
Continues improvement to the quality of life through imagination and creativity
To utilize funds of the bank for investment including financing and economic
development.
Maybank also provides many online services via the Maybank2u portal services such as:
Transfer between accounts
Transfer to third party accounts
Payee to selected payee corporation
Third party payment to credit card and loans
27
4.2.2 IT Organization Structure
IT Department in Maybank is divided into sub division as follows:
IT Department
Core Banking
Division
User Support
Services
IT Security
Division
Data Warehouse
Division
IT Governance
Division
IT Strategy &
Architecture
Division
Figure 4.2.2 IT Organization Structure
Quality Assurance
Division
28
4.3. Current IS/IT Applications
The current IS/IT systems in Maybank are divided into 2 categories such as Client Server
environment and mainframe environment. Examples of both the categories are such as:
a. Client Server System
Data Warehouse System
Maybank Account Payable System (MAPS)
Citrixs System
b. Mainframe System
General Ledger Application
Fixed Deposit System
Current Account System
4.3.1 Problem Statement in the Organizational Context
Currently the users of Maybank Account Payable System (MAPS) in Maybank do not have
a system to log problems to IT Technical Support. The users are using the conventional
method to log the problem and to seek the assistance of the IT Technical Support. Due to
this, there is no proper mechanism for problem logging and tracking. The current flow is
explained in the As –Is Process.
29
4.4 As - Is Process
As mentioned in the previous chapters, there isn’t any existing process to log a problem to the
Technical IT Support. There are two conventional methods currently used by the users to log a
problem such as:
4.4.1 Phone Call
When a problem arises, the user calls the IT Technical Support via the phone. Most of the
time, the problem faced is not logged immediately because the technical support is not
available in their workstation at that moment of time.
4.4.2 Email
This method is not commonly used by the users to log a problem. Very seldom the users
take the trouble to send an email to log the problem faced. Sometime when the email is
sent, it is not complete because important information such as the type and description of
problem id not included. So the Technical Support has to spend a considerable amount of
time to obtain the problem information even before solving it.
30
Use Case Diagram for As - Is Process
Make Phone Call
Email
User
IT Technical Support
Attend Problem
Solve Problem
Inform User
Figure 4.4: Current Process to Log a Problem
Figure Description:
The figure illustrates the current method used by the users to log a problem to the IT
Technical
Support. The users will send an email or make a phone call to the IT Technical Support. The IT
Technical Support will then attend to the problem and once the problem is solved, the users will
be informed accordingly.
31
4.5 Use Case Description
Use Case Number: 1
Use Case Name: Make Phone Call
Brief description
This use case is used by the actor (users) to make a phone call to the IT Technical Support to
log a problem.
Flow of Events-Basic Flow
1. An actor will make the phone call to the IT Technical Support
2. Actor will then log the problem faced to the IT Technical Support
Alternative Flow
If actor fails to contact the IT Technical Support via phone, then the user will send an email
to log the problem.
Special requirements
None.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
If the use case was successful, the actor has logged the problem to the IT Technical Support.
Extension Points
None.
32
Use Case Number: 2
Use Case Name: Send Email
Brief description
This use case is used by the actor (users) to send an email to the IT Technical Support to log
a problem.
Flow of Events-Basic Flow
1. An actor will send an email to the IT Technical Support
2. Actor will log the problem in the email
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
None.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
If the use case was successful, the actor has successfully logged the problem to the IT
Technical Support.
Extension Points
None.
33
Use Case Number: 3
Use Case Name: Attend & Solve Problem
Brief description
This use case is used by the actor (IT Technical Support) to attend and solve a problem
logged by the user.
Flow of Events-Basic Flow
1. An actor will analyze the problem logged by the user
2. The actor will then solve the problem with the expertise in the field
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
None.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
If the use case was successful, the actor has successfully fixed the problem faced by the user
Extension Points
None.
34
Use Case Number: 4
Use Case Name: Inform Users Problem Solved
Brief description
This use case is used by the actor (IT Technical Support) to inform the users that the
problem logged has been successfully fixed or completed.
Flow of Events-Basic Flow
1. An actor will inform the users that the problem has been completed.
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
None.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
If the use case was successful, the actor has then closed the problem
Extension Points
None.
35
4.6 Online Helpdesk Modules
There are 7 modules of the system will be included in this chapter such as FAQ, Glossary,
Tutorial, Email, Statistic and Management Report to provide the functionality of those modules.
4.6.1 Frequently Asked Question (FAQ) Module
FAQ is defined as well written answers to the most common users queries from users. Well
written FAQ states both the question and answer clearly and are self-service and basically
enable helpdesk to proactively address the users needs. With FAQ queries within a system
can be answered to clarify a doubt. FAQ satisfies users because they are able to find a
solution and answer on their own and users prefer FAQ because they can find answers and
questions that they are reluctant to ask to the technical support. FAQ within this helpdesk
system will be divided into two categories such as:
General FAQ
Procedures and processes
General FAQ educates users about the MAPS system itself. It will provide general
information about the system to surface the users with basic knowledge of the system.
Procedures and processes will provide detailed explanation of processes done within the
MAPS system. For example the processes involved paying a vendor from the time the
invoice is issued. All of this procedure will then be documented under this section to enable
users to have a clearer picture of the process within the system.
4.6.2
Glossary Module
Glossary is a link that provides definition of specific words used by the system. Glossary
provides meaning of words or abbreviation, which is found in the system. By providing
meaning of most words, which exist in the system, the users can always refer to a word,
which creates confusion. The user can refer to words they are not familiar with and the
36
users will have a better understanding about the entire system. The glossary will contain
meaning of words starting from alphabet A to Z that is applicable to the system.
4.6.3
Tutorial Module
Tutorial is one of the most important aspects of helpdesk system because it is usually an
interactive process. Tutorial provides information on how to get around the system by each
level of users. Users can learn how to use system effectively and the type of task that can
be done by each user will be clearly stated. With the comprehensive information provided
in this section, users will find it easy to use the system.
