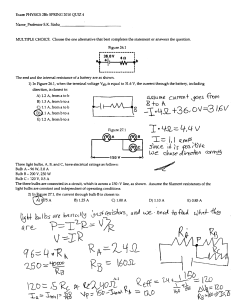
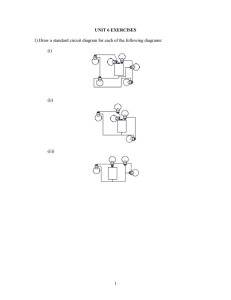
1
advertisement

1 Unit 3 The Characteristics of Electricity ( pg 296 ) Day 1 ______________- study of static electricity _____________ - materials that do not carry a charge ______________ allow charges (electrons) to flow through them easily. E.g. _______________________ Therefore no matter how hard that you rub a metal tap no static charge will build up because the electrons that you are giving the tap just keep on moving up the tap and down the water line until they reach a ground. ____________do not allow charges to flow through them. The charge builds up on its surface eg. _______________ Both a positive and a negative charge can build up on ____________________ Only ______________ can obtain a static charge. Conductors, Insulators and in – between (pg 308) Conductivity is the ability of materials to allow electrons to move freely in them. Materials that hold onto their electrons and do not allow them to move easily are called electrical insulators.An electrical insulator is a solid, liquid, or gas that resists or blocks the movement of electrons. Dry wood, glass, and plastic are all examples of electrical insulators. An insulator can hold a static charge because static charges remain nearly fixed in place. Since electrons cannot move through an insulator they can be very useful to us to protect us from shocks. For example a simple electric kettle would be very hazardous if the two wires that supplied electricity to it did not have a rubber coating over them See Table pg 308 for some common insulators and conductors. ___________________ are good conductors since e’s can jump from one atom to the next _________________ are insulators since they hold their e’s tightly Why do you get more shocks in the winter than in the summer? - This is because in winter the air is far dryer than in the summer and dry air is an ______________ and therefore does not take any of the charges our body might pick up during the day. So when we go and touch another conductor (a door handle) ZAP we receive a shock. 2 The Electrical Nature of Matter pg 301 electric charge- can be positive or negative _____________- they have an even number of positives and negatives an object has a ____________charge if it has more negatives than positives an object has a _____________charge it it has fewer negatives than positives The Law of Electric Charges- like charges ____________one another, unlike charges ____________ one another, charged objects are attracted to uncharged objects A Model for the Electrical Nature of Matter : The atom is composed of electric charges. Protons –____________charge, found in nucleus, cannot move Neutrons- _______________charge, found in nucleus, cannot move Electrons- _______________charge, found orbiting nucleus, can move from atom to atom A model for the electrical nature of matter. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. All matter is made up of submicroscopic particles called ______________. At the center of each atom is a ___________, with two kinds of particles: the positively charged _____________and the uncharged _____________. ___________ do not move from the nucleus when an atom becomes charged A cloud of negatively charged particles called _____________ surround the nucleus. An electron has the same amount of charge as a _______________, but the kind of charge is ________________. When atoms become charged, only the _________________ move from atom to atom. ___________charges repel each other; _______________ charges attract each other. In some elements, such as copper, the nucleus has a weaker attraction for its electron than in others, and electrons are able to move freely from atom to atom. In other elements, such as sulfur, the electrons are strongly bound to each atom. In each atom, the number of electrons surrounding the nucleus equals the number of _______________ in the nucleus. A single atom is always electrically neutral. If an atom gains an extra electron, the net charge on the atom is ________________, and it is called a ________________ ion. If an atom loses an electron, the net charge on the atom is ____________________and it is called a _________________ ion. Charging by contact (Friction) pg 302 When two objects made of different materials rub together, electrons can be transferred from one object to the other. This is because different atoms (which make up the objects) have a different ability to attract electrons and a different ability to hold onto their own electrons. 3 The Electrostatic Series -a list of common materials showing how their ability to hold onto their electrons compares acetate glass wool fur, hair calcium, magnesium, lead silk aluminum, zinc cotton paraffin wax ebonite polyethelene (plastic) carbon, copper, nickel rubber sulphur platinum, gold Weak hold on electrons Strong hold on electrons To determine what charges will form, compare the location on the table of the two objects. The object that is higher on the table will ______________ electrons and become _________________. Eg. when cotton and human hair rub what charge will form on each object? ___________ is lower on the list than ___________. __________ will hold its electrons better. ____________ will lose its electrons to the ________________Cotton will become ___________. Hair will become ________________Consider the following pairs are rubbed together. Give charge on each : Plastic ________ Silk _______; Fur __________ Rubber ; glass ____ silk ______ Vinyl ______ Plastic ______ ; Ebonite _________ wool _____________ Questions 1. Where are electrons in the atom? 2. What does “static” mean in “static electricity”? 3. What happens when two objects made out of different materials are rubbed together? 4. What term describes an atom’s tendency to hold on to electrons? 5. In each of the following pairs, state which one is more likely to give up electrons. (a) wood or human hair (b) plastic wrap or steel (c) cotton or silk Complete pg 300 ( 1-4 ) pg 306 (1-5 ) 4 Day 2 Induction (pg 303) Charging by induction- charging without direct contact When a negative charge approaches a neutral object, the electrons inside the neutral object are _____________. This causes an induced __________ charge on the side closest to the negative object and an induced ___________ charge on the opposite side. Diagram When a positive charge approaches a neutral object, the electrons inside the neutral object are ____________. This causes an induced __________ charge on the side closest to the positive object and induced __________charge on the opposite side. diagram If a ground is attached to the neutral object, electrons can flow into or out of it to make it “feel” neutral. Diagram Induction is used in photocopiers, lightning, dust filters and electrostatic painting. CHARGE BY INDUCTION -no direct contact (e- move within a substance because of nearby objects) (-) object goes near neutral object, (-) charge is repelled, (+) charge is attracted in neutral object (+) charge is induced by (-) object (+) object goes near neutral object, (+) charge is repelled, (-) charge is attracted in neutral object (-) charge is induced by (+) object 1. 2. Draw the normal spread of negative charges on this piece of tissue (a neutral object) Draw the build-up of negative charges on this balloon, AFTER it has been rubbed with a cloth 3. 4. The tissue is now stuck to the balloon. Draw the charges as they now appear. Draw the same balloon as in stage 1. Draw the charges in the tissue paper so that all the negative charges are far away from the negative charges on the balloon. As they get closer together the tissue is attracted to the balloon 5 When a neutral object is given a temporary charge, this is called _____________. If the object with a temporary charge is light enough it can be _____________ towards the object that caused the temporary charge. Conclusion : objects charged by induction receive the _________________ charge to the charged object ; in the case above it is temporary ; the charge can become permanent if grounding is used. GROUNDING -earth is large and absorbs large numbers of electrons, ground wire is connected to earth to "dilute"the charge by carrying it to the earth 1. 2. Rub one end of the polyethylene strip with fur. Mount the strip on an evaporating dish.. Rub one end of another polyethylene strip with fur. Bring this charged end of the strip close to, but not touching, the charged end of the strip on the dish. (a) Record your observations. ____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. 4. 5. Bring the uncharged end of the polyethylene strip close to the charged end of the polyethylene strip on the dish.