vii TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER
advertisement

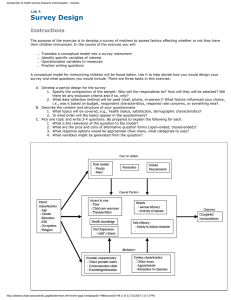
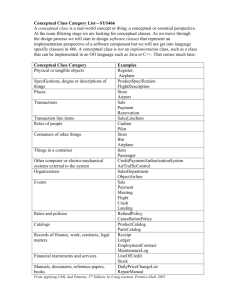
vii TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 TITLE PAGE DECLARATION ii DEDICATION iii ACKNOWLEDGEMENT iv ABSTRACT v ABSTRAK vi TABLE OF CONTENTS vii LIST OF TABLES xii LIST OF FIGURES xiii LIST OF APPENDICES xv LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS xvi INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction and Background 1 1 1.1.1 Background of Prevention through Design 4 1.1.2 Factors Impacting Implementation of PtD Concept 5 1.2 Problem Statement 6 1.3 Aims and Objective of Study 7 1.4 Objectives of Study 8 1.4.1 Objective 1 8 1.4.2 Objective 2 9 viii 1.4.3 2 9 1.5 Research Scope and Limitations 10 1.6 Significant of Study 11 LITERATURE REVIEW 12 2.0 Introduction 12 2.1 Definition of Prevention through Design (PtD) 12 2.2 The Building Design Process 15 2.3 2.4 3 Objective 3 2.2.1 History of Design Process Models 17 2.2.2 Definitions of Design and Process 18 2.2.3 Architectural Design Process Models 19 2.2.4 RIBA Plan of Works (2007) 20 2.2.4.1 Preparation/Pre-Design Process 22 2.2.4.2 Design Process 23 The factors affecting the Design Process 26 2.3.1 Integrated Design Team Process 28 2.3.2 Procurement method 28 2.3.3 Communication 28 2.3.4 Adverse Attitude 28 2.3.5 Competency of Designer 29 2.3.6 Time for design work 29 2.3.7 Knowledge of owner about construction 30 Study of Proposed Conceptual Design Process RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 31 36 3.0 Introduction 36 3.1 Phase One 36 ix 3.1.1 3.2 3.3 Phase Two 4 5 36 37 3.2.1 Establishing the Aims and Objectives 37 3.2.2 Literature Review 37 Phase three 3.3.1 3.4 Identification of Problem and Scope of Project Data Collection Phase four: Data Analysis and Conclusion 38 38 38 3.4.1 Data Analysis 38 3.4.2 Conclusion and Recommendations 38 3.5 Research Methodology Flow Chart 39 3.6 Research Model 40 3.7 Layout of Questionnaire 41 3.8 Results and Findings 41 DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS 42 4.1 Data Collection 42 4.2 Respondent Selection Criteria 42 4.3 Respondent Analysis 43 4.5 Reliability tests (Validity Assessment) 45 4.6 Relative Importance Index 45 4.7 Likert scaling method 46 4.8 Building Design Process 47 4.9 Factors Affecting the Design Process 59 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 5.1 Achievements on Objective One 5.1.1 Pre-Design Phase 64 64 64 x 5.1.1.1 Feasibility Study or Project Appraisal 64 5.1.1.2 Procurement Method 65 5.1.2 Design Phase 66 5.1.2.1 Design Brief 66 5.1.2.2 Conceptual Design 68 5.1.2.3 Design Development 69 5.1.2.4 Detail/Technical Design 70 5.1.3 Important aspects of Building Design Process 71 5.1.3.1 Types of Design Firms 72 5.1.3.2 Who lead the design process 72 5.1.3.3 Design Process Approvals 72 5.1.3.4 Role of Authority 73 5.1.3.5 Time taken to each design process 73 5.2 Achievement on Objective Two 73 5.3 Conceptual Framework for Implementation of PtD 75 5.3.1 78 Design Brief Work Stage 5.3.1.1 PtD Inputs for Design Brief work stage 78 5.3.1.2 Tools and Techniques 78 5.3.1.3 Outcome of Design Brief work stage 79 5.3.2 Conceptual Design work stage 80 5.3.2.1 Input for Conceptual Design 81 5.3.2.2 Tools and Techniques 81 5.3.2.3 Outcome of Conceptual Design 82 5.3.3 Design Development Work Stage 82 5.3.3.1 Inputs for Design Development 82 5.3.3.2 Tools and Techniques 83 5.3.3.3 Outcome of Design Development 83 xi 5.3.4 83 5.3.4.1 Input for Detail Design 84 5.3.4.2 Tools and Techniques 85 5.3.4.3 Outcome of Detail Design 86 5.3.5 6 Detail Design Work Stage Construction Phase 87 5.3.5.1 Input for construction phase 88 5.3.5.2 Tools and Techniques 88 5.3.5.3 Outcome of construction phase 89 CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS 90 6.1 Conclusion 90 6.2 Recommendations 91 REFERENCES APPENDICES A-D 92 95-111 xii LIST OF TABLES TABLE NO. TITLE PAGE 2.1 RIBA Outline Plan of Work 2007 (Amended Nov. 2008) 25 2.2 Critical Success Factors collaborative multi-disciplinary 27 design Projects. 