Tutorial interface will be divided into two categories such as:
4.6.3.1
Getting started with MAPS
9Clerk
9Officer
9Manager
4.6.3.2
Processes for payment
9Processing invoice
9Processing purchase order
9Processing delivery order
4.6.4
Email Module
In this module, the users of the system will be able to send email to the IT Technical
Support staff. The email can be sent when the users are unable to reach the technical
support staff via telephone. The email can also be sent when the users logs a problem to the
helpdesk system. The email can be sent when:
9A new case is submitted
9An existing case is closed (email is send to the IT Manager)
37
4.6.5 Statistic Module
The group of users for the online helpdesk system will be divided into four group of
users which comprises:
9Users (Property and ISD Department)
9Manager
9IT Technical Support Staff
9Administrator
Each of the users will be provided with a login id to differentiate the login of a user, IT
Technical Support, Manager and Administrator. The statistic module will only be
available in the IT Technical Support and manager login. The statistic module will
contain statistical data of problem logged in the system when an incident or case is
opened. When an incident or case is opened, the users will choose the category of
problem. The category chosen will be updated to the statistic module. The type of
report that will be generated by the statistic module is such as:
4.6.5.1 Statistic of Problems
This report contains the categories of problems identified in the system. The
example of problems is such as:
i. Password Reset
ii. Network / Line Failure
iii. Installation of MAPS software for new users
iv. Investigation (data related)
v. Reloading of TX data
vi. Reloading of Proman data
vii. Others (not related to the above problem)
38
When a user opens a case and selects the category of problem, the report will be
updated automatically. The report captures the problem id, reported date, status of the
ticket and whether the ticket is closed. With this report the management will be able to
view the category of problem, which has the highest number of cases logged. Figure
4.6.5.1 illustrated the Statistic of Problems Report.
Figure 4.6.5.1: Statistic of Problems
39
4.6.6
Incidents / Cases Module
Incident or cases is the module used by the users or IT technical support to log or
update a problem within the system. The users use this option available in the incident
or cases module to open a new case. The IT technical support uses the module to view
and update the cases opened by the users. The IT technical support can also view,
update, close and delete a case. The options available in the incident or case module
are as follows:
i. Open case
ii. View Case
iii. Update Case
iv. Close Case
v. Delete Case
4.6.7
Management Report Module
Management reports will be produced by the system when an IT Technical Support
closes a case to indicate that the particular problem log has been solved. The types of
report that will be generated in this module is such as:
4.6.7.1 Problem Status Report
These report will contain the breakdown of each cases opened by the user. For
example the report will capture information such as problem id, reported by,
reported date, reported time, closed time, closed by and the status. This report will
provide an overall view of the problems raised by the users. Closed by field
represents the IT Technical Support who has resolved the problem. The status field
indicates whether the problem was resolved before time, within the time frame, or
40
exceeded the time frame. With these report the management can closely monitor
each cases opened by the users. Figure 4.6.7.1 illustrates the problem status report.
Figure 4.6.7.1 Problem Status Report
41
4.6.7. 2 IT Support Status Report
This is the summary report generated by the system. This report shows the number of
problems resolved by each IT Technical Support. The report represents the each IT
Technical Support with the number of problems resolved on time, before time and
exceeded time. The IT Manager can only view this report. With the reports available,
the manager can have a proper performance monitoring to provide a fair rating during
the KPI evaluation. Once the management has decided on the new KPI structure, then
the manager will be able to gauge the performance of the IT Technical Support. Figure
below represents the report.
Figure 4.6.7.2 IT Status Support Report
42
4.6.7.3 AMD & ISD Statistic Report
AMD & ISD Statistic Report is designed to provide a breakdown of statistic, which
represents the users who have opened a case for each category of problem. The users
will be represented by their respective departments such as AMD and ISD. For
example password reset category will contain the number of cases opened by users
both of the departments. With this report, management will be able to evaluate the
reason for the users to have problem with each of the problem category. One of the
reasons can be lack of training within a particular area. By analyzing the problematic
areas, management can further identify strategies to overcome the problems faced.
They can even identify whether those areas of problem belongs to the system vendor
for refining or it needs to be attended by the IT Technical Support team. Figure below
represents the statistic report.
43
Figure 4.6.7.3 AMD & ISD Statistic Report
44
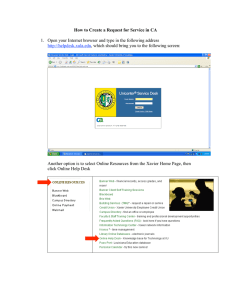
4.7
System Design
Figure 4.7: Main Page for MAPS Online Helpdesk
45
Figure 4.7 illustrates the system design for the Online Helpdesk for Maybank Account
Payable System. The login and password will be a compulsory field for all the four users
of the system. All the four users will be given their unique user id and password.
The home option in the screen will display the main screen of the system, which has the
login and password option. The FAQ, Glossary and Tutorial option will be useful for the
system users to obtain information. Incident/Case option will be available for users to open
a case or to log a problem. When this option is selected, all the detailed information about
the case can be logged. This will be the same option used by the IT Technical Support
Staff to update, close or delete a case in the system.
Statistic and management report option will only be activated for managers login. The
other users of the system will not be able to view both this option since they contain
confidential data to be only reviewed by higher management.
Add new user, maintaining existing user and delete existing user will only be available
upon administrator login. The role of an administrator is to maintain the users of the
Online Helpdesk System.
46
4.8
System Interface Chart
4.8.1 User Interface Chart
Login
Search Case
Open Case
View Case
Lookup FAQ,
Glossary, Tutorial
Submit Case
Generate
Problem Id
Send Email
4.8.2 Administrator Interface Chart
Login
Add User
Maintain User
Delete User
47
4.8.3 Manager Interface Chart
Login
View Statistic
View Management
Report
Lookup FAQ,
Glossary, Tutorial
4.8.4 IT Technical Support Interface Chart
Login
Search Case
View Case
Update Case
Close Case
Generate
Management Report
Delete Case
48
The interface chart above is represented for each user within the Online Helpdesk System. The
functions is as follows:
Login
Is used by each user to log in the system. If the user id and password is incorrect, the system will
prompt with message “ Wrong id and password, please try again”.
Open Case
This function is only used by the user to log a problem to the IT Technical Support. The
description of the problem is keyed in this option.
Submit Case
This function is used to submit the case to the IT Technical Support.
Generate Problem ID
When a new case is submitted to the IT Technical Support, a problem id will be automatically
generated by the system. The user can keep this problem id for further references.
