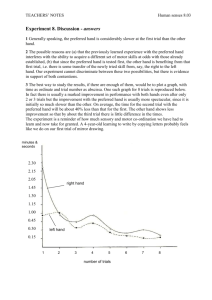
The Experience in China
advertisement

How Clinical Research Promoted by Health Industries Can Contribute to Improve The Quality of Care? The Experience in China Jiyao Wang, MD, MSc, AGAF Zhong Shan Hospital, Fudan University Center of EBM, Fudan University Bench To Bedside : Interdependence Bench To Bedside The 3T’s The Innovation Interface •Basic/clinical science •Technology focus •Public health •Policy/ Culture Dougherty, D. et al. JAMA 2008;299:2319-2321 Category of Clinical Research For product development Discovery Launched by pharmaceutical company Preclinical Toxicology Phase I Phase II Phase III Time(years) Phase IV Launched by investigators Regulatory Filing Efficacy & safety in selected population Effectiveness & safety in real clinical practice Long term Clinical outcome What, Exactly, is IMCT ? • Include a larger number of participants • Different geographic locations • The possibility of inclusion of a wider range of population groups with different – genetic – environmental – and ethnic or cultural backgrounds Current Status of IMCT • Globalization of clinical trials is a reality • Clinical trials across multiple regions of the world have become common practice • China is an increasingly important source of patients to test new drugs – As of April 28, 2015, there were 18,9109 clinical trials globally – Up to 6040 in mainland China Source: www.clinicaltrial.gov Search date: 2015-4-28 Current status of clinical trials Source: www.clinicaltrial.gov Search date: 2015-4-28 18,9109 Current status of IMCT in China Source: www.clinicaltrial.gov Search date: 2015-4-28 Registry on clinicaltrial.gov Mainland Hong Kong Taiwan 6040 1059 3917 Open studies of IMCT 527 46 201 What we are doing Type Phase I Phase II Phase III Phase IV IMCT Ongoing multi-center clinical trials in our hospital 3 8 24 13 25 Sponsor: Large pharmaceutical companies in Europe and America IMCT , Areas of Impact Simultaneous Global Development Clinical Practice Research Regulatory Ethical Impact of Clinical Research Promoted by Health Industries • • • • Key opinion leaders Principle investigators Doctors Hospital teams Key opinion leader • • • • Organize professional activities Write and promote guidelines Practice new evidence in the specialty Become the primary investigators for the clinical trials • Impact on the quality of care of medical practice – The standard of care – Healthcare system Benefits of participation for the key opinion leader in the country for his/her expertise development in his/her speciality • More access to acquire resources – More patients – More facilities, both from hospitals and pharmacies • Newer information to be caught • More experience in the design, management and evaluation for the whole protocol Benefits of participation : principle investigators • Be familiar with GCPs • Know the responsibilities as the “PI” • Establish excellent communication with external sites • Establish excellent communication with international colleagues • Build an international research reputation • As a local PI, I have participated a lot of clinical trials (phase II and III) lunched by pharmaceutical companies (such as Searl company, Astrazeneca, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roch, etc) since 1992. • I am familiar with GCP, established SOPs and became member of local ethics committee. • I have been invited to participate the international multicenter clinical trials organized by famous experts in the world. • I have organized multicenter clinical trial within China in order to get more evidence for improving quality of health care. 1Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands; 2Infectious Diseases, Ruijin Hospital, Jiaotong University, Shanghai, China; 3Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Zhong Shan Hospital, Fu Dan University, Shanghai, China; 4Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Shanghai Public Health Center, Fu Dan University, Shanghai, China; 5Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty, Istanbul, Turkey; 6National Institute of Infectious Disease, Bucharest, Romania; 7University of Ankara, Medical School, Ankara, Turkey; 8Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands; 9Department of Gastroenterology, Fundeni Cinical Institute, Bucharest, Romania; 10Division of Infectious Diseases and Hepatology, Wroclaw Medical University, Wroclaw, Poland; 11Department of Internal Medicine, Fundeni Cinical Institute, Bucharest, Romania; 12Department of Gastroenterology, Yuksek Ihsitas Hospital, Ankara, Turkey; 13Department of Infectious Diseases, Silesian Medical University, Katowice, Poland; 14Department of Public Health, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands; and 15Toronto Center for Liver Disease, Toronto Western and General Hospital, University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. • (AASLD 2014 presentation and published in Hepatology 2015;61:15121522) Genetic study of peginterferon treatment in chronic hepatitis B To identify genetic polymorphisms associated with response to interferon therapy in chronic Hepatitis B patients Benefits of participation: Doctors (1) Need to conduct clinical trial according to Good Clinical Practice(GCP) Standards •GCP is a standard for the design, conduct, monitoring, analyses, and reporting of clinical trials •The practice of GCP were standard in all Member Sites, before 2002, only a minority of hospital in China had previously were familiar with the obligations of the different parties of GCP •IMCT introduced GCP principles to ensure that trials are conducted in accordance with high standards of ethics and science Benefits of participation: Doctors (2) Drive the Quality care of patients •IMCT helps doctors ensure continuous quality improvement of diseases treatment by aligning clinical care with evidence-based guidelines •More access to acquire resources – More patients – More facilities, both from hospitals and pharmacies •Newer information to be caught •More experience in the design, management and evaluation for the whole protocol Benefits of participation: the hospital team • Access to the most up-to-date research and scientific publications • Professional education opportunities, such as workshops and webinars • Clinical tools and resources • Patient education resources • A competitive advantage in the healthcare marketplace • National and local recognition for hospital team program achievement • Quality improvement, broaden knowledge of short- and long-term benefits and risks • Established ethical committee in Hospital level IMCT Areas of Impact:Research Improve China clinical trial design and research level(1) • Investigator training • Plan in the protocol : SOPs and Manuals, including Global Clinical SOPs, data handling SOPs, operational SOPs • Adaptive/flexible designs setting Improve China clinical trial design and research level(2) • Quality Assurance • eCRF • Electronic Data Capture (for use in clinical trials) • Data management and data quality • power estimation / sample size • Methods for subgroup analysis; Randomization issues / stratification • How to describe/present data The quality of clinical research changed: 2003-2015 •Somewhat Structured •SOPs not available •Less Experienced •Well organized and Structured •SOPs and Processes in place •Experienced team IMCT Areas of Impact:Ethical • • • • Informed Consent Local Ethics Committees, IRB’s Integrity of research conduct Data collection/privacy Pros and Cons for patients in terms of participation of IMCT • Pros • Cons – Patients will be benefited – Information not balanced, from free new effective misunderstood medications already on the – Under-treatment if control arm is market in Europe and not well designed, like placebo America – Safety concern for the very new – Patients will be benefited treatments from tailored follow-up , – Impact on activities of daily living? and will decrease cost – Some are worried about privacy, – More convenient for a asynchronous communication can clinic (saving time, good be more efficient. doctors and nurses) – Cost saving IMCT Areas of Impact: Regulatory On 12/1/2002, ‘Drug Registration Regulation’ was issued by CFDA, the first regulation for approval of an international multi-center trial, then , international multi-center clinical trial showed an increasing trend in China. On 30/1/2015 , China Food and Drug Administration(CFDA) issued ‘International multi-center clinical trial Guideline’ as a framework for good management in trials of medicines in China Encountered problems of IMCT in China today Compared with developed countries, there is a gap • Less IMCT: For example, Cancer Patients, enrolled in one of a clinical trial – >90% , USA – About 9% , China • Among the ongoing IMCL in mainland China, the majority IMCL are industry-sponsored trial ( IST), while investigator-initiated clinical trial ( IIT) were viewed as of higher academic value Types of Ongoing IMCT • Therapeutic : >90% • • • • • Prevention Early detection/diagnostic Disease Management Correlative Population-based studies: • Epidemiological • Observational • Quality-of-life Rare disease research, diagnosis or treatment compared to marketed drugs and other new uses Areas not covered Need MORE Investigator-initiated clinical trial A report including combined data from approx. 1140 studies shows that industry-sponsored clinical trials are significantly more likely to reach conclusions in favor of the industry vs non-industry studies- possibly publication bias or selection of an inappropriate comparator to the drug being evaluated J. E. Bekelman, Y. Li and C. P. Gross J. Am. Med. Assoc. 289, 454–465; 2003 We has done much to promote national multi-center clinical trials • • • • • • Investigator Initiated Trials (IITs) Investigator Initiated Studies (IISs) Investigator Sponsored Trials (ISTs) Investigator Initiated Research (IIR) Non Registration trials (NRTs) Non Sponsored Trials Investigator-initiated China regional multicenter clinical trial in China What are Today’s Challenges? • Each participating site needs to be visited numerous times, making this a large, and time-consuming administrative activity, not only for the monitor, but also for the physicians involved. Monitoring is associated with high costs • With Limited funds: – How to protect the enthusiasm and commitment of the physicians and attract them to involve. – Time-consuming, in some cases even to the extent that they declared not to participate in these kind of studies again in the future. How to improve • A well designed protocol – Background to evaluate the feasibility of the new treatment and control arm, based on the best clinical practice guideline – Ethical committee fully consider the safety for all the participants – Mostly understanding and fully consent to attend by the participants and their family – Reimbursement should be prepared and easily got accessed • Independent supports from large pharmaceutical companies Quality Assurement • Team building including investigators, nurses, CRC(clinical research coordinator), CRA(clinical research associate),statistician • Timely audit for the projects, both inside hospital and outside hospital • supplements including office, network, and storage space • Central study pharmacy inside hospital is promoting Conflict of Interest (COI) • COI issues are real – Focus on financial only – Tone: non – collaborative – Unintended consequences – effecting collaborative efforts • Debate needs broader view: goal - improve public health • Alternative position – Include all types of conflicts – Improve public health is a primary interest – Checks and balances in place – Collaboration/ cooperation/ learning /teaching Future : Integration/Collaboration • Clinical trial is a good clinical practice • Only the medical team with good practice can start a good clinical trial • Increasing realization that institutions can’t go it alone • Collaborative efforts in complex systems, Sharing the rewards • Focus on unmet medical need/public health value The bridge between bench and bed Knowledge gap unknown Knowing-doing gap Known Clinical Research Action Improve quality of care Thank you! Trials are short; real-clinical practice has no time limit