LAB PROCEDURE 1.
advertisement

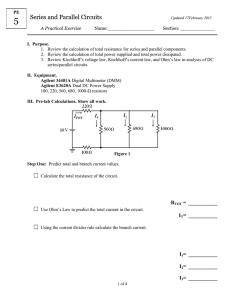
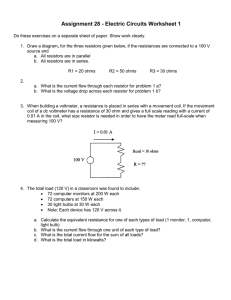
Revised 02/28/01 mjh LAB 3 BASIC ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LAB LAB PROCEDURE 1. LOCATE the following PIECES and PARTS in your ELECTRONIC PARTS KITS or on the TABLE: A power supply with wire leads, a Digital Multi-Meter (DMM), a switch, two 330 ohm resistors (orange/orange/brown color bands), a 2200 microfarad capacitor, a light emitting diode (LED), a wire jumpers kit, and a prototyping board. 2. UNPLUG the power supply from the outlet. 3. On the prototyping board, CONNECT one LEAD of the SWITCH to a POWER (+5 Vdc) hole. CONNECT the other LEAD to a hole in any one of the 5-hole terminal sets. 4. CONNECT a 330 ohm resistor from that same set to another nearby set. 5. CONNECT an LED from that nearby set to ground. Note that the LED must be oriented properly for it to work. The lead with a spearhead shape to it inside the LED is the positive lead. 6. CONNECT LEADS from the POWER SUPPLY to the prototyping board. INSURE that the POSITIVE LEAD goes to the GREEN POST while the NEGATIVE LEAD (ground) goes to the BLACK POST. At the same time, CONNECT JUMPER WIRES from the POSTS to the POWER BUS sets. The +5 (GREEN POST) should wire to the RED STRIPED sets while the GROUND (BLACK POST) should go to the BLUE STRIPED sets. 7. PLUG IN the POWER SUPPLY to the 120 Vac ELECTRICAL OUTLET. 8. PRESS SWITCH LEVER and the LED should EMIT LIGHT. RELEASE the LEVER and the LED should STOP EMITTING LIGHT. 9. SET the DMM to a 20 Vdc range (three ‘clicks’ counterclockwise from OFF position). 10. LOCATE the points AA, BB, and CC on the SCHEMATIC DRAWING. Now LOCATE the SAME ELECTRICAL POINTS on your prototyping board. 11. PRESS and HOLD the SWITCH LEVER. 12. PLACE BLACK DMM LEAD so it CONTACTS BLACK POST METAL (or equivalent point CC). PLACE RED DMM LEAD so it CONTACTS POINT AA. RECORD the READING of the DMM DISPLAY. 13. PLACE BLACK DMM LEAD so it CONTACTS BLACK POST METAL (or equivalent point CC). PLACE RED DMM LEAD so it CONTACTS POINT BB. RECORD the READING of the DMM DISPLAY. 14. RELEASE the SWITCH LEVER. 15. CONNECT ANOTHER 330 OHM RESISTOR in PARALLEL with the EXISTING RESISTOR. Lab 3 Procedure Revised 02/28/01 mjh 16. REPEAT STEPS 11 THROUGH 14. Does the LED output seem different? If so, how is it different? 17. CONNECT a 2200 MICROFARAD CAPACITOR from the HOLE SET of the JUNCTION OF THE SWITCH LEAD AND RESISTOR LEAD ( AA ), TO the SYSTEM GROUND (SETS OF HOLES MARKED BLUE). INSURE THE CAPACITOR LEAD MARKED – (negative) IS CONNECTED TO THE BLUE MARKED HOLES (ground). 18. PRESS the SWITCH LEVER. 19. NOTE and RECORD what happened to the LED OUTPUT. 20. RELEASE THE SWITCH LEVER. NOTE and RECORD what happened to the LED OUTPUT. 21. PRESS the SWITCH LEVER, WAIT a moment, then RELEASE the SWITCH LEVER. BEGIN TO COUNT when you release the SWITCH LEVER. HOW LONG does it take for the LED to BE COMPLETELY OFF? TRY THIS A FEW TIMES AND RECORD AN AVERAGE TIME in seconds. 22. USE the DMM to MONITOR point AA (RED LEAD TO AA, BLACK LEAD TO CC). Now REPEAT STEP 21 BUT COUNT the TIME it takes for the VOLTAGE LEVEL at AA to DROP TO 1.7 Vdc after the SWITCH LEVER is RELEASED. 23. REMOVE ONE of the 330 OHM REISITORS and REPEAT STEPS 21 and 22. 24. YOU HAVE COMPLETED THE MEASUREMENT STEPS FOR THIS LAB ! Lab 3 Procedure Revised 02/28/01 mjh ENGINEERING 182 BASIC ELECTRONICS MEASUREMENT RECORDING AND NOTATIONS: STEP 12(one resistor): _____________ Volts STEP 13(one resistor): _____________ Volts STEP 12(two resistors): ___________ Volts STEP 13(two resistors): ___________ Volts What can you conclude about the variation of voltage across the LED? Is a diode (LED) a regulator (‘maintainer’) of voltage? Explain your answer. Notes for Step 16: _____________________________________________________________________________ Notes for STEP 19: Notes for STEP 20: _____________________________________________________________________________ Time for LED to completely turn off: ____________________ seconds (STEP 21, 2 resistors). Time for voltage level to reach 1.7 Vdc: _________________ seconds (STEP 22, 2 resistors). Time for LED to completely turn off: _____________________ seconds (STEP 21, 1 resistor). Time for voltage level to reach 1.7 Vdc: __________________ seconds (STEP 22, 1 resistor). Lab 3 Procedure Revised 02/28/01 mjh What can you conclude about the effect of resistance (along with capacitance) on the time response of the circuit? Lab 3 Procedure