Send Email
When a new case is submitted, an email will be automatically send to the IT Technical Support
with the problem id number. With the email, the IT Technical Support will be able to monitor all
new cases submitted in the system.
View Case
This option can be used by the user as well as the IT Technical Support. This option is used to
view the status of the ticket and also to view the new case opened by the user.
49
Search Case
This option is used by the IT Technical Support to view a new case opened by the user. The
problem id number is used to search a case submitted.
Update Case
This option is used by the IT Technical Support to update the status of the ticket. The status is
updated to show whether work is in progress or to show the current status of the ticket.
Close Case
A case is closed only if the problem has been solved and to indicate to the user that the problem
has been fixed.
Delete Case
A case can only be deleted by the IT if the status of the case is closed.
Add User
This function is used by the administrator to add a new user to the Online Helpdesk System. The
user id and password will be later provided to the user.
Maintain User
This function is used by the administrator to maintain the information of the users in the database.
The administrator will be able to edit the user information when it is required.
50
Delete User
This option is used by the administrator to delete a user who is no longer using the system. The
reason is because the particular user has resigned from the organization or the particular user has
transferred to a different department.
View Statistic
This option is used by the IT Technical Support and the Manager to view the statistic report
generated in the system. The statistic report contains the breakdown of cases opened for each
category of problem classification.
View Management Report
This option is only active upon the manager’s login. The management report contains three
different categories of report as stated in the management report module.
51
4.9 Design Techniques - UML
UML or better known as Unified Modeling Language by Object Management Group (OMG) is
the method used to show interaction between actor and the system. UML is an object-oriented
graphical modeling language for specifying and communicating the structure and dynamics of
software systems. It is used to create business models for requirements analysis, analysis models
and design models. Actors are defined, as the person, organization, or external system that plays
a role in one or more interactions with the system and an actor is drawn as stick figures.
The OMG’s Unified Modeling Language (UML) helps to specify, visualize, and document
models of software systems, including their structure and design in a way that meets all of these
requirements. By using any one of the large number of UML based tools, future application’s
requirements can be analyze and solutions that meets them can be designed. UML is also capable
in representing the results using UML’s twelve standard diagram types. UML is methodologyindependent and regardless of the methodology used to perform analysis and design, UML can
be used to express the result.
UML defines twelve types of diagrams, divided into three categories: four diagram types
represent static application structure; five represent different aspects of dynamic behavior; and
three represent ways you can organize and manage application modules. Structural diagrams
include the Class Diagram, Object Diagram, Component Diagram, and Deployment Diagram.
Behavioral Diagrams include the Use Case Diagram, Sequence Diagram, Activity Diagram,
Collaboration Diagram and State-chart Diagram. Model Management Diagrams include
Packages, Subsystems, and Models.
52
4.9.1
To – Be Process
The interaction between the actor and the system is represented with the Use Case Diagram. Use
Case Diagram is categorized under Behavioral Diagram, which captures some user visible
function. The modeling between the system and system actors are clearly shown and the
boundaries are easily understood. Figure 4.2 below illustrates the use case diagram for each actor
of the system such as the user, manager and IT technical support.
53
UML Diagram for Online Helpdesk System
Login
Open Case
Users
View Case
Lookup FAQ ,
Tutorial , Glossary
Search Case
IT Technical Support
Update Case
Close Case
Delete Case
View Statistic
Manager
View Management
Report
Figure 4.9.1: System Use Case Diagram
54
The Use-Case illustrated in the Figure 4.9.1 represents an overview of all the cases / processes
within the system. The use-case described includes three (3) actors of the system, which is the
user from the Property and ISD Department, IT Technical Support and the IT Manager.
The actor Property and ISD Department user represents the use-case of using the helpdesk
system. The users will be able to lookup for glossary, FAQ and refer the tutorial module. The
users also will be able to open a case when there is a problem to be logged. The user will also be
able to view the case opened to see the status of the case. By viewing the status, the user can
identify whether the problem is in progress, closed or waiting for vendors reply.
Next, the IT Technical Support is represented by the several use cases. The IT Technical support
will also be able to view a case when user logs the problem. Besides that IT Technical support
will be able to update a case to show the status of the case and also will be able to close the case.
The case will be closed when a problem has been completely attended. This use case extends the
statistic and management report use case. This use case will produce statistic of problems and
will also produce report for the management to keep track of problems resolved by IT Technical
Support. The IT Technical Support will be able to delete records for database maintenance
purpose. A case can be deleted only if the status is closed.
The manager will be able to view the statistic within the system. The system will contain
information pertaining problem faced by the system users. Besides that the manager will also be
able to view reports to keep track of cases closed and resolved by the technical support to
facilitate during the KPI review.
An administrator is responsible for user maintenance purposes. An administrator will be able to
add a new user, maintain delete an existing user. When a new user is added to the database, the
user will be able to log into the Online Helpdesk System.
55
4.9.1.1 IT Technical Support
IT Technical Support UML
Login
Search Case
View Case
IT Technical Support
Update Case
Close Case
Delete Case
View Statistic
Figure 4.9.1.1: IT Technical Support Use Case Diagram
Figure Description:
Figure 4.9.1.1 illustrates the activities that can be done by the IT Technical Support. The IT
Technical Support will be able to login in the system and search a new case opened by the user.
The IT Technical Support can view a case and also updated the status of the case. Once the case
has been resolved, the IT Technical Support will close the case. The IT Technical Support will
be able to delete a case to maintain the records in the database. Last but not least, the IT
Technical Support will be able to view the statistics report generated by the system.
56
4.9.1.2 Use Case Diagram – Manager
Manager UML Diagram
Login
View Statistic
Manager
View Management
Report
Figure 4.9.1.2: Manager Use Case Diagram
Figure Description:
Figure 4.9.1.2 illustrates the activities that can be done by the IT Manager. The Manager can
login in the system. Once the login is successful, the manager can view the statistic report.
Finally the manager can view the management report that consists of Problem Status Report,
IT Support Status Report and AMD & ISD Status Report.
