Descriptive Statistics III REVIEW S
advertisement

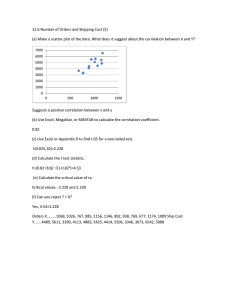
Descriptive Statistics III REVIEW • Variability • Range, variance, standard deviation S2 X M n 1 2 S S 2 • Coefficient of variation (S/M): 2 data sets • Value of standard scores? X M Z S T 50 10 z p 50 z ( percentile ) Correlation and Prediction HPHE 3150 Dr. Ayers Variables Dependent • • • • • • (ordinal/continuous: #) Presumed effect Consequence Measured by researcher Predicted Criterion Y Y dv X iv Independent • • • • • • (categorical: name) Presumed cause Antecedent Manipulated by researcher Predicted from Predictor X Correlation (Pearson Product Moment or r) •Are two variables related? •Car speed & likelihood of getting a ticket •Skinfolds & percent body fat •What happens to one variable when the other one changes? •Linear relationship between two variables •1 measure of 2 separate variables or 2 measures of 1 variable •Provides support for a test’s validity and reliability Attributes of r magnitude & direction N e g a t i v e P o s i t i v e 1 . 0 0 . 7 0 0 . 3 0 0 0 . 3 0 0 . 7 0 1 . 0 Perfect High Low Zero Low High Perfect Scatterplot of correlation between pull-ups and chin-ups Chin-ups (#completed) (direct relationship/+) 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 2 4 6 8 Pull-ups (#completed) 10 12 14 Scatterplot of correlation between body weight and pull-ups Pull-ups (#completed) (indirect/inverse relationship/-) 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 120 130 140 150 Weight (lb) 160 170 180 Scatterplot of zero correlation (r = 0) Figure 4.4 Y 8 6 4 2 0 0 2 4 6 X 8 10 Correlation Formula (page 60) r n X n XY – X Y 2 – X n Y – Y 2 2 2 Correlation issues • Correlation ≠ causation • -1.00 < r < +1.00 • Coefficient of Determination (r2) (shared variance) • r=.70 r2=.49 49% variance in Y accounted for by X Y dv X iv • Negative correlation possibly due to: • Opposite scoring scales • True negative relationship • Linear or Curvilinear (≠ no relationship; fig 4.6) • Range Restriction (fig 4.7; ↓ r) • Prediction (relationship allows prediction to some degree) • Error of Prediction (for r ≠ 1.0) • Standard Error of Estimate (prediction error) Limitations of r Figure 4.6 Curvilinear relationship Example of variable? Figure 4.7 Range restriction Limitations of r Correlation & Prediction I REVIEW • Bivariate nature of correlations • X (iv) & Y (dv) • +/- relationships • Range of r? • Coefficient of Determination (r2) (shared variance) • Coefficient of variation (S/M): 2 data sets • Low V (.1-.2=homo): M accounts for most variability in scores • Curvilinear relationship? • Correlation/Causation? Fitness/PA Uses of Correlation • Quantify RELIABILITY of a test/measure • Quantify VALIDITY of a test/measure • Understand nature/magnitude of bivariate relationship • Provide evidence to suggest possible causality Misuses of Correlation • Implying cause/effect relationship • Over-emphasize strength of relationship due to “significant” r Correlation and prediction % Fat Skinfolds Sample Correlations Excel document Standard Error of Estimate (SEE) Average error in the process of predicting Y from X Standard Deviation of error S e Sy 1 r As r ↑, error ↓ As r ↓, error ↑ Is ↑r good? Why/Not? Is ↑ error good? Why/Not? 2