UW-Madison Records Management Program File Plans
advertisement

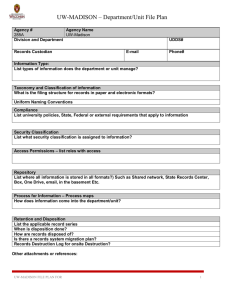
UW-Madison Records Management Program File Plans 2015 UW-Madison Records Management Program University of Wisconsin-Madison Archives & Records Management A T I P Accountability Transparency Integrity Protection C A R D Compliance Availability Retention Disposition ARMA International publishes the Generally Accepted Recordkeeping Principles®. More information about the Principles can be found at www.arma.org/principles. “records are the memory of your business, holding knowledge and evidence of commercial activities forgotten when people T. Blair, founder of the move on” Barclay Information Governance Initiative Photo courtesy of UW-Parkside Archives What is a File Plan? A “File Plan” is a well thought out plan on how records are managed. Think of this as a roadmap to how your Dept./Units manages their records. A good file plan will assist with: Documenting department/units activities effectively Identify records consistently Retrieve records quickly Disposition records no longer needed Meet legal and organizational requirement See JOB AID: Documentation of Records Management Practices aka File Plan Creation What Why (Information) (Taxonomy, Compliance,) Who Where (Custodian, Security) (Repository) When How (Retention, Disposition) (Process) Integrity Compliance Accountability Protection Availability Transparency Retention Disposition This is the level at which the information or document type is identified. Information that is dependent on the needs of the business. What information does the department create or use? File Plan: Taxonomy and Classification What is a taxonomy? taxis (arrangement) + nomia (method) A filing system is the “systematic indexing and arranging of records based on established procedures” Classification should be applied to both paper and electronic records and subject to the same retention and disposition. Records could be filed in many different ways: Chronological order Alphabetical or Numeric order Alpha-Numeric order Electronic Format Use of Standardized Naming Conventions for records. Define the folder structure for both paper and electronic records that meets the department business needs. Determine the records management categories for the folder structure using uniform naming conventions. Electronic Formats for Files and Documents Metadata is “Data about Data "It conveys Content, Context & Structure Examples of descriptive metadata: Rules about the management of information cannot be defined and documented unless a role in the organization has been identified as accountable for the management of the information. This is not necessarily the person or persons responsible for creating, approving, or using the information. The Custodian is typically in an organizational leadership role. It is the person who has Accountability. • You are responsible for all activity that occurs under your login. Do not share your credentials. • Make business passwords different than personal passwords. • Treat all information as confidential unless categorized otherwise. • Organization resources (hardware, software, etc…) should be used for business purposes only. • See CIO Policy: Handling University Data and your responsibility https://www.cio.wisc.edu/security/guides-students-faculty-staff/handling-university-data/ Permissions applied to the repository (e.g.: file share, applications, hosted SharePoint site) will list what permissions as they actually are, not what they should be. This may be more rigor than some would want as it requires AD to align with the file plan. Role University Records Mgt. Advisory Create X All Employees (access limited) Corporate Communications Manager Public (access limited) Read X Update Delete X X X X X X X X In this section will be the container of the information. Information Types are contained within File Type. Files are contained within a Repository. The drawings below will help to make this point. Note: For illustration purposes a paper file structure is represented. This same concept is applicable for all formats (paper documents, digital documents, databases). To ensure the integrity of information, a repeatable process should be employed. This section of the file plan can either detail how to retain, reference, and remove information; or can reference a document that contains this information. Retention Schedules are good for documenting why (citations) information should be kept for a particular time period, and how long (retention period).