57
4.9.1.3 Use Case Diagram – User
User’s UML Diagram
Login
Open Case
Users
View Case
Lookup FAQ ,
Tutorial , Glossary
Figure 4.9.1.3: User Use Case Diagram
Figure Description:
Figure 4.9.1.3 illustrates the activities that can be done by the system users. Users will be able to
login in the system. Once the login is successful, users can open a case to report the problem
faced. Users will be able to view the status of the case opened. Besides that users will be able to
lookup to the FAQ, Tutorial and Glossary module for extra information pertaining to the
system.
58
4.9.1.4 Use Case Diagram – Administrator
Administrator’s UML Diagram
Add User
Maintain User
Administrator
Delete User
Figure 4.9.1.4: Administrator Use Case Diagram
Figure Description:
Figure 4.9.1.4 illustrates the activities that can be done by an administrator. The administrator
is responsible to add a new user in the system. Once the user is added, the user name and
password will be provided to the user. The administrator will also be able to maintain the
records of a user. The administrator can update the information or reset the password of the
user by clicking on the maintain user option. Finally an administrator will be able to delete a
user from the system if the user has resigned or is no longer attached to the same department.
59
4.10
Use Case Description
This section will provide brief description of each use cases used in the use case diagram. The
description provides information of each use cases and the basic flow of events.
Use Case Number: 1
Use Case Name: Login
Brief description
This use case allows authorized users (user, IT Technical Support, Manager, Administrator)
to access to the Online Helpdesk System.
Flow of Events-Basic Flow
1. An actor will key in the login ID in the Login field.
2. Actor will key in the password in the password field.
3. Actor clicks the login button to access the system.
Alternative Flow
If actor keys in invalid login ID and/or password, the system will prompt the actor “Login
failed – please wait….”
Special requirements
None.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
If the use case was successful, the actor is now logged into the system.
Extension Points
None.
60
Use Case Number: 2
Use Case Name: Exit
Brief description
This use case allows users to exit from the online helpdesk system.
Flow of Events-Basic Flow
1. Actor can enter this button to exit from the Online Helpdesk System.
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
None.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
If the use case was successful, the actor is now logged out completely from the system.
Extension Points
None.
61
Use Case Number: 3
Use Case Name: Open Case
Brief description
This use case allows the actor (user) of the system to log a problem to the IT Technical
Support.
Flow of Events-Basic Flow
1. An actor will click the open case button.
2. Actor will key in the details & the problem faced.
3. Actor then will click the submit button.
Alternative Flow
None
Special requirements
None.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
If the use case was successful, the problem will be logged in the system and the IT Technical
Support will be prompted with an email.
Extension Points
None.
62
Use Case Number: 4
Use Case Name: Update Case
Brief description
This use case allows the actor (IT Technical Support) to update a case opened by the user.
Flow of Events-Basic Flow
1. Actor clicks the update case button.
2. Actor will then update the status of the problem
3. Actor will click the enter button.
4. Now the case is updated according to the category selected.
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
None.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
If the use case was successful, the case opened will be updated successfully and the latest
status will be displayed.
Extension Points
None.
63
Use Case Number: 5
Use Case Name: Close Case
Brief description
This use case allows the IT technical support to close a case that has been resolved.
Flow of Events-Basic Flow
1. Actor selects the close case button.
2. Actor updates the problem log accordingly.
3. Actor clicks the enter button.
4. The case is successfully closed.
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
None.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
If the use case was successful, management report will be updated & email will be send to
the manager to indicate the job has been completed.
Extension Points
None.
64
Use Case Number: 6
Use Case Name: View Case
Brief description
This use case allows the actor (IT Technical Support) to view the case. This use case is used
by the user to view the status of the ticket.
Flow of Events-Basic Flow
1. Actor will click the view case button.
2. Actor can view the problem logged and also the status of the case.
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
None.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
If the use case was successful, the actor will be able to view the problem and status of a case.
Extension Points
None.
65
Use Case Number: 7
Use Case Name: Search Case
Brief description
This use case allows the actor (IT Technical Support) to search for a particular case opened.
Flow of Events-Basic Flow
1.
Actor will key in the ticket number in the problem log option.
2.
Actor will click the enter button.
3.
The case opened will be displayed for the actor’s next course of action.
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
None.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
If the use case is successful, the actor will be able to view the case opened.
Extension Points
None.
66
Use Case Number: 8
Use Case Name: View Statistic
Brief description
This use case allows the actor (Manager & IT Technical Support) to obtain the statistics of
problems logged in the system.
Flow of Events -Basic Flow
1. Actor clicks the statistics button.
2. Actor can view the statistics of problem logged.
3. The actor will be able to analyze the problems faced frequently within the system
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
The statistics module will be only updated when a case has been successfully closed.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
None.
Extension Points
None.
67
Use Case Number: 9
Use Case Name: View Management Report
Brief description
This use case allows the actor (Manager) to view the management report produced by the
system.
Flow of Events -Basic Flow
1.
Actor will be prompted with an email when a case has been successfully closed.
2.
Actor can click on the management report button.
3.
Actor can view the management report to be used for KPI review.
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
The management report will be only updated when a case has been successfully closed.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
None.
Extension Points
None.
68
Use Case Number: 10
Use Case Name: View Glossary, Tutorial & FAQ
Brief description
This use case allows the actor (users) to obtain information for the system.
Flow of Events -Basic Flow
1.
The actor will either click on the glossary, FAQ or Tutorial button.
2.
The users can obtain all detailed information about the system and processes within the
system.
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
None.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
None.
Extension Points
None.
69
Use Case Number: 11
Use Case Name: Add User
Brief description
This use case allows the actor (Administrator) to add a new user to the system.
Flow of Events -Basic Flow
1. The actor will click on add user button
2. The actor will key in the relevant information pertaining to the user.
3. The actor will generate a user id for the user.
4. The actor will generate a password for the user.
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
The user must be a valid user from either of the departments.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
None.
Extension Points
None.
70
Use Case Number: 12
Use Case Name: Maintain User
Brief description
This use case allows the actor (Administrator) to maintain the existing user of the system.
Flow of Events -Basic Flow
1. The actor will key in the user name
2. The actor will be able to change the password of the user
3. The actor will be able to change particulars information of the user.
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
None.
Pre-Conditions
None.
Post-Conditions
None.
Extension Points
None.
71
Use Case Number: 13
Use Case Name: Delete User
Brief description
This use case allows the actor (Administrator) to delete the existing user of the system
Flow of Events -Basic Flow
1. The actor will key in the particular user information.
2. The actor will delete the user from the database
3. The actor will save the changes made.
Alternative Flow
None.
