Introduction to Engineering Exam 4 SHOW CALCULATIONS AND UNITS FOR ALL ANSWERS
advertisement

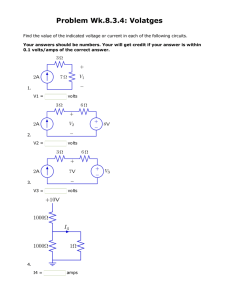
Introduction to Engineering Exam 4 SHOW CALCULATIONS AND UNITS FOR ALL ANSWERS Problem 1a: The voltage source for the circuit shown below is 12 V: (15 Points) a. If all three resistors were to be replaced with one single equivalent resistor, what would be its resistance value? b. What would be the current flow, i, in this circuit? c. Which of the following resistors, R1, R2, or R3, would have the largest voltage change across it? Given: R1 = 6 V = 10 Volts R2 = 8 R3 = 2 a. Req R1 R2 R3 6 8 2 16 b. i V 10 0.625Volts Req 16 R3 8 V 10 5 Volts Req 16 Problem 1b: Assume for the circuit shown that the R’s are the light bulbs and that you have been able to measure and determine the following values: (19 points) c. R3 Source Voltage V = 120 Volts Source Current ix = 15 Amps VR3 i1 = 10 A i3 = 3 A Calculate the missing parameters of: V 120 12 i1 10 V 120 60 b. R2 i2 2 a. R1 c. i2 i x i1 i3 15 10 3 2 Amps Calculate the equivalent resistance, Req, for all three resistors combined 1 1 1 Req R1 R2 R3 1 1 1 1 12 60 40 1 8 R3 V 120 40 i3 3 If R1 (first bulb) is removed or turned off, what would be the new ix? i x i2 i3 5 Amps 612896223 1 Problem 2: While on vacation, you see a giant sequoia (tree) and wonder how high it is. You have your max flash camera with you and, from your lab experiments, you know the focal length of this camera is about 30 mm. You pace off the distance from the place you took the picture to the base of the sequoia and find it to be 120 meters. When you get the prints back you measure the image of the giant sequoia on the negative and find it to be 20 mm high. Given this information, how tall is the sequoia? (10 points) Tree d f Image This is a problem of similar triangles: Tree Height d 120 60 120 f 0.02 0.040 meters f Image Height f 0.02 60 Problem 3: In the camera, the flash capacitor can still be dangerous even with the batteries removed. Why is this? (6 points) Capacitors are energy storage devices. Thus even with the power source (i.e. the batteries) removed, it is possible that there is still energy stored in the capacitor that when discharged will pose a possible threat to safety. Problem 4: Two common assembly methods are fixed material location and sequential assembly. Briefly describe each method. Discuss one common problem with the sequential assembly line method and briefly describe how you would attempt to solve it. (9points) Fixed material location is when all of the materials for a product are brought to a single location and the product is not moved as it is assembled. Sequential assembly (also known as an assembly line) is when the product being assembled is moved from one location to the next location and a new component/components are added to the product. -- One common problem with this method is called a bottleneck. This occurs when one location is significantly behind the others and the product begins to pile up at that location. A possible solution is assign additional labor to the location. 612896223 2 Problem 5: The following saw tooth waveform was measured on an oscilloscope similar to the ones that you used in lab. What is the voltage at 11 milliseconds? What is the frequency and period of the waveform? (6 points) NOTE: The reference voltage (zero voltage) is indicated by the arrow with the ground symbol in the middle of the display. @ 11 ms the voltage reading is +5 Volts To find the frequency we note that the waveform repeats every 8 milliseconds. Thus the frequency is: f 612896223 1 1 250 Hertz T 0.004 3 Problem 6: Using CADKEY create an isometric (3-D) drawing of the object whose multi-view drawing is shown below. PRINT THE (3-D) DRAWING. DO NOT LEAVE YOUR SEAT. THE INSTRUCTOR WILL COLLECT THE DRAWING FROM THE PRINTER. Make sure your name appears on the drawing! Use print preview to see the drawing you are sending to the printer. (35 Points) 1 grid space = 0.5 inches 612896223 4