(a) Record your observations. ____________________________________________________________ Repeat steps 5, 6, and 7, but substitute acetate strips that have been rubbed with silk. (a) Record your obervations. ________________________________________________________________________ Charge a polyethylene strip with fur and mount it on the dish. Charge one end of an acetate strip with silk, and bring it near e charged end of the polyethylene strip in the dish. a) Record your observations. _______________________________________________________________________ CHARGE BY CONTACT -rub material to build up electrons on object (-) or lose electrons from object (+) (+) object touches neutral object and takes e-, both objects now have e- spread out, both are (+) (-) object touches neutral object and gives e-, both objects now have extra e-, both are (-) Balloon and cloth BEFORE being rubbed together r Balloon and cloth AFTER being rubbed together The negative charges will jump from the places where there are the most number to where there are the least. Complete the following diagrams by adding negative charges (electrons) or a static electricity spark: a. b. c. d. 6 Negative charges (or electrons) will always move from where there are the (greatest/fewest) number to where there are the (greatest/fewest) number. If there is a big enough difference and the two objects are close enough together, this jumping may cause a ____________. . see page 309. Where we see the greatest spark when the air is dry or when there is high humidity ? _______________________________ Conclusion : charging by contact the neutral object becomes the _________________ charge as the charging object. Transferring Charge by Contact sparks produced by a charge transferred by contact can be dangerous transferring a charge by friction is difficult to avoid; when charging by contact occurs, one object is already electrically charged the other object may or may not be charged, the important factor is that there is a DIFFERENCE in the charge on the two objects 7 Day 3 PITH BALL ELECTROSCOPE LAB Purpose: To use a pith ball electroscope to determine charges. Materials and Methods: 1. Bring a negatively charged ebonite rod close to (don't touch) the uncharged pith ball, and then remove it. 2. Repeat step 1 with a positively charged acetate strip. 3. TOUCH the uncharged pith ball with a charged ebonite rod, remove the rod, and then slowly APPROACH (don't touch) with the same charged ebonite rod. Now APPROACH (don't touch) with a charged acetate strip. 4. Gently touch the pith ball with your fingers to "ground" (discharge) it. 5. TOUCH the uncharged pith ball with a charged acetate strip, remove the strip, and then APPROACH (don't touch) with the same charged acetate strip. Now APPROACH (don't touch) with a charged ebonite rod. Observations: step 1 step 2 step 3 step 5 Questions: (Answer on a separate sheet) 1. Draw a neat, well-labelled diagram (in pencil) to illustrate each of the following. In each diagram, label the pithball electroscope, fur or plastic, ebonite rod, positive and negative charges that do or don't move, any movement of pith ball. a) How to charge an ebonite rod negatively. b) How to charge a pith ball electroscope negatively with an ebonite rod. c) How the pith ball electroscope reacts to an ebonite rod after both have been charged negatively and the rod is brought close. 2. What charge is transferred to the pith ball when an ebonite rod rubbed with fur is touched to it? How do you know the charge you indicated was transferred (ie. think of how the pith ball reacts when the rod is brought near it after contact). Are electrons moving from the rod to the pith ball or from the pith ball to the rod? 3. What charge is transferred to the pith ball when a acetate rod rubbed with silk is touched to it? How do you know the charge you indicated was transferred (ie. think of how the pith ball reacts when the rod is brought near it after contact). Are electrons moving from the rod to the pith ball or from the pith ball to the rod? 4. Define the "Law of Attraction and Repulsion" (pg. 301). 5. In step 4 you "grounded" the pith ball electroscope by touching it with your fingers. Read the section on GROUNDING in your text and briefly explain the process (pp. 311-312). 8 Day 4 INDUCTION LAB: METAL LEAF ELECTROSCOPE Purpose: To charge a metal leaf electroscope by induction. Materials and Methods: (If at any time the leaves stick together, touch the metal ball with your fingers and use a pencil to GENTLY separate the leaves) 1. Observe the metal leaves of a neutral electroscope noting their position. (Make a sketch of the electroscope and leave room to add labels and charges later) 2. Approach the metal ball of the uncharged electroscope with a negatively charged ebonite rod (do not touch the electroscope) and observe the leaves. (Make a sketch of the electroscope with the rod close and leave room to add labels and charges later) 3. Repeat with a positively charged acetate strip. (Make a sketch of the electroscope with the rod close and leave room to add labels and charges later) 4. Connect one end of an insulated wire to the neck of the electroscope just under the metal ball. Connect the other end of the wire to a metal water tap or gas valve. Bring a negatively charged ebonite rod near (do not touch) the ball of the electroscope. While the rod is still very close to the electroscope, remove the wire from the water tap or gas valve without touching any part of the electroscope. After you have done this, remove the charged rod and observe the leaves. (Make a sketch of the electroscope with the wire still attached but showing the final position of the leaves once the rod has been removed and leave room to add labels and charges later) 9 Questions: (Answer in full sentence on separate page) 1. Explain what happened in step 2 in terms of the movement of electrons. Explain why the leaves did what they did. 2. What kind of charge was induced on the metal-leaf electroscope by the ebonite rod? 3. Explain what happened in step 3 in terms of the movement of electrons. Explain why the leaves did what they did. 4. What kind of charge was induced on the metal-leaf electroscope by the acetate strip? 5. Explain what happened in step 4 in terms of the movement of electrons. Explain why the leaves did what they did. 6. Write a summary statement identifying the kind of charge (positive or negative) transferred to an object when it is charged by induction by an ebonite rod and by an acetate strip. 10 Charging Neutral Objects By Induction 1. Only applies to charging metals! 2. Charge is induced on the object without direct contact. 3. The object takes on the opposite charge of the rod or other object being used to induce a charge. Rod (+) Object (-) Rod (-) Object (+) Scenario #1 – Charging Using a Positive Rod Step 1: Start with a positively charged rod (+). Step 2: Approach the positive rod to the object (+) without touching it. Step 3: Electrons inside the object are attracted to the rod. Only the electrons move closer to the rod but they do not jump. Step 4: Add a grounding wire but keep the negative rod close to the object. Results: The electrons from the ground enter the object (opposite charges attract) Step 5: Remove the grounding wire first. Pull the rod away second. The object is now permanently charged by induction and it has become negatively charged. Scenario #2 – Charging Using a Negative Rod Step 1: Start with a negatively charged rod (-). Step 2: Approach the negative rod to the object (-) without touching it. Step 3: Electrons inside the object are repelled by the rod. Only the electrons move away from the rod but they do not jump out of the object. Step 4: Add a grounding wire but keep the negative rod close to the object. Results: The electrons from the object are repelled and move down the wire and into the ground (like charges repel). Step 5: Remove the grounding wire first. Pull the rod away second. The object is now permanently charged by induction and it has become positively charged. 11 watch on youtube : What is Static Electricity ? ( Animation ) go to http://www.stmary.ws/highschool/physics/home/review/StaticElectricityReview.htm try animations 12 Key Concept Review 1. (a) Draw a diagram of an atom that has four protons, five neutrons, and four electrons. (b) Label each particle with its name and whether it is positive (+), negative (–),or neutral. 2. (a) What is friction? (b) Explain how friction can be used to transfer electrons. Use two substances from the triboelectric series in your answer. 3. Explain why this statement is false: “A neutral object contains no charge.” 4. State the two laws of static electric charges. 5. Where are static charges held? 6. Why might a plastic rod that contains a large number of electrons not have a static charge? 7. (a) What is the difference between a conductor and an insulator? (b) What is an example of a conductor? (c) What is an example of an insulator? 8.Do two identical objects become statically charged when you rub them together? Explain why they do or do not. 9. What does an electroscope detect? 