CHW 3M1 – Government in Ancient Greece Open Book Quiz
advertisement

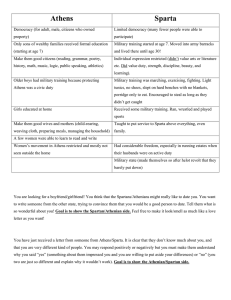
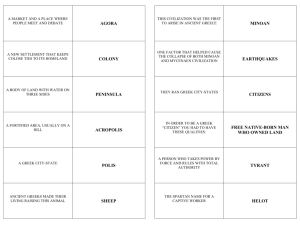
CHW 3M1 – Government in Ancient Greece Open Book Quiz Name: __________________________ Part A: Mix and Match (25 Marks) Using your completed notes, match each term with its most appropriate definition by writing the letter in the space provided. Column A Column B a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) j) k) l) m) n) o) p) q) r) s) t) u) v) w) x) y) Strategos Ostracism Ostraka Magistrates Basileus Archon Thesmothetai Polemarch Homoioi Helots Ephorate Ephor Gerousia Aristocracy Demokratia Oligarchy Monarchy Tyrant Draco Cleisthenes Solon Peisistratus Phalanx Hoplite Athens 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 25 24. 25. _____ The state is ruled by nobility and determined by heredity based on family ties, social rank and wealth. _____ In Athenian Democracy, the name given to the 10 generals who were appointed by the Council of Five Hundred; were eventually elected by the assembly and were responsible for promoting domestic policy and directing military operations. _____ In Sparta, the 5 overseers of the government who were elected each year and held the most power because they were responsible for directing the affairs of the state. _____ The chief Religious officer in the Athenian government. _____ The process whereby at least 6000 people were required to exile an individual; citizens would scratch the name of the individual they most distrusted on a shard of pottery then the individual with the most votes cast against them would have to leave Attica for up to ten years. _____ The assembly could vote into exile any men considered a threat to the city state’s democracy. _____ The state is ruled by a small group of citizens; the ruling group controls the military; practiced in Sparta by 500 BCE. _____ Anyone who seized power unconstitutionally (for good or bad); b/c power was sized by force and some did govern harshly, the word is most commonly associated with a cruel or unjust ruler. _____ A Greek foot soldier equipped with bronze body armour, shin guards (greaves), round shields, helmet and spear. _____The largest of the city-states and a leading cultural centre of Greece located in a area called Attica. _____ The majority of people who lived in Sparta who were the descendants of a civilization of people who had originally inhabited the area. Most were slaves who farmed the land for their Spartan masters. _____ The state is ruled by a King; rule is hereditary and is usually based on divine right. _____ A system of government where citizens govern themselves through voting; Majority rule decides the vote. _____ Considered a tyrant because he got his power over the city of Athens after three failed attempts, then finally won a battle to solidify his reign; Once paraded a woman named Phye through the streets of Athens dressed like the goddess Athena, claiming that she come to restore him to power. _____ First set apart the ancient division of Athenian citizen’s into four tribes based on clan relationships and then created an equitable division of citizen’s into 10 new tribes. He replaced the old council of 400 with a new Council of 500, with 50 members elected from each tribe. _____ The term given to all who were considered equals and who were permitted to vote in the Spartan Assembly. Usually composed of both rich and poor Spartans, aristocrats and ordinary people who had a share in Spartan land and could benefit from the work of enslaved helots. _____ The name given to the 5 Ephors who were elected annually to the Spartan government. They acted as magistrates and judges and presided over the Council and Assembly and supervised the state education system. _____ The term given to special positions or executive officers in the Athenian Democracy. Some positions included the Basileus, the Polemarch and the Archon. _____ A battle formation employed by the Greeks that had hoplite soldiers line up side by side that created an almost impenetrable mass spear and shield wall. This form of battle defeated the old style of fighting quite easily. _____ The Chief Army Officer in the Athenian Government. _____ Made up of 28 male citizens who were elected for life whose primary role was to advise the kings, propose legislation and act as judges. _____ One of the most important magistrates in Athenian government; The chief civil administrator and judge. _____ As chief administrator, he codified a set of laws and related punishments for all Athenians. His name is now synonomous with punishments or measures that are extremely severe or oppressive. _____ Lesser judges in the Athenian Government. _____ Most significant reform allowed all wealthy men, aristocrat or not, to run for the highest government offices; Created the Council of 400.