Outside-in Business Unit Strategy: The Five Competitive Forces Framework of... What is the Five Forces
advertisement
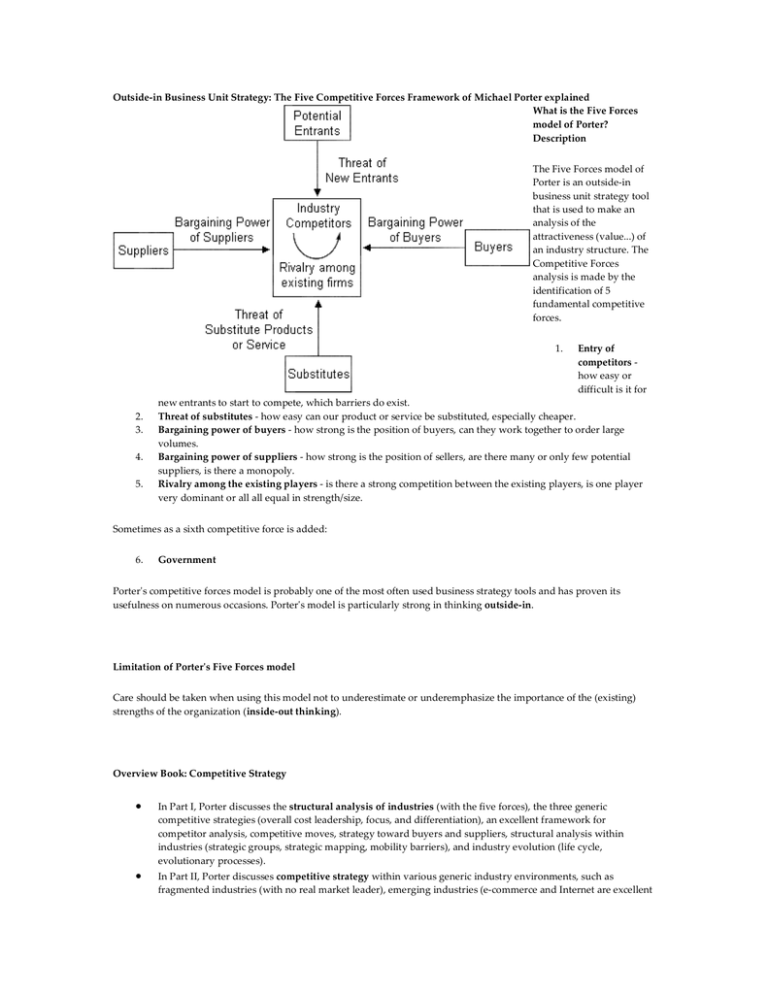
Outside-in Business Unit Strategy: The Five Competitive Forces Framework of Michael Porter explained What is the Five Forces model of Porter? Description The Five Forces model of Porter is an outside-in business unit strategy tool that is used to make an analysis of the attractiveness (value...) of an industry structure. The Competitive Forces analysis is made by the identification of 5 fundamental competitive forces. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Entry of competitors how easy or difficult is it for new entrants to start to compete, which barriers do exist. Threat of substitutes - how easy can our product or service be substituted, especially cheaper. Bargaining power of buyers - how strong is the position of buyers, can they work together to order large volumes. Bargaining power of suppliers - how strong is the position of sellers, are there many or only few potential suppliers, is there a monopoly. Rivalry among the existing players - is there a strong competition between the existing players, is one player very dominant or all all equal in strength/size. Sometimes as a sixth competitive force is added: 6. Government Porter's competitive forces model is probably one of the most often used business strategy tools and has proven its usefulness on numerous occasions. Porter's model is particularly strong in thinking outside-in. Limitation of Porter's Five Forces model Care should be taken when using this model not to underestimate or underemphasize the importance of the (existing) strengths of the organization (inside-out thinking). Overview Book: Competitive Strategy • • In Part I, Porter discusses the structural analysis of industries (with the five forces), the three generic competitive strategies (overall cost leadership, focus, and differentiation), an excellent framework for competitor analysis, competitive moves, strategy toward buyers and suppliers, structural analysis within industries (strategic groups, strategic mapping, mobility barriers), and industry evolution (life cycle, evolutionary processes). In Part II, Porter discusses competitive strategy within various generic industry environments, such as fragmented industries (with no real market leader), emerging industries (e-commerce and Internet are excellent • examples, although not mentioned in this book as it was written in 1980), mature industries, declining industries, and global industries. In Part III, Porter discusses strategic decisions which businesses/firms can take, such as vertical integration (forward, backward, partnerships), capacity expansion, and entry into new industries/businesses. Book: Michael E. Porter - Competitive Strategy - www.amazon.com/exec/obidos/ASIN/0684841487/valuebasedman-20 Compare with: Porter Competitive Advantage | Four Trajectories of Industry Change | Parenting Advantage | Core Competence | Delta Model | Resource-Based View | BCG Matrix | Greiner | Kay | Organizational Configurations | 3C's | Porter Diamond Model | Bricks and Clicks | Twelve Principles of the Network Economy Return to Management Hub: Decision-making / Valuation | Finance / Investing | Marketing | Strategy | Supply Chain / Quality More on Management


![[5] James William Porter The third member of the Kentucky trio was](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007720435_2-b7ae8b469a9e5e8e28988eb9f13b60e3-300x300.png)