Special requirements
None
Pre-Conditions
A user can only be deleted if there are no longer using the system, resigned or transferred out
of the department.
Post-Conditions
None.
Extension Points
None.
72
4.11 Sequence Diagram
4.11.1 IT Technical Support
IT Technical Support Sequence Diagram
System Interface
IT Technical Support
Problem Log
View Case
Update Case
Close Case
Delete Case
Login ()
Enter problem id ()
View case displayed ()
Update problem status ()
Close case ()
Delete a case ()
Figure 4.11.1 Sequence Diagram - IT Technical Support
73
4.11.2 Manager
Manager Sequence Diagram
Manager
System Interface
Statistic
Management Report
Login ()
View Statistic ()
View Management Report ()
Figure 4.11.2: Sequence Diagram -Manager
74
4.11.3 User
User Sequence Diagram
User
System Interface
Open Case
View Case
Glossary , FAQ & Tutorial
Interface
Login ()
Open a new case ()
View Case Status ()
Lookup Glossary , FAQ & Tutorial ()
Figure 4.11.3: Sequence Diagram - User
75
4.11.4 Administrator
Administrator Sequence Diagram
Administrator
Add User
System Interface
Maintain User
Login ()
Add new user ()
Maintain Existing User ()
Delete Existing User ()
Figure 4.11.4 Sequence Diagram – Administrator
Delete User
76
4.12 Activity Diagram
4.12.1 User Activity Diagram
User Activity Diagram
[Invalid]
Login
[Valid]
Lookup FAQ, Glossary, Tutorial
Open Case
Figure 4.12.1 Activity Diagram - User
View Case
77
4.12.2 Manager Activity Diagram
Manager Activity Diagram
[Invalid]
Login
[Valid]
View Statistic
View Management Report
Figure 4.12.2 Activity Diagram - Manager
78
4.12.3 IT Technical Support Activity Diagram
IT Technical Support Activity Diagram
[Invalid]
Login
[Valid]
Search Case
View Case
Update Case
Close Case
Delete Case
Figure 4.12.3 Activity Diagram – IT Technical Support
79
4.12.4 Administrator Activity Diagram
Administrator Activity Diagram
[Invalid]
Login
[Valid]
Add User
Maintain User
Delete User
Figure 4.12.4 Activity Diagram - Administrator
80
4.13 Activity Diagram – Sub Module
4.13.1 Lookup FAQ, Glossary, Tutorial
Lookup FAQ, Glossary & Tutorial
[Not Available]
Lookup FAQ, Glossary, Tutorial
[Available]
Display Information
Figure 4.13.1: Lookup FAQ, Glossary, Tutorial
81
4.13.2 Open Case
Open Case
Select Problem Category
Fill in other information
Submit Case
Figure 4.13.2 : Open Case
82
4.13.3 View Case
View Case
Enter Problem No
Search Problem Log
View Case Status
Figure 4.13.3 View Case
83
4.13.4 View Statistic
View Statistic
Select Category of Statistic
View Statistic
Figure 4.13.4: View Statistic
84
4.13.5 View Management Report
View Management Report
Select Cateogry of Report
View Report
Print Report
Figure 4.13.5 View Management Report
85
4.13.6 Update Case
Update Case
Update Case Category
Save changes made
Figure 4.13.6: Update Case
86
4.13.7 Close Case
Close Case
[Not Completed]
Check Case Status
[Completed]
Close Case
Submit
Figure 4.13.7: Close Case
87
4.13.8 Delete Case
Delete Case
[Not Closed]
Check Case Status
[Closed]
Delete Case
Save
Figure 4.13.8: Delete Case
88
4.13.9 Add User
Add User
Add user info
Generate user id
Generate password
Save
Update Database
Figure 4.13.9: Add User
89
4.13.10 Maintain User
Maintain User
Enter user name
Update user info
Save
Update Database
Figure 4.13.10 Maintain User
90
4.13.11 Delete User
Delete User
Enter user name
Delete user
Save
Update Database
Figure 4.13.11 Delete User
91
4.14 Problem Categorization
Problem classification is the process to identify the types of problems. All problems logged to
the Online Helpdesk System is categorized as follows:
No Type of Problem
Description of Problem
Resolution Time
1
Password Reset
The users password is locked out because
of two reasons:
The user has entered a non valid
password more than 3 times
The user account is inactive for more
than 3 months
Based on experience, this
problem
should
be
resolved by 30 min from
the time the problem is
logged.
2
Network
Failure
3
Installation
of This request is made when there is a new Based on experience, this
MAPS software
user. The installation of MAPS has to be problem
should
be
done in parallel with installation of SQL.
resolved by 3 days from
the time the problem is
logged.
Investigation (data This problem occurs when the PO, DO or Based on experience, this
related)
Invoice files are not loaded to the system problem
should
be
automatically.
resolved by 2 hours from
the time the problem is
logged.
Reloading of TX or TX or Proman data has to be reloaded into Based on experience, this
Proman data
the server because the files were not problem
should
be
loaded automatically.
resolved by 2 hours from
the time the problem is
logged.
Others
(not This problem may or may not be related The duration has not
specified above)
to the above problems.
been set because the
complexity of problem is
unknown.
Table 4.14: Problem Categorization
4
5
6
/
Line This problem occurs when the internet Based on experience, this
services is down in Maybank. The users problem
should
be
can’t access the system.
resolved by 2 hours from
the time the problem is
logged.
92
4.15 Physical Design
Physical design illustrates the physical aspect of the implementation. Example of physical
design is such as database design used in the system.
4.15.1 Database Design
Two tables have been used for data storing purposes. The tables are as follows:
i. Caselog
This table is used to store the information when a new case is opened. The fields of the
table is as follows:
No
Field Name
Field Type
Description
1
cID
Char
A field that is automatically generated when a
user opens a case. It is represented by the date
and the ip address of the pc.
2
cProblemID
Char
This id is created when a user opens a new case.