10. In the contact method of charging, what charge does a neutral substance gain compared to the object that touched it? 11. In induction, what charge does a neutral substance gain compared to the object brought near it? 12. What is the difference between charging by contact and charging by induction in terms of electron transfer? 13. What is grounding? 13 Day 5 LIGHTNING (pp. 313-315) Strong ___________ and the collision of ___________ _____________ and ___________ _______________ in the clouds strip ___________________ from some particles and deposit them on others. Strong updrafts in the _______________ of the ___________________ carry smaller ____________ crystals and particles up while larger ones fall down. __________________ charges collect at the ________________ of the clouds whereas the higher, ________________ parts of the clouds are _________________ charged. The negative charges on the ___________________ of the clouds repel _________________ on the surface of the ___________________, leaving the ground _________________ charged just below the cloud. This is an example of charging by ___________________ (contact? friction? induction?). The strong _____________________ between the __________________ cloud and the ____________________ ground pull ___________________ off atoms and molecules in the air. This occurs mostly over the _____________________ point on the ground. A chain of ______________ forms and a gigantic ___________________ occurs between the _________________ and the ____________________. So many ___________________ crash through the air so fast, colliding with other _____________________, that the air both __________________up and __________________ up (ie. the temp. can reach ____________________ near a lightning bolt). The heat causes the air to __________________ rapidly. ______________ molecules colliding with other ____________ molecules produce a _____________ wave that we hear as _____________________. If the lightning hits a person, it can stop the ___________________ or _______________________. The best way to control a lightning strike is to direct the flow of _______________ away from buildings and prevent fires. Electrons travel most easily through ___________________. ___________________ rods are based on this principle. A lightning rod is charged by ___________________, just like the sphere on your ___________________. The _______________ charged lightning rod is the ____________________ point in the area. It attracts the ____________________ ions that have formed in the ______________, while the cloud attracts the ___________________ ions. A chain of ____________ thus forms between the cloud and the lightning rod. This chain acts as a ____________________ providing a path for the __________________ _________. When the lightning bolt strikes, it hits the ___________________ __________. The ____________________ are carried into the _________________ by a heavy conductor, often made of braided ________________. Although the light from lightning travels so fast it almost takes no time to reach us. But the sound from the thunder takes about __________ seconds to travel one _________________. Imagine you heard thunder six seconds after you saw a lightning flash. How far are you from the lightning bolt? ___________ km. - watch video www.teachersdomain.org Electricity And Magnetism: Lightning Lightning and Electricity And Magnetism: Lightning 14 Van de Graaff Electrostatic Generator The American physicist Robert Jemison Van de Graaff invented the Van de Graaff generator in 1931. This device has the ability to produce extremely high voltages (as high as 20 million volts). When the motor is turned on, the lower roller (charger) begins turning the belt. Since the belt is made of rubber and the lower roller is covered in silicon tape, the lower roller begins to build a negative charge and the belt builds a positive charge. As long as there is air between the lower roller and brush assembly, the Van de Graaff generator will continue to charge the belt. Theoretically, the Van de Graaff generator can continue to charge forever. Unfortunately, dirt and other impurities in the surroundings will limit the actual charge that develops on the sphere. - watch video on youtube : Bill Nye The Science Guy on Static Electricity (Full Clip) 15 SNC1D Name _______________________________ Static Electricity Assignment: The Practical Use of Static Charges You have now seen three different ways that static charges can be gained by substances: 1. Friction – in which the charge given is determined by the electrostatic attraction the two substances have, the one with the greater attraction becoming negative and the one with the weaker attraction becoming positive 2. Contact – in which the charge given is the same as the charge on the charging object 3. Induction – in which the charge given is opposite the charge on the charging object. Much of our discussion of Static Electricity has focused on some of the negative effects (lightning strikes, and shocks for instance). This assignment deals with some of the more positive uses of static charges. Photocopying Many people are unaware of the fact that common photocopy machines make use of static electric effects. While the motors and lamps within the photocopier work on current electricity ( the topic of the 2 nd part of this unit) the photocopy process itself uses static charges. 16 Summarize the process by completing the following (read page 310 in your text) Inside a photocopier… 1. A bar rubs up against a selenium coated drum in order to ____________________________________ 2. A light shines on the page to be copied. This creates an image which is projected onto the selenium drum by using both a _________________ and a __________________. 3. The bright light hits the drum and causes the charges to _______________________. The shadow areas (areas not affected by the light, remain __________________ charged. 4. In the toner cartridge of the photocopier, negatively charged toner is picked up by a brush. As this brush comes into contact with the selenium drum it sticks to the drum because __________________ 5. Paper from the paper tray is given a ______________________ charge. As this paper rolls under the selenium drum it transfers its ______________________ onto the paper. 6. The paper is then heated with a lamp to ____________________________________ In this space summarize the following uses of static electricity Electrostatic precipitators _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ Electrostatic spray guns ________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Try this on your own! You can demonstrate the usefulness of static forces with a simple experiment described in your text. On a sheet of paper, sprinkle a few grains of salt and pepper. Using a plastic ruler and a wool sweater, charge the ruler by friction. Hold the ruler over the mess you made on the paper, and you can demonstrate the essential elements of an electrostatic cleaner. Which of the two, salt or pepper is attracted to the ruler? Can you see how this fact could be used in more practical applications? 17 Electrical Discharging( pgs 311-312 ) - When a charged object has its charge removed it is said to be discharged or ______________ - The simplest way to discharge something is to __________it. This means to connect it to the Earth by means of a ______________. - When a charged object is grounded it shares its whole charge with the Earth, and since damp soil is a fairly good conductor the charge spreads out over the whole surface. - Since the Earth is so large it effectively removes all the excess charge given to it - Examples: Lightning rods, gas pumps - You can also discharge an object at a point. Conductors that are shaped into a point at one end loose their charge extremely fast because there is a build up of negative charge in a very small surface so the electrons are repelled right out of the conductor. - Discharging at a point is an extremely effective way for airplanes to get rid of their charge since attaching them to a ground just wouldn’t be practical. - A third way an object will discharge is just letting it sit, over a period of time the charge will leak out of it into the water molecules in the air. Independent Research analyse the design of a technological device that improves its electrical efficiency or protects other devices by using or controlling static electricity (e.g., paint sprayers, photocopiers, lightning rods, grounding wires) Questions: How does eliminating static electricity help or hinder the performance of a device? How have static electricity controls helped in developing new technologies? - Complete pg 318 (1-4) pg 320 (1-18), 21,22,24,28,31,32 18 Day 6 Electricity and Electric Circuits p. 324 Electric current: The movement or flow of electric charges from one place to another. Electric circuit: A controlled path for electrons to flow through. The 4 parts of an electric circuit: 1. Source of Electrical Energy- eg. solar cells, batteries, wall outlets 2. Electrical Load- anything that converts electrical energy into another form of energy eg. lamp, motor 