Document 14581674
advertisement
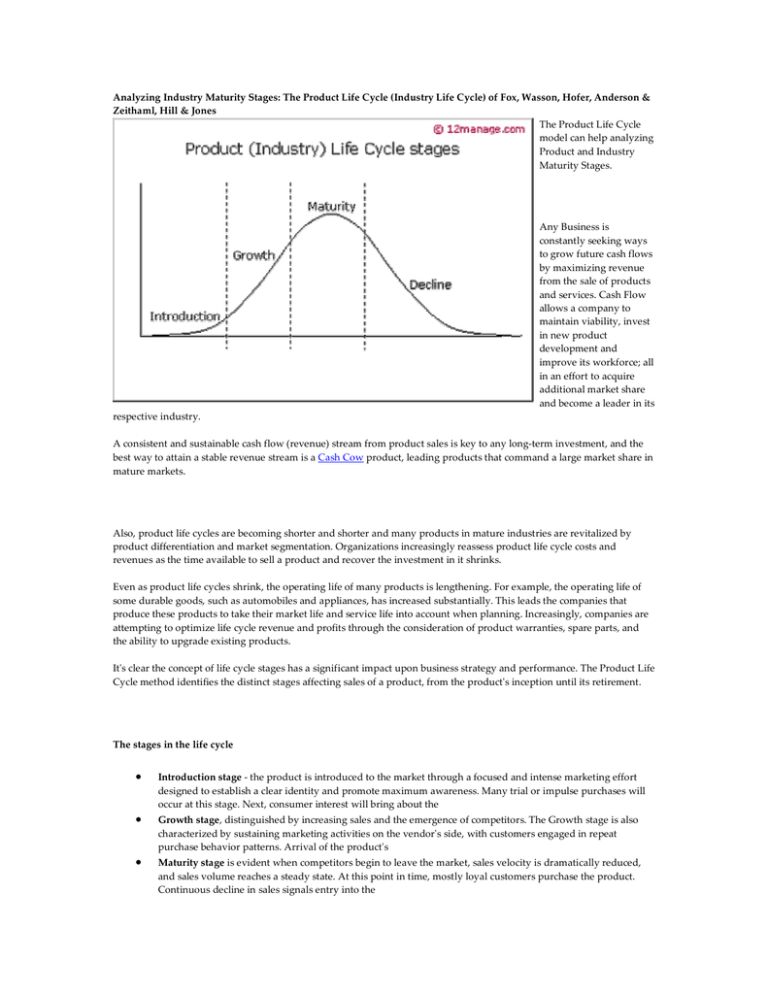
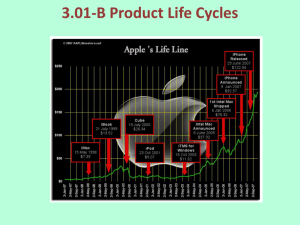
Analyzing Industry Maturity Stages: The Product Life Cycle (Industry Life Cycle) of Fox, Wasson, Hofer, Anderson & Zeithaml, Hill & Jones The Product Life Cycle model can help analyzing Product and Industry Maturity Stages. Any Business is constantly seeking ways to grow future cash flows by maximizing revenue from the sale of products and services. Cash Flow allows a company to maintain viability, invest in new product development and improve its workforce; all in an effort to acquire additional market share and become a leader in its respective industry. A consistent and sustainable cash flow (revenue) stream from product sales is key to any long-term investment, and the best way to attain a stable revenue stream is a Cash Cow product, leading products that command a large market share in mature markets. Also, product life cycles are becoming shorter and shorter and many products in mature industries are revitalized by product differentiation and market segmentation. Organizations increasingly reassess product life cycle costs and revenues as the time available to sell a product and recover the investment in it shrinks. Even as product life cycles shrink, the operating life of many products is lengthening. For example, the operating life of some durable goods, such as automobiles and appliances, has increased substantially. This leads the companies that produce these products to take their market life and service life into account when planning. Increasingly, companies are attempting to optimize life cycle revenue and profits through the consideration of product warranties, spare parts, and the ability to upgrade existing products. It's clear the concept of life cycle stages has a significant impact upon business strategy and performance. The Product Life Cycle method identifies the distinct stages affecting sales of a product, from the product's inception until its retirement. The stages in the life cycle • • • Introduction stage - the product is introduced to the market through a focused and intense marketing effort designed to establish a clear identity and promote maximum awareness. Many trial or impulse purchases will occur at this stage. Next, consumer interest will bring about the Growth stage, distinguished by increasing sales and the emergence of competitors. The Growth stage is also characterized by sustaining marketing activities on the vendor's side, with customers engaged in repeat purchase behavior patterns. Arrival of the product's Maturity stage is evident when competitors begin to leave the market, sales velocity is dramatically reduced, and sales volume reaches a steady state. At this point in time, mostly loyal customers purchase the product. Continuous decline in sales signals entry into the • Decline stage - the lingering effects of competition, unfavorable economic conditions, new fashion trends, etc, often explain the decline in sales. Several variations of the industry life cycle model have been developed to address the development of the product, market, and/ or industry. Although the models are similar, they differ as to the number and names of the stages. Here are some major ones: variations of the life cycle model 1973: Fox: precommercialization - introduction - growth - maturity - decline. 1974: Wasson: market development - rapid growth - competitive turbulence - saturation/maturity - decline 1984: Anderson & Zeithaml: introduction - growth - maturity - decline 1998: Hill and Jones: embryonic - growth - shakeout - maturity - decline Compare with Product Life Cycle: Bass Diffusion model | ADL Matrix | BCG Matrix | Relative Value of Growth | Positioning | GE Matrix | Innovation Adoption Curve | STRATPORT | Profit Pools | Marketing Mix | Four Trajectories of Industry Change | Co-Creation | Disruptive Innovation Return to Management Hub: Change / Organization | Decision-making / Valuation | Finance / Investing | Marketing | Strategy | Supply Chain / Quality More on Management