3
cReportedBy
Char
Captures upon the user logon
4
dtReportedDate
Date
Stores the date the user has opened a case
5
dtReportedTime
Date
Stores the time the user has opened a case
6
cProblemCategory
Char
Stores the problem category chosen by the user
7
cProblemDescription Char
Stores the problem description given by the user
8
cStatus
Char
Captures the status of the ticket
9
cClosedBy
Char
Captures the IT Technical Support who has
closed the case.
10
bCaseClosed
Char
Stores the status of the ticket, whether the ticket
is open or closed.
Table 4.15.1: Caselog Table Details
93
ii.
Userdetail
This table is used to store the information of the user in the system. The fields of the
table is as follows:
No
Field Name
Field Type
Description
1
cID
Char
A field that is automatically generated when a user
opens a case.
2
cUserName
Char
Stores the name of the user
3
cPassword
Char
Stores the password of the user
4
cDesc
Char
Stores the description of the user e.g. last name
5
cUserType
Char
Stores the type of user e.g. manager, IT Technical
support and user.
6
CEmailID
Char
Stores the email address of the user
7
CLoginKey
Char
Unique key generated at every users login
Table 4.15.2:UserDetail Table Details
94
4.16 Software Requirements
i. PHP (hypertext preprocessor)
PHP is a server-side scripting language designed specifically for the web. The goal of the
language is to allow web developers to write dynamically. PHP allows interfacing to many
different database systems that provides an open database connectivity standard (ODBC) such as
MySQL, Oracle, Microsoft products and others. Other advantages are low cost and availability
of source code. PHP is portable across multiple platforms and is created as an open-source
technology based on C, Perl, and Java that can run on multiple operating systems and multiple
web servers.
ii. MySQL
MySQL is an open source relational database management system (RDBMS) that uses
Structured Query Language (SQL), the most popular language for adding, accessing, and
processing data in a database. MySQL is noted mainly for its speed, reliability, and flexibility. It
is fast, robust and scalable relational database management system. My SQL is a true multi-user,
multi-threaded SQL (structured programming language) database server.
iii. Apache web server
The apache web server is the software that responds to client requests by providing resources,
such as XHTML documents. Apache has other powerful features included in a large set of
modules, including mod perl, and many authentication modules.
iv. Microsoft Visio professional 2003
This software is used to create UML diagrams such as use case diagrams and sequence diagrams
for system representation.
v. Microsoft Office 2000
Software package used to prepare Gantt chart, estimation of cost, project monitoring and monitor
project progress.
95
4.17 Hardware Requirement
i. Servers
Pentium-based server or equivalent
Network interface card
Hub/ switch
ii. Client
Pentium-based pc or equivalent
Network interface card
4.18 Test Plan
The Software Test Plan (STP) is designed to prescribe the scope, approach, resources, and
schedule of all testing activities. The plan will identify items to be tested, the features to be
tested, the types of testing to be performed, the personnel responsible for testing, the
resources and schedule required to complete testing. The purpose of the software test plan is
such as:
To achieve 100% CORRECT code and ensure all Functional and Design
Requirements are implemented as specified in the documentation.
To provide a procedure for Unit and System Testing.
To identify the test methods for Unit and System Testing.
4.18. 1 Process of Test Plan
Identify the requirements to be tested. All test cases shall be derived using the current
design specification.
Identify particular test to use to test each module.
96
Review the test data and test cases to ensure that the unit has been thoroughly verified
and that the test data and test cases are adequate to verify proper operation of the unit.
Identify the expected results for each test.
Perform the test.
Document the test data, test cases used during the testing process.
4.19 Testing Method
The test plan outlines the entire testing process and includes the individual test cases. Test
plan is usually designed to plan the testing to be done. The types of testing that will be
deployed are as follows:
4.19.1
Unit Testing
Unit testing is conducted to verify the implementation of the design for one software
element (e.g., unit, module) or a collection of software elements. The purpose of
component testing is to ensure that the program logic is complete and correct and
ensuring that the component works as designed. All individual units will be tested
separately. The following module were tested:
4.19.1.1 Interface Testing
Login Module
Open Case Module
View Case Module
Update Case Module
Delete Case Module
Add/ Edit / Delete User Record Module
Display Statistic Module
Display Management Report Module
View Glossary, FAQ and Tutorial Module
97
4.19.2 Integration Testing
In this method of testing, I have tested the integrity between PHP and MySQL. The testing
shows that all the updates done in PHP are automatically updated in MySQL.
4.19.3 System Testing
System testing is done to test the entire system. The system should behave as stated in the
requirements portion.
4.19.4 User Acceptance Testing
User acceptance testing is done when the system is completed and the system is ready for
delivery. During this testing, the users will test the system to confirm that it complies with the
requirement.
4.20 Chapter Summary
As a summary, this chapter has illustrated the organizational analysis in terms of the As-Is
Process. The current process has clearly defined the need for an automated system. With the user
requirement, the To-Be Process has been designed for the Online Helpdesk System. The system
is represented with several UML diagrams to show the interaction between the user and the
system.
98
CHAPTER 5
5.0 DESIGN IMPLEMENTATION AND TESTING
5.1 Introduction
This chapter emphasizes on system implementation. The system has been transformed
from user requirement into a workable product. The purpose of system implementation
is to make sure that the correct application is delivered to the end user. Besides that, this
chapter also emphasizes on the testing done to confirm it meets the user requirement.
5.2 Coding Structure
The structure used represents the structure of PHP and HTML. PHP is the back
end processing language while HTML is used for the design of the website. Following
is one of the snapshots of critical programming codes. The codes below is used to
generate the primary key when a case is opened in the website. This key will be then
concatenated with the date and the ip address of the particular pc.