3. Electric Circuit Control Device- turn flow on or off eg. timer, switch, fuse, circuit breaker 4. Connectors- allow electrons to flow from part to part eg. wires Schematic diagrams o Use circuit symbols instead of drawings of components o Simpler to read, no artistic talent needed. o Universal method of communicating circuits. Copy the symbols on pg 324 /600 used to represent the following components of a circuit: Part Cell 3 cell battery Wall outlet Switch Fuse Resistor Light bulb Symbol Function Part Voltmeter Ammeter Conducting wire Ground connection Symbol Function 19 Water Flow Analogy Electric Circuit Electric Current pg 325 Electric Current Definition Symbol SI unit Measuring device Safety a measure of the rate at which charges move past a certain point in a circuit ________________ ________________ Ammeter connected in _____________(pg 600) The more current, the more electrons that travel into you, the more damage that can occur. Current causes your heart to stop beating.0.005 A is maximum safe amount of current Compared to water Water in a river vs water in a stream. They may both move at the same speed (energy) but the river has more potential to do work because there is more water in it (more current) - one ampere = 1 coulomb of electrons per second passing a given point in a circuit 18 - a coulomb is 6 241 460 900 000 000 000 electrons or 6.241 x 10 - an ammeter is the instrument used to measure current - ammeters are always connected in series within a circuit The flow of current from batteries direct current (DC)because the current flows in only one direction but the current that flows through cords plugged into the wall sockets in your home is called alternating current. Alternating current (AC) flows back and forth at regular intervals called cycles. This is the current that comes from generators and is carried by the big power lines to your home. Electric Potential pg 330 Definition The energy difference between electrons at two locations in a circuit Symbol SI unit Measuring device Safety ___________ ___________ Voltmeter connected in __________________________ (601) The higher the voltage, the more energy electrons can release. This can result in burns when they release heat energy. A waterfall has potential energy that is transferred to the water to make a river run. If the river looped back to the waterfall, a complete circuit would be made. The water is like electrons. Compared to water 20 - electric potential is measured in volts and electric potential is often called voltage (symbol V) - a voltmeter measures the electric potential of a source of electrical energy - voltmeters are always connected in parallel with a load (because without a load there is no drop in voltage) Connecting a voltmeter in parallel A model of electric potential Analogy Falling water used to turn water wheels Falling water gives up gravitational potential to turn the wheel electric charges released from a dry cell give up their energy to turn the electric motor Pump has lifted water to the top of the building, water has some stored, or potential energy As long as the pump inside the building gives the water at the bottom potential energy by pumping it back up to the top, it will again fall from the top of the building to continue turning the wheel dry cell gives a huge amount of electric charges (electrons) a certain amount of electric potential energy the energy each electron gains is released to it by the chemical reactions that occur electrons have electrical potential energy at the ______________terminal of a dry cell Electricity from Chemical Reactions Even if dry cell is not connected to a circuit, the stationary electrons at the negative terminal have electric potential energy. Chemical reactions occur and exert a force on the electric charges that pushes a certain number of them on to the terminals of the dry cell. An excess of electrons accumulates on the negative terminal, thus giving it a negative charge and a matching amount of positive charges remain on the positive terminal Electrons are released with electric potential energy when the switch is closed As the electrons move through the circuit, they release the energy to the electrical load in the circuit Complete pg 329 (1,2,4,5) pg 336(1-5) 21 Day 7 Electrochemical Cells pg 383 - electrochemical cells are also known as _______________ cells or ___________________ cells In 1800 ________________________ invented the first battery ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS -stored chemical energy is converted into ________________energy ; consists of ____________________ and an ___________________________ PRIMARY CELLS (disposable energy) electrical current flows from primary cells, and chemical reactions occur, using up some material -when all material is discharged, primary cell is used up (a) VOLTAIC CELLS - non-rechargeable primary cell -two pieces of ____________ (electrodes) placed in liquid (_________________________) ELECTRODE -electrical conducting plate in solution eg. Al, Cu ELECTROLYTE -liquid that conducts electrical current eg. H2SO4 See diagram fig 12.3 page 383 - electrons flow from the __________________ to _______________________ through the ___________________________ __________________ - the aluminum electrode is called the anode and has a neg. charge - aluminum atoms lose __________________ and become ______________________ - over time the aluminum electrode will get __________________________ - at the copper strip which is called the cathode and has a positive charge ______________ ions pick up electrons forming __________________ gas Do lab activity pg 384. Copy out chart pg 384 22 Post Lab 1. Copper strip – evidence of a chemical reaction : formation of _________ ___________ 2. As time passed booth the voltage and current __________________________ 3. Potential difference was effected when a) aluminum was used instead of ____________ and when ___________________ metals were used Current – removing bubbles _______________ current and decreasing surface area of the electrodes ______________________ the current. 4. Potential difference – combination of __________________ used and the length of time cell operated 5. Current was increased when the surface area of the metals was ________________ and when the bubbles of gas were ____________________. 6. Largest current was when the whole electrode was submerged and only a few bubbles were present. 7. _________________ and zinc produced the greatest potential difference 8. In designing a voltaic cell electrodes of _______________ and _________________ should be used and immersing them ________________ in the liquid. To increase the life of the cell _______________ the surface area of the electrodes. - car battery is good example of a wet cell ; the negative electrode is made of _____________ and positive electrode is made of ___________________; the electrolyte is _____________________ - it is called a ______________________ cell since it can be recharged Disadvantages of using Wet cells : - the ________________ electrode is used up - bubbles of ________________ gas form on the __________ electrode reducing __________ flow. - _____________ gas is very _________________________ - the electrolyte __________________ acid is very _________________; may _________________ or ___________________. (b) DRY CELLS (pg 387) - works like a wet voltaic cell, but electrolyte is a ___________ or a ________(not a liquid) advantages = less chance of spilling electrolyte ; explosive hydrogen gas is not produced - negative terminal is made of ________________________ - positive terminal is a __________________ rod surrounded by ______________________ - separating the 2 electrodes is a paste made of ______________, _______________ and ____________________. - 2 disadvantages : ______________________ and _________________________ 23 Day 9 Lab : Building Batteries ( pg 390 ) Voltage Brightness of Bulb One Cell 2 cells in series 3 cells in series 2 cells in parallel 3 cells in parallel Analyze : 1. _____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 3. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Conclusion : 4. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 5. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 6. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 7. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 24 Cells in Series and Parallel Cells in Series series circuits – one pathway for electrons, connected so that _________terminals touch _________terminals parallel circuits – more than one pathway for electrons, connected so that negative terminals touch _____terminals - As electrons travel through each new battery, they get a new boost of energy. Eg. If three 1.5 volt cells are connected in series, electrons receive 1.5V from each cell. 1.5 + 1.5 + 1.5 = 4.5V total This is similar to water travelling down subsequent waterfalls. As it falls over each one, the water travels faster. Water analogy: to get twice as much energy from the same amount of water, we would lift the water twice as high and double the gravitational potential energy Cells in Parallel o Electrons only travel through one cell. o The extra cells act as backup and the cells last longer. Eg. If three 1.5V cells are connected in parallel, electrons receive 1.5V energy only. o This is similar to two waterfalls on rivers next to each other. Water only travels down one waterfall. Water Analogy: If you pump twice as much water to the top of the building, you could turn the wheel for twice as long however, all of the water will only have the gravitational potential energy from being lifted just one level Complete pg 394 (1-3) 25 Day 10 Lab Activity: Loads in Series Purpose: To investigate the characteristics of electric circuits with loads in series. Materials: 2 cells, 3 bulbs, 3 bulb holders (sockets), connecting wires, voltmeter and ammeter (or digital multimeter) Method: 1. Construct a circuit with two (2) cells in series and one (1) bulb. 2. Measure the electric potential across the cells and record the results in the "Electric Potential" table below. (Remember, electric potential is measured across the device; the circuit does not need to be disconnected in order to make a measurement with the voltmeter). 3. Measure the electric potential across the bulb and record the results in the table below. 4. Measure the current at the negative terminal of the battery and record the result in the "Current" table below. (Remember, current is measured in the circuit; the circuit must be disconnected in order to connect the ammeter). 5. Measure the current in the circuit "after" the bulb and record the result in the table below 6. Repeat steps 3 to 5 with two (2) bulbs in series and then again with three (3) bulbs in series. Observations: Electric Potential (V) Two cells connected in series:______V # of bulbs Across bulb #1 Across bulb #2 Across bulb #3 1 2 3 *hint for teacher: the sum of the electric potential across each row should be 3.0 V. Current (A) # of bulbs After battery After bulb #1 After bulb #2 After bulb #3 1 2 3 Questions: 1. Draw a separate schematic circuit diagram for each arrangement of bulbs in the activity and label the electric potential and current readings at the appropriate connection points. 2. What happens to the brightness of the light from the bulbs as each bulb is added? _______________________________________________________________ 26 3. a) What happens when one of the bulbs is unscrewed? Explain why. ____________________________________________________________________________ b) How many paths for current flow are there in a series circuit? ________________ 4. What conclusion can be made about the amount of current flowing in a series circuit? _____________________________________________________________________ 5. For each of the three series circuits, compare the electric potential of the cells to the electric potential measured across the bulb(s). What general relationship seems to exist? ________________________________________________________________________________ Schematic Diagrams : 1. 2. 3. 27 Day 11 Lab Activity: Loads in Parallel Purpose: To investigate the characteristics of electric circuits with loads in parallel. Materials: 2 cells, 3 bulbs, 3 bulb holders (sockets), connecting wires, voltmeter and ammeter (or digital multimeter) Method: 1. Construct a circuit with two (2) cells in series and one (1) bulb. 2. Measure the electric potential across the cells and record the results in the "Electric Potential" table below. (Remember, electric potential is measured across the device; the circuit does not need to be disconnected in order to make a measurement with the voltmeter) 3. Measure the electric potential across the bulb and record the results in the table below. 4. Measure the current at the negative terminal of the battery and record the result in the "Current" table below. (Remember, current is measured in the circuit; the circuit must be disconnected in order to connect the ammeter) 5. Measure the current in the circuit "after" the bulb and record the result in the table below. 6. Repeat steps 3 to 5 with two (2) bulbs in parallel and then again with three (3) bulbs in parallel. Observations: Electric Potential (V) Two cells connected in series:_______V # of bulbs Across bulb #1 Across bulb #2 Across bulb #3 1 2 3 Current (A) # of bulbs After battery After bulb #1 After bulb #2 After bulb #3 1 2 3 Questions: 1. Draw a separate schematic circuit diagram for each arrangement of bulbs in the activity and label the electric potential and current readings at the appropriate connection points. 2. What happens to the brightness of the light from the bulbs as each bulb is added? ____________ 3. What happens when one of the bulbs is unscrewed? _____________________________________ 4. How does the electric potential measured across the dry cell compare to that measured across the three bulbs? ________________________________________ 5. Compare the amount of electric current flowing from the cells compared to the current flowing through each of the three bulbs. _________________________________________________ 6. Suppose 15 light bulbs were connected in series, and one bulb burned out. How could defective bulb be found? _______________________________________ the 28 7. How could one defective bulb be identified if the 15 bulbs were connected in parallel? Explain. ______________________________________________________________________ 8. Are the electric wall outlets in homes wired in series or parallel? Explain. ______________________________________________________________________ Schematics : 1. 2. 3. 29 Investigation Parallel and Series Circuits (pg 360) The Series Circuit: current flows through a ____________path consisting of parts of the circuit which are wired to one another Analogy (fig 11.1 pg 354) Electrons push on the electrons ahead resulting in a smooth, even flow of current.The current at any one point in a series circuit is exactly the same as the current as any other point in the circuit. A series circuit can be compared with a race track. Cars are like electrons flowing around in a series circuit. All cars are filled with gas at a pit stop and travel smoothly around the same closed path. The Parallel Circuit: current flows through ________________paths called __________ circuits Analogy (fig 11.2 pg 355)SP In a parallel circuit, charges flow around two or more different loops. After leaving the power source, some charges take one path, while other charges take the other. A parallel circuit is like city streets where Cars have many paths to travel. One path might be a six lane freeway, while another is a two lane side street. Like cars on a freeway compared to a side street, the current in a parallel circuit is not the same at different points. The fact that electrons in a series circuit flow around a single path and electrons in a parallel circuit flow around in different paths (branches) brings us to the following Laws. Current Law: At any connection in an electric circuit, the current flowing into the connection is equal to the total current flowing out of the connection. Series: It = I1 = I2 = I3 Parallel: It = I1 + I2 +I3 Voltage Law: The algebraic sum of the potential differences around any closed pathway or loop must equal zero. Series: Vt = V1 + V2 + V3 Parallel: Vt = V1 = V2 = V3 . Sketch schematics below for a series and parallel circuit . See page 354 and 355. Diagram A ; 3 1.5 cells in series; Current from source = 1 amp ; 3 bulbs connected in series Diagram B : 3 1.5 V cells in series ; current = 1amp ; 3 bulbs connected in parallel Complete page 358 ( 1-4 ) 30 Series Circuit One path for the electricity to flow means that charges making up the current flow from one load to the next moving through all loads until coming back to the source again. Current (I in amperes A) at any point in the circuit is the same as the current at any other point in the circuit. Parallel Circuit Two or more paths for the electricity to flow means that charges making up the current flow through different paths and therefore do not move through all loads before coming back to the source again. 1.5 A 1.5 A + + Sum of Current in a Circuit Series Is = I1 = I2 = I3 Parallel Is = I1 + I2 + I3 I3 1k I2 1k I2 1k Is 1.5 I1 1k I1 1k Is 1.5 I3 1k The current passing through each of the 3 resistors and the current entering and leaving the source are exactly the same. The sum of the current passing through the 3 resistors is the same as the current entering and leaving the source. I. Use the Electricity Book web site to answer the next few questions http://www.uce.ac.uk/education/research/cript/electricity%20book/frame%20start.htm Start with the section Series and Parallel Series – Explain what happens when the bulb breaks? Paralle1 – Explain what happens when the bulb breaks? Christmas Tree with bulbs in series – Why do newer Christmas tree lights use parallel circuits? II. Use the Ohm Zone to answer these questions and complete listed activities. http://www.article19.com/shockwave/oz.htm Follow the hand and select Building a Simple Circuit first to see how the program works. Notice that this web site shows the flow of current from the positive side to the negative side but our course (and Ministry of Education) requires that we use the model with the flow from the negative terminal of the battery (excess electrons) to the positive terminal of the battery (deficiency of electrons). 