4.1 Ranges of Reliability Coefficients 45 4.2 Classification of Rating Scale (Section B & C - Questionnaire) 46 4.3 Analysis of most common procurement method 47 4.4 Analysis of who lead the design process 48 4.5 Analysis of which design process takes more time and 49 difficult to manage 4.6 Analysis of design process input 50 4.7 Analysis of collaboration tools used by designers 52 4.8 Analysis of role of authority in design process 53 4.9 Analysis of main design approving authority 54 4.10 Showing analysis when design required client approval 55 4.11 Showing analysis firm’s design priority 56 4.12 Showing analysis client’s design priority 57 4.13 Analysis of factors affecting the design process by mean, 62 RII, ranking, category and design process. xiii LIST OF FIGURES FIGURE NO. TITLE PAGE 1.1 Time/Safety/cost Influence Curve 3 2.1 Integrated Design Process Elements 17 2.2 RIBA Plan of Works (2007) Bar Chart 21 2.3 RIBA Plan of Work (2007) Life Cycle with Internal and External Factors affecting the design Process 30 2.4 The factors affecting the Design Process 31 2.5 Moving prevention from an afterthought (during execution) to a forethought (design) in process 32 2.6 CHAIR review process. 33 2.7 The Hazard Elimination and Risk Reduction Process at Design Stage 34 2.8 The ERIC model 35 3.1 Research Methodology Flow Chart 39 3.2 Research Methodology Model 40 4.1 Respondent Analysis 43 4.2 Level of Management 44 4.3 Respondent Experience 44 4.4 Analysis of most common procurement method 48 4.5 Analysis of who lead the design process 49 xiv 4.6 Analysis of which design process takes more time and difficult to manage 50 4.7 Analysis of design process input 51 4.8 Analysis of collaboration tools used by designers 52 4.9 Analysis of role of authority in design process 53 4.10 Analysis of main design approving authority 54 4.11 Showing analysis when design required client approval 55 4.12 Number of times approvals are required from client 56 4.13 Showing analysis firm’s design priority 57 4.14 Showing analysis client’s design priority 58 4.15 Cost of project is considered during the design process 58 4.16 Factors Affecting the Design Brief 59 4.17 Factors Affecting the Conceptual Design 60 4.18 Factors Affecting the Design Development 61 4.19 Factors Affecting the Detail Design 61 5.1 Factors Affecting the Design Process on each work stage 75 5.2 Design Process Technique 77 xv LIST OF APPENDICES APPENDIX TITLE PAGE A Sample of Questionnaire Form 95 B Sample of Interview from Design Professionals 105 C Design Process Flow Chart 108 D Proposed PtD Conceptual Framework 110 xvi LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS ASSC = American Society of Safety Consultant ASSE = American Society Of Safety Engineers BAA = British Airports Authority BS = British Standards CAD = Computer Added Drawing/Design CDM = Construction Design and Management CHAIR = Construction Hazard Assessment Implication Review CHPtD = Construction Hazard Prevention through Design CIRIA = Construction Industry Research and Information Association CSF = Critical Success Factors DESIGN ASSOCIATES = Electrical, HVAC, Public Health Engineers (not part of design firm) DFS = Designing for Safety ERIC = Elimination, Reduce, Inform and Control GDP = Gross Domestic Production MEP = Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing NIOSH = National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health NZCIC = New Zeeland Construction Industry Council xvii OSHA = Occupational Safety and Health Act PMBOK = Project Management Body Of Knowledge PMI = Project Management Institute PtD = Prevention through Design RIBA = Royal Institute of British Architects UK = United Kingdom USA = United States of America WBDG = Whole Building Design Guide