//Generate Primary Key
function cfuncGeneratePrimaryKey() {
//date and time
$curDateTime=date('YmdGis');
//generate random no
$curRandomNo=rand();
$curRandomNo='00000' . $curRandomNo;
$curRandomNo=substr($curRandomNo,strlen($curRandomNo)-5,5);
99
//get the running no from param.txt
$curRunningNo=ifuncGetRunningNo();
//increment and update the running no
funcSetRunningNo($curRunningNo + 1);
$curRunningNo='00000' . $curRunningNo;
$curRunningNo=substr($curRunningNo,strlen($curRunningNo)-5,5);
//get ip add
$curIpAdd=$_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'];
$primaryKey=$curDateTime . $curRandomNo . $curRunningNo . $curIpAdd;
return $primaryKey;
}
//get the running no for generation of Primary Key from param.txt
function ifuncGetRunningNo() {
$filename=FILENAME_PARAM_TXT;
$handle = fopen($filename,'r');
$runningNo = fgets($handle);
fclose ($handle);
return $runningNo;
}
//set the Running No user for generation of Primary Key in params.txt
function funcSetRunningNo($runningNo) {
if($runningNo>=999999)
$runningNo=0;
$filename=FILENAME_PARAM_TXT;
$handle=fopen($filename,'w');
//write string to the file handle
fputs($handle,$runningNo);
//close file
fclose($handle);
}
100
5.3 Test Cases and Test Result
5.3.1 Login
No
Test
Case
1. Normal
Login
2. Login
denied
Objective
Input
Expected
Output
Redirect to user,
IT Technical
Support,
Manager and
Administrator
section.
Actual Output
To gain access to the
system with appropriate
access level
a. User
b. IT Technical
Support
c. Manager
d. Administrator
To deny access for
unauthorized user
Valid user id
& password
Redirect to user, IT
Technical Support,
Manager and
Administrator
section.
Invalid Login
And/or
Invalid
Password
Login Failed
Redirect to login
page
5.3.2 Open Case
No
Test Case
Objective
Input
Expected
Output
Actual Output
1
Open Case
To open a new case in
the system
Category of
problem and
description of
problem
A problem id
will be
generated
when the user
clicks the
submit button
A problem id is
generated and
displayed to the
user.
Objective
Input
Actual Output
To allow the user and IT
Technical support view
the case
Problem ID
Expected
Output
Display the
particular case.
5.3.3 View Case
No
1
Test
Case
View
Case
Display the case
101
5.3.4 Update Case
No
1
Test
Case
Update
Case
Objective
Input
Expected Output
Actual Output
Update case to show the
latest progress of the
case.
IT Technical
Support
updates
status of
problem field.
Status of case
is updated
correctly.
Display the status
correctly.
Objective
Input
Expected Output
Actual Output
Delete case to be able to
maintain the database
records.
IT Technical
Support
deletes a
closed case
IT Technical
Support
deletes a
case which is
not closed
Case can be
deleted
successfully
Case record is not
shown in database.
Case can’t be
deleted
Case record is still
shown in database
5.3.5 Delete Case
No
1
2
Test
Case
Delete
Case
Delete
Case
Delete case to be able to
maintain the database
records.
5.3.6 Add User
No
Test Case
Objective
Input
Expected Output
Actual Output
1
Add User
To add a new user in the
system
Full Name
Email
Address
User Name
Password
System will
record user
information in
database
Display user
information
correctly.
5.3.7 Maintain User
No
Test Case
Objective
Input
Expected Output
Actual Output
1
Maintain
User
To maintain the record of
the existing user in the
system
Details which
needs to be
updated
System will
record updated
user information
in database
Display updated
user information
correctly.
102
5.3.8 Delete User
No
Test Case
Objective
Input
Expected Output
Actual Output
1
Delete User
To delete the record of
the user in the system.
Eg user transfer
department and resign
Username
System will
delete user
information from
database
User information is
not stored in
database.
5.3.9 Display Statistic
No
Test Case
Objective
Input
Expected Output
Actual Output
1
Display
Statistic
To allow IT Technical
Support & Manager view
the statistic report
IT Technical
Support and
Manager
Login
Display statistic
report by two
categories, e.g.
statistics of
problems and
statistic of users.
Display statistic by
problem
Display statistic by
user
5.3.10 Display Management Report
No
Test Case
Objective
Input
Expected Output
Actual Output
1
Display
Manageme
nt Report
To allow Manager view
the management report
Manager
Login
Display
management
report by two
categories, e.g.
Resolved/closed
cases and KPI of
IT Technical
Support.
Display report of
resolved / closed
cases
Display IT
Technical Support
KPI
5.3.11 View FAQ, Glossary & Tutorial
No
Test Case
Objective
Input
Expected Output
Actual Output
1
View FAQ,
Glossary &
Tutorial
To allow users view the
FAQ, Glossary & Tutorial
Login
Display FAQ,
Glossary &
Tutorial
information
Display the
information as
expected.
103
5.4 User Manual For Administrator
This section intends to provide the administrator on the understanding of installation and
maintenance of the system. This system is developed using Open Source technology.
5.4.1 Hardware Configuration or Setup
Operating System - Windows XP & Windows 2000
Web Server - Apache 2.0.48
Database - MySQL 4.0.12
Scripting Language - PHP 4.1, Java Script
Front End – HTML
Browser – Internet Explorer 6.0
RAM – 240 MB
5.4.2 Installation Procedure
5.4.2.1 Install Apache
1.
Double click the Apache setup file
2.
Settings:(can be change in httpd.conf in C:\MAPS\Apache\Apache2\conf)
3.
Network Domain
= mapsonline.com
x Server Name
=www.mapsoline.com
x Admin E-mail Add =shobhi@mapsonline.com
4.
Select – for All users
5.
Select Typical
6.
Install directory
=C:\MAPS\Apache
** Test in browser to ensure Apache is running
104
5.4.2.2 Install PHP
1. Double click the Php zip file
2. Extract folders and files to C:\MAPS
3. Rename folder in C:\MAPS to php (for example php4.3.4 to php)
5.4.2.3 Install Apache To Run PHP
1. Open install.txt which is located in php folder
2. Find for LoadModule
3. Copy these 3 lines:
x LoadModule php4_module c:/php/sapi/sapi/php4apache.dll
x AddModule mod_php4.c
x AddType application/x_htpd_php php
4. Open httpg.conf file which is located in C:\MAPS\Apache\Apache2\conf
folder
5. Find for LoadModule (the long list of LoadModule)
6. Paste the 3 lines copied from install.txt
7. Delete the second line
8. Edit the first line to D:/MAPS/php/sapi/php4apache2.dll
9. Move php4ts.dll from php folder to the sapi folder
10. In php folder, rename php.ini-dist to php.ini
11. Move php.ini to C:\WINNT folder
5.4.2.4 Install MySQL
1. Double click the MySQL zip file and click Install
2. Install to C:\MAPS\mysql
3. Select Typical
4. Click winmysqladmin.exe to run MySql
5. Set the username=root and password=root
105
5.5 Chapter Summary
This chapter illustrates in detail the system implementation and testing carried out. It involves the
testing conducted the test the system output. User manual for administrator provides guide on the
installation processes, and maintainance of the system.