31 Click on the hand again and select Building a Series Circuit this time. In a series circuit, elements are connected _____ after __________. This provides ______________________________________________. Follow the instructions to remove the bulb. If a connection in a series circuit is broken, the current _________ through all other elements will ____________. Click on the hand again and select Building a Parallel Circuit. A ________ circuit provides two or more _______ for the current to follow. In the circuit, notice that the current flows from the battery to point A, where it _____________________________. Try out the activity. At point B, the 2 ____________________________________ into ___________ to return to the battery. If one of the parallel connections is broken, _____________________________________________________________________. Click on the hand again and select Building Combination Circuit. Try out the activity and read this section. Notice the combination circuits follow the principles of series circuits in the areas that have series connections and follow the principles of parallel circuits in the areas that have parallel connections. Click on the hand again and select Current in a Series Circuit. The current intensity in a ________ circuit is the _________ through each circuit element. Try moving the ammeter around to see what the reading is at each point in the circuit. Click on the hand again and select Current in a Parallel Circuit. In parallel circuits, the current intensity will be highest in the circuit element that has the lowest resistance (true because of Ohm’s Law). To find the current (I) first find the resistance (R) by hovering over each element. Next, use the voltmeter to find the potential difference (V). You can find the current now by using Ohm’s law (V=IR, I=V/R) or you can just use the ammeter to check it. Add up the current reading at A, B, and C to get a reading of ____A. Now place the ammeter after the battery and notice the reading is 1.15 A too! This means that Is=IA + IB + IC for parallel circuits. Complete CYU 11.1 2,4 using www.tina.com or paper and pencil to make drawings and find the current at different points in the circuits. III. For additional review and problems use the bite size website http://www.bbc.co.uk/scotland/education/bitesize/standard/physics/electricity/series_and_parallel_circuits_ rev1.shtml Review Parallel And Series Circuits and answer question 1. Move to Current in a Series Circuit and try the activity. Move to Current in a Parallel Circuit and try this activity. This is good review. 32 WORKING WITH CIRCUITS 1. Label the parts of Figure A with the following terms: chemical (energy) electrical (energy) light and heat (energy) source conductor load ______________ energy Figure A _____________ energy _____________ energy Figure B 2. What kind of circuit is this? __________________ 3. How many paths do the electrons have to follow? _______ 4. How many loads does this circuit have? ______ 5. Is the circuit complete or incomplete? _______________ 6. Are the loads working? __________ 7. If one bulb were to blow out, the other bulb would _________________ 8. Adding another bulb would make the other two give off less light / the same amount of light? (circle one) Figure C 9. What kind of circuit is this? _____________ 10. How many loads does this circuit have? ________ 11. How many paths do the electrons have to follow? ______ 12. Is the circuit complete or incomplete? __________________ 13. Are the loads working? ______________ 14. If one bulb were to go off, the other bulb would give off less light_/ the same amount of light__ (circle one) 33 15. Adding another bulb would make each bulb give off less light_/ the same amount of light__ (circle one) 16. Is this a good way to wire a home? ____________ Figure D 17. What kind of circuit is this? _____________________ 18. How many paths do the electrons have to follow? ___________ 19. How many loads does this have? _________ Name them. ____________ ___________ Continue referring to Figure D. 20. Is the circuit complete or incomplete? ________________ 21. Are the loads working? ________________ 22. Is your home wired this way?_____________ Figure E Look at Figure E 23. What kind of circuit is this? _______________________ 24. How many paths do the electrons have to follow? _________ 25. How many loads does this circuit have _________ Name them ________________ __________________ 26. How many switches does this circuit have? ________ 27. Which appliance is working?____________________ 28. Which appliance is not working? ________________ 29. Is your home wired this way? ___________ Look at Figure F 30. What kind of circuit is this? _________________________ 31. How many paths do the electrons have to follow? ________ 32. How many loads does this circuit have? __________ 34 Name them ______________________________________ Figure F 33. How many switches does this circuit have? _________ 34. Which loads are working? ___________________________ COMPLETE THE CHART (Place a check in the correct column) Parallel Circuit 1. only one path for the electricity to follow. 2. more than one path for the electricity to follow 3. loads work or shut off one at a time 4. all loads are on or all loads are off 5. appliances share the voltage 6. appliances do not share the voltage 7. good way to wire a home 8. not a good way to wire homes 9. an extra bulb makes the others less bright 10. an extra bulb does not change the brightness of the others Series Circuit 35 Day 12 Electric Circuits with Multiple Loads Series Parallel Electric Current Constant Electric Potential Energy is shared by the loads. The sum of the loads should equal the source voltage. It= I1= I2… Vt= V1 +V2+… Each pathway allows a certain amount of current to flow. The sum of each pathway is the total current for the circuit. Each pathway receives the same energy. The potential difference for each pathway is the same as the source. I1 + I2… =It Vt= V1= V2… Advantages of a series circuit: 1. Less energy (voltage) is used. 2. Simpler to set up. 3. Less current= safer Disadvantages of a series circuit: 1. One load stops, all stop. 2. One switch controls all loads. Advantages of a parallel circuit: 1. Loads are independent. 2. Loads get maximum voltage. Disadvantages of a parallel circuit: 1. More current with each load- can be unsafe. 2. Uses more energy. 36 Electricity Search 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. An electric current is a flow of (A). The path the (A) take is called a (B). Current only flows when the (B) is complete, or closed. The most common device to open and close the (B) is a (C). In a DC (B), a (D) is used to give extra potential energy to the (A) to flow through the (B) again. This potential energy is also called a (E), and the "push" that the (D) gives the (A) is measured in (F). 7. This potential is needed because the (G) in the (B) is converting the (H) energy into another form of energy. 8. This other form of energy could be (I) energy if it produces motion, or (J) energy if it produces heat. connectors amps protons kinetic battery load cell thermal switch volts circuit wire(s) voltage electrons light bulb electrical static Chemical physical A B C D E F G H I J Day 13 Electrical Resistance and Ohm’s Law (pgs. 337– 339) Electrons move easily through a good conductor e.g _____________is a good conductor. Electrons l________ very little energy when they collide with __________atoms as they move through. Thus, little electrical energy is converted into ____________. Tungsten, the filament in light bulbs, is a _________conductor. Electrons lose much more of their energy when they collide with tungsten atoms. Thus, much electrical energy is converted into heat and light. Tungsten’s resistance is ______________ x that of copper’s resistance 37 The ability of a substance to impede the flow of electrons is called ___________. Some electrical devices used in circuits are designed for this purpose and are called __________. The symbol of electrical When electrons flow through a conductor, the electrical resistance causes a _________ of electric potential (voltage). This loss is referred to as electric potential difference, voltage drop, or the potential difference across a conductor. resistors- are designed to impede the flow of electrons Symbol: R SI Unit: Ohm (Ω) Voltage Drop – depends on resistance and amount of current V= IR Ohm’s Law Potential Difference (Voltage Drop) = Current x Resistance Ohm’s Law only applies to “ohmic resistors”. They are not affected by temperature changes. FACTORS THAT AFFECT RESISTANCE (342) a. TEMPERATURE -higher temperature, _________resistance (harder for electrons to flow through disorganized, fast moving electrons) b. LENGTH - ____________ resistance with wire length (resistance __________as length doubles...harder to flow greater distance relative to shorter distance) c. CROSS SECTIONAL AREA - ____________ resistance with larger area (more area for electrons to flow...easier) d. MATERIAL -structure of atoms may allow electrons to move better or worse, depending on how well atom holds onto electrons 38 Day 14 Resistance Voltage or Potential = Current Difference (Amperes) (Volts) x Resistance (Ohms) V=IxR I =V/R R=V/I Questions 1. In what units are the following measured: (a) voltage or potential difference (b) current (c) resistance? 