Eucaryotes . vs Bacteria
advertisement
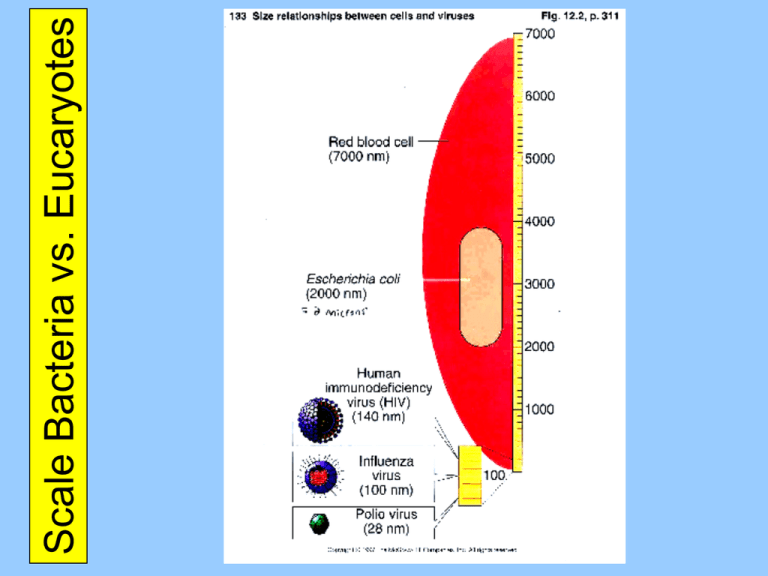
Scale Bacteria vs. Eucaryotes Bacteria vs. Eucaryotes Three Cellular Domains 16S rRNA Three Cellular Domains Ribosome Image Diversity of Bacterial Shapes Coccus (pl. Cocci) Diversity of Bacterial Shapes Coccobacillus Diversity of Bacterial Shapes Vibrio Diversity of Bacterial Shapes Bacillus (pl. Bacilli) Escherichia coli Diversity of Bacterial Shapes Spirillum Diversity of Bacterial Shapes Spirochete Bacterial Cellular Arrangements Filamentous Bacteria Bacterial Anatomy (Overview) Nucleoid Endospores Bacterial Anatomy (Cell Envelopes) Gram Positive Cell Envelope Gram Negative Cell Envelope Lipopolysaccharide Endosymbiosis Mitochondrian Chloroplast Bacterial Anatomy (Plasma Membrane) Plasma Membrane Movement Across Membranes water Osmosis & Tonicity Cell Walls Plasmolysis Protoplast & Spheroplast Isotonic or Hypertonic medium Hypotonic medium A Protoplast is a Gram-Positive bacterium without its cell wall A Spheroplast is a Gram-Negative bacterium lacking most of its cell wall Bacterial Anatomy (Flagella) Flagellum (p. Flagella) (1/2) also “atrichous” Flagellum (p. Flagella) (2/2) Taxis Negative Chemotaxis is away from specific substances Positive Chemotaxis is towards specific substances Negative Phototaxis is away from light Positive Phototaxis is towards light Axial Filament (EndoFlagella) Bacterial Anatomy (Pili) Pilus (pl. pili) -- Fimbria Sex Pili Cell-Surface Fibrils Electron micrograph of an ultra-thin section of a chain of group A streptococci. The cell surface fibrils, consisting primarily of M protein, are clearly evident. The bacterial cell wall, to which the fibrils are attached, is also clearly seen as the light staining region between the fibrils and the dark staining cell interior. Incipient cell division is also indicated by the nascent septum formation (seen as an indentation of the cell wall) near the cell equator. The streptococcal cell diameter is equal to approximately one micron. Bacterial Anatomy (Glycocalyx) Glycocalyx Bacterial Anatomy (Overview)