106
CHAPTER 6
6.0
ORGANIZATIONAL STRATEGY
6.1 Introduction
This chapter discusses the strategy of the organization towards introducing the system. This
chapter will introduce the roll out strategy taken by the organization to implement the web based
Online Helpdesk System for the two departments.
6.2 Roll Out Strategy
Application Rollouts is the process of extending the pilot implementation to other business units
and locations. Objective of implementation is to design and implement the solution blue print, in
a rollout strategy. The approach chosen to for the roll out strategy depends on the scope of the
initiative. The approach chosen is as follows:
6.2.1 Pilot Strategy
Pilot selection can have crucial impact on the speed and success of the roll out plan. Pilot
strategy is chosen since the users will be users from two different departments. Property
Department users will deploy the system first. Once the users are able to use the system in a
web based environment, then the system will be introduced to ISD Department users. The
Property Department users will serve as the test bed for this implementation purposes.
107
6.3 Change Management
Change management is crucial because it often involves people in the organization. People most
of the time prefers to practice the same routine of work because they are already in the comfort
zone and they are used to doing things in the same way for years. People usually resist changing
to a new concept or technology because they fear its outcome. Change needs to be managed
effectively, so that, people won’t fear using the latest technology in the organization. Some of the
reasons people fear for change is as follows:
Users will feel threatened with the new system
The system is not easy to use initially
Sufficient training pertaining to the system is not provided to users
Although the developed system makes the users life easier, but some level of change
management training should be given to the users. One of the best techniques to address change
issues is providing training to users. It is an effective way for the users to ask questions regarding
the system.
All users for Online Helpdesk System will be given separate training to ensure they are familiar
wit the system functionality. The training will emphasis on the role and accessibility of each user
within the system.
108
6.4 Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
Business Continuity Planning involves devising a plan to guards against business disruption in
case of unforeseen events. It is also the process of identifying critical data system and business
functions, analyzing the risks of disruption to the data system and functions. It also determines
the probability of disruption occurring and developing business resumption plan (BPR) to enable
the system to be resumed in the event of disruption.
If Online Helpdesk System is inaccessible due to natural disaster, system crash or other
unforeseen reasons, then the following steps will be taken as a backup plan.
Users to use the manual method of problem logging to the IT Technical Support
Have a backup of the hardware and software (application files) to be used if the system
crashes.
Have an off site data backup (data can be restored if the database corrupts)
6.5 Expected Organizational Benefit
By deploying the Online Helpdesk for Maybank Account Payable System, there is some
significant benefit for the organization as follows:
Firstly it allows IT Department to provide excellent services to the business users.
There is a proper mechanism to log problem to the relevant party (IT Technical Support)
As a result, tracking and monitoring of problems and cases raised are more systematic.
Management will be able to gauge the performance of IT Technical Support
Proper allocation of resources and expertise.
Turnaround time can be saved because a particular problem is escalated to the appropriate
party for further action
109
6.6 Chapter Summary
This chapter illustrates the organizational strategy in terms of the roll out strategy. The pilot roll
out strategy is chosen because the roll out will be done according to locations. The roll out will
be done in Property Department and if the implementation is successful, then the roll out will be
extended to the ISD department. Besides the roll out strategy, it is essential to have a change
management approach to manage resistance towards change. Besides that, business continuity
plan is important if the system is unavailable due to disaster, system crash or other reasons. Last
but not least, this chapter illustrates the benefits of deploying the web based Online Helpdesk
System.
110
CHAPTER 7
7.0 DISCUSSION & CONCLUSION
7.1 Achievements
The Online Helpdesk for Maybank Account Payable System is designed based on the study done
on the current organizational analysis. The findings and information pertaining to the Online
Helpdesk System was gained from the analysis and literature review done. The main
achievement of this project is the ability to automate the problem logging process in Maybank.
Problem monitoring and tracking also becomes more systematic with the Online Helpdesk
System.
During initial design process, I tried to apply my knowledge and skills that I have acquired from
previous UTM courses for my project. I transformed the user functional requirement to the ToBe System. Last but not least, I have managed to complete the proposed system within the time
frame allocated by the university.
111
7.2 Constraint and Challenges
Although the system is able to address the current organizational problems, but the system
still have some drawbacks as follows:
This current system only focuses on issues such as problem logging, monitoring and
tracking of problems.
The management report produced for KPI purpose only emphasizes on the KPI aspect for
each of the IT Technical Support. The KPI report does not give a breakdown of
calculation based on any formula because the management has not decided on the latest
KPI structure.
Besides the constraints faced, some of the challenges during the development of the system is
as follows:
Lack of experience and knowledge to develop web based system
Resources are limited, including capital and technical people.
Short time provided to complete the system and the thesis.
7.3 Aspiration
It is hoped that the system developed will be useful for the users as well as the organization. It is
also hoped that the system developed will be used for the daily activity in Maybank and the
problems faced by the user and management will be reduced. Besides that, it is hoped that the
system can be further enhanced according to the users need and expectation. Some features that
needs to be added are such as:
More management reports should be added to help management make decision.
Should add knowledge-based repository to store information pertaining to problem and
possible solution.
Reports should be customized to be weekly and monthly based on the management’s
requirement.
112
In future, top 10 problems encountered within the system should be listed with the
possible solutions to enable users solve the problem if it does not require the assistance of
the IT Technical Support.
7.4 Chapter Summary
This chapter discusses the achievement in the system implementation process, constraint and
challenges faced. It also gives a brief overview of the future development, which should done to
further refine the system.
113
REFERENCES
1. Alan Dennis, Barbara Haley Wixom.2000. System Analysis and Design: Hermitage
Publishing Service.
2. Donna Knapp.1999. A Guide to Customer Service Skills for Helpdesk Professional:
Course Technology Publishing.
3. Ian Sommerville.1995. Software Engineering. Addison Wesley Publishing
4. Leland.1995.Customer Service for Dummies: IDG Books Worldwide
5. http://www.auditnet.org/docs/Help%20Desk%20and%20Problem%20
Management.pdf
APPENDIX A