2. State how voltage and current are measured. Potential Difference (Volts) 12 9 6 3 Current (Amps) 4 3 2 1 Resistance (Ohms) Current (amps) Potential Difference (volts) 3. On the axes above, graph the above data with potential difference on the X-axis and current on the Yaxis. (a) What do you notice about the graph? (b) Using the resistance rule, calculate the resistances in the table. What do you notice? 4. What voltage or potential difference is used by an electrical appliance that draws 0.4 amps of current and has a resistance of 3 ohms? 5. A light bulb uses 240 volts of electricity and draws a current of 2 amps. What is its resistance? 6. Calculate the current used by a television that runs on 240 volts and has a resistance of 600 ohms. 7. Three light bulbs each drawing 240 volts and 0.3 amps are connected in series. What is the resistance of each light bulb and what is the total resistance? 8. Complete the following table: (a) (b) © (d) (e) Answers Current (amps) Resistance (ohms) 0.1 0.25 0.4 0.5 600 1000 1000 Voltage (volts) 240 240 200 1. (a) straight line graph (b) R = 3 ohms 2.(a) volt (b) amp (c) ohm 3. Voltage measured by voltmeter wired in parallel; Current measured by ammeter wired in series 4. 1.2volts 5. 120 ohms 6.0.4 ohms 7. 800 ohms ; Add them if they are in series to get 2400 ohms 8. (a) 60 volts (b) 250 volts (c)600 ohms (d) 480 ohms (e) 0.5 amps 39 Resistance Calculations Worksheet resistance = potential difference current Units: R is Ω (ohms) V is V (volts) I is A (amperes) R=V I 1. Find the unknown quantity: a) I = 10 A R = 1500 Ω V=? b) I = ? R = 200 Ω V = 240 V c) I = 15 A R=? V = 110 V 2. Find the unknown quantity (CONVERT FIRST to the unit with no prefix) a) I = ? R = 2000 Ω V = 20 mV = ________ V b) I = 25 mA = _________ A R=? V = 110 V c) I = 1 kA = ________ A R=? V = 50 mV = ________ V WORD PROBLEMS 1. How much resistance does a light bulb create if it has a current of 25 mA around it in a 9 V circuit? 2. A heating coil offers a resistance of 2.5 kΩ. What voltage is required so that 1.5 A of current pass through it? 3. The human body offers a very small amount of resistance (let’s say 1 mΩ for argument). If a lightning bolt (said to have 1.21 GV of potential according to a famous movie called Back to the Future released in 1984), hits you how much current is flowing through your body. Complete page 342 ( 1-6 ) 40 SNC 1D Grade Nine Science Current Electricity Review Complete this sheet after a review of your notes and chapter 10 of your text book. 1. A coulomb is __________________ electrons and is also a measure of ________________. The symbol for this quantity is ________. 2. An Ampere measures ____________________ and is equal to one ________________ per second. The symbol for this quantity is _____________. 3. Knowing the relationship current = charge moving past a point/time…predict which current will be greater, the current passing through an electric razor or the current passing through an electric iron, when each is plugged into a 120 V home outlet. (hint refer to table 10.2 on page 325) _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 4. What relationship do you notice between the type of appliance and the amount of current they require (refer to table 10.2) Consider the type of energy produced by the high current devices. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 5. A volt is a measure of ______________________________________ and can be determined by dividing the _______________ by the _______________ for a circuit. A volt is equal to one Joule per ____________ 6. The relationship between potential difference (volts) and current (amps) is given by ohm’s law. An ohm is a unit of _______________ and the symbol is the Greek letter ____________. In mathematical form, Ohm’s law can be stated…. Resistance = ---------------------7. Carefully read page 337 on resistance and explain why the filament of light bulbs is made up of tungsten rather than copper. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Carefully review the model problem on page 338. This problem illustrates the relationship between resistance, current and electric potential for a typical electric heater connected to a 120 V home outlet. Use this information, and sample problem to determine the different resistances of a colour TV and an electric kettle connected to a 120 V home outlet. (hint, remember the current needed for these devices is listed in table 10.2 on page 325) Use the back of this sheet to solve this problem. 41 Day 15 Resistance in Series and Parallel Worksheet(356-358) Resistors in series Resistors in parallel Requivalent = R1 + R2+ R3 = 1 1 Requivalent = R1 + 1 + 1 = R2 R3 1. Find the equivalent resistance of these series circuits (in Ω) : a) R1 = 100 Ω R2 = 20 Ω R3 = 55 Ω b) R1 = 7500 Ω R2 = 1.5 kΩ R3 = 25 Ω c) R1 = 0.1 Ω R2 = 0.2 Ω R3 = 50 mΩ 2. Find the equivalent resistance of these parallel circuits (in Ω) : a) R1 = 100 Ω R2 = 20 Ω R3 = 55 Ω b) R1 = 7500 Ω R2 = 1.5 kΩ R3 = 25 Ω 3. Calculate the equivalent resistance of the following circuits: a) R1 = 5 Ω R2 = 10 Ω b) R1 = R2 = R3 = 1.5 Ω c) R1 = 0.1 Ω R2 = 0.2 Ω R3 = 50 mΩ 42 c) R1 = 12 Ω R2 = 5 Ω R3 = 8 Ω 4. Three light bulbs of 4 Ω resistance each are in a parallel with a 9V power supply. Draw the circuit, and find the current. Day 16 POWER (343) -the amount of energy that can be converted into heat, light, sound, etc. per second Power (units = W...watts) = Energy (J) / Time (s) P = E/t Also, P = VI Power Calculations Worksheet power = energy time P=E t 1. Find the unknown quantity: a) E = 10 J P = 100 W t=? b) E = ? P = 75 W t = 20 s Units: P is W (watts) E is J (joules) t is s (seconds) c) E = 15 kJ P=? t = 20 s 43 2. Find the unknown quantity (CONVERT FIRST to the unit with no prefix) a) E = 1.2 kJ = ________ J P = 75 W t=? b) E = 55 J P=? t = 2.25 hrs = _________ s c) E ? P = 200 MW = ________W t = 0.5 hrs = __________s WORD PROBLEMS 1. How much energy passes through your bedroom lamp (containing a 100 W light-bulb) every evening when you read for half an hour before you going to bed at 9:45pm? 2. 100 MJ of energy passes through a generating station every minute. What is its power rating? 3. How long will a 75 W bulb glow for on 1 kJ of energy? Questions 1. A gasoline-powered generator consumes 15 000 J of energy in 5.0 minutes. How much power did it produce in this time? Calculations: 2. A toaster connected to a 110 V power source has 6.0 A of current flowing through it. How much power is dissipated as heat? Calculations: 3. A light bulb draws 1.25 A of current from a 120 V gasoline-powered generator. (a) How much power does the generator produce? Calculations: (b) If the generator runs for 5.0 minutes, how much energy will the lamp convert into heat and light? Calculations: 44 Day 17 Science, Gr. 9 Characteristics of Electricity – Measuring Electricity Mixed Electricity Problems DON’T FORGET TO CHANGE TO THE UNIT WITH NO PREFIX FIRST! ALL OF THESE NEED TWO DIFFERENT FORMULAS 1. How many coulombs of charge pass through a 95 W amplifier plugged into a 110 V wall socket over the course of a 2 hour concert. 2. A bulb plugged into a 110 V wall socket has a resistance of 100 Ω. Find how many seconds it takes to pass 2000 C of charge. 3. 2500 coulombs of charge is passed over a 2 hour period across a certain capacitor. What is the resistance of this capacitor if the voltage across it is 200 mV. 4. What is the power of a microchip that passes 1 C of charge with a potential difference of 0.01 mV in 1 second. 5. A simple circuit has a 9V battery attached to it. How long does it take to pass 1C of charge through that battery if its resistance is 150 Ω. 6. What is the current in an electric stove element that creates 150 J of heat at 240 V over a 5 minute period. 45 Day 18 Measuring Electrical Energy Energy ~ the ability to do work Electrical Energy ~ The energy transferred to an electrical load by moving electric charges Symbol E the SI unit for measuring energy is the joule ( enough energy to light a 100 W light bulb for a one hundredth of a second) Because the joule is so small, energy is also measured in larger units such as the watt hour and the kilowatt hour. The watt hour is 3600 times larger than the joule Three Factors Determine the Amount of Electrical Energy 1. Voltage Drop ~ a measure of the energy each electric charge gave up as it moved through the circuit 2. Electric Current ~ A measure of the rate at which a the electric charges flowed out of the battery 3. Time ~ the time that the electric charges were flowing in the circuit while the light bulb was glowing. Calculating the Amount of Electrical Energy If you connect a battery to any type of electrical load until it is discharged, multiply the voltage drop, current and time, you always get the same number. Scientists express this relationship in the form of a formula: Electrical Energy = Voltage Drop x Electric Current x Time Interval E = V x I x t Where E is the electrical energy measured in joules (J) and V is the voltage drop measured in volts (V) I is the electric current measured in Amperes ( I) t is the time interval measured in seconds (s) Rated Capacity = Electric Current x Time Interval ENERGY SYSTEM -a device that converts one form of energy into another eg. electric kettle converts electrical energy into sound and thermal energy FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS -"energy is not created or destroyed, it just changes forms" INPUT ENERGY = WASTE ENERGY + USEFUL OUTPUT ENERGY input energy = amount of energy used to operate a system output energy = amount of useful energy obtained from a system waste energy =energy that is not useful (often thermal) unit of energy = Joule (J) = 1000 J = 1 kJ (kilojoule) EFFICIENCY =[ENERGY OUTPUT / ENERGY INPUT] X 100 eg. 500 kJ energy goes to electric kettle, which uses 490 kJ to heat water,and loses 10 kJ as heat and sound kettle efficiency = E out/ E in X 100 = 490 kJ / 500 kJ = 98 % efficiency waste = 100 % - 98% = 2 % energy wasted 46 Efficiency Calculations ( pg 348 ) Questions 1. A clothes dryer has a power rating of 4356 W. It takes an average of 45 minutes to dry a load of clothes. If the dryer used 8820 kJ of energy during this time, how efficient is this dryer? Calculations: 2. Reading for an hour followed by an hour of homework, a student decides to check the efficiency of the halogen desk lamp used. The lamp is rated at 20 W and used 20.88 kJ of energy, how efficient is it? Calculations: 3. In conducting a science inquiry into how efficient a kettle design is, a student discovers that in 264 seconds 26°C water increases in temperature by 70°C for kettle “a” and 65°C for kettle “b.” The energy transferred to 1 Kg of water in kettle “a” is therefore 292 600 J, and 271 700 J for kettle “b.” Each design is a 1500 W kettle, what percentage of efficiency is kettle “a” and “b?” Calculations: 4. Based on your answer to question 3, how much money does it cost to run each kettle for a 30-day month? For what reason, therefore, would you choose between the kettles? Assume that the kettles operate 30 minutes daily, and that electricity costs 10¢ per kilowatt hour. Calculations: 47 Calculating Electric Power Electrical power is a measure of the rate at which electrical energy is being used. The SI unit is the watt and the symbol is W. Electrical Power (E) = Electrical Energy (J) = Watts Time Interval (s) Formulae P= E= E t P x t t = E P Answer in: Watts Joules E t P seconds This formula is not often used because you have to measure both the energy and the time interval to be able to solve the problem. Although the joule (J) is the normal unit for energy, the large amounts of energy used in a home would require the use of very large numbers. In the electrical meter, the energy is measured in kilowatt hours (kW.h). Power is measured in kW and time is measured in hours (h). There are 3 600 J in one W.h or 3 600 000 J in one kW.h., Power can also be calculated using the voltage and current: Electrical Power = Voltage Drop x Electric current Formulae P= VxI V= P I Answer in: Watts I =P V P Volts Amps V I To find the cost of the electricity, multiple the rate charged by the electric company by the energy used. Examples: 1. Calculate the power of a toaster that uses 72000J of energy in 50 s (time). 2. Calculate the power of a vacuum cleaner if the operating voltage is 120 V, and the current (I) flowing through it is 7.90 A. 48 3. How many kilowatt hours (kW.h) of electrical Energy are used in four weeks by a clothes dryer that has a power rating of 5 kW (P) and is operated for 4.5 hours (time) each week? 4. Calculate the cost of the electricity required to operate a freezer ( 500 W) for one month if it uses 75 kWh of energy (E). The rate charged for the electricity is $ 0.08/ kWh. ELECTRICAL POWER PROBLEMS 1. Calculate the power rating of an electric toaster that uses 210 000 J of Energy while toasting bread for 140 s (time). 2. Calculate the power rating of a coffee grinder that operates on a voltage of 120V. A current of 1.7 A flows in the motor. 3. Calculate the Energy used by a coffee maker that has a Power rating of 0.900 kW and for a time of 17 h. operates 4. How much Energy is used by a 1.5 kW (P) electric kettle that operates for a time of 0.80 h per day for two weeks. 5. What is the current (I) drawn by a 100 W light bulb operating at a voltage drop of 120 V? 6. What is the voltage drop across a 1248 W baseboard heater that draws 5.20 A ? 49 7. What is the maximum power that may be used in a circuit with a voltage drop of 120 V and a 20 A fuse? 8. Calculate the cost of operating a 3.6 kW oven for 3.0 h, at a rate of $0.08/kW·h. 9. Calculate the cost of operating a 400 W spotlight for 2.0 h a day for 30 days , at a rate of $0.08/kW·h. 10. What is the cost to a store owner of leaving a 40 W light burning near his safe over the weekend, for 60 h, if electricity costs $0.08/kW·h? 11. The blower motor on an oil furnace, rated at 250 W, comes on for an average of 5.0 min at a time, a total of 48 times a day. What is the monthly (30 day) cost of operating the motor, if electricity costs $0.08/kW·h? 12. A 300 W refrigerator compressor operates for an average of 6 h per day. Calculate the annual cost of operating the refrigerator, if electricity costs $0.08/kW·h. Ans. 1) 1500 W 2) 204 W 3) 15.3 kW·h 4) 16.8 kW·h 5) 0.833 A 6) 240 V 7) 2400 W 8) $0.86 9) $1.92 10) $0.19 11) $2.40 12) $52.56 Pg 348 (1-5) 50 Day 19 Electrical Energy Use in the Home (368) What unit is used to measure the amount of energy your house uses? ________________ Look at the meter on page 368 : October 28 # of kilowatt hours (kW.h) = ____________________ August 30 # of kilowatt hours (kW.h) = ___________________ Subtract the 2 values = _____________________ = amount of kW.h used If the cost = 8.0 cents per kW.h . Calculate the total cost = total energy used kW.h x cost in $/kw.h ___________ x ___________= ____________________ The Price of Energy Questions 1. A meter reader determines that a business has used 3550 kW•h of energy in two months. If electricity costs 10 cents per kW•h, calculate the bill. Calculations: 2. An electric heater draws 1100 W of power. Electricity costs eight cents per kW•h. How much does it cost to operate the heater 3 h a day for 30 days? Calculations: 3. A 750 W toaster and a 1200 W electric frying pan are plugged into the same 100 V outlet. How much will it cost to operate the two appliances at eight cents per kW•h? Calculations: 4. A toaster is used an average of 5 h per month. The toaster draws 8 A of current from a 110 V outlet. If electricity costs eight cents per kW•h, how much will it cost to operate the toaster for one year? Calculations: Pg 350 (1-6),8,11,13,14,17,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28 Pg 378 (1-7),8,10,11,17,21,22 51 Independent research produce a plan of action to reduce electrical energy consumption at home (e.g., using EnerGuide information when purchasing appliances), and outline the roles and responsibilities of various groups (e.g., government, business, family members) in this endeavour [IP, AI, C] Issue: Replacing incandescent light bulbs with compact fluorescent bulbs can reduce the energy needed to light a home by 75%. Although the bulbs are more expensive than incandescent bulbs, electrical companies sometimes provide coupons to reduce the price. Also, the Ontario government is phasing out incandescent bulbs, which will further reduce energy consumption. Questions: What are EnerGuide and ENERGY STAR, and how can they be used when purchasing appliances or electronics? What is the difference in energy consumption between a conventional and a front-loading washing machine? What appliances consume electrical energy even when they are not in use? 52 Which Light Bulb Is Best? Light bulbs are used for many different purposes in a home. In your own room, you likely have a desk lamp, a ceiling light, and maybe a bedside lamp. Bulbs used to come in standard wattages of 40, 60, and 100 W. Now, different energy-efficient types of bulbs are available. How much longer do these new bulbs last? Are they cost-efficient as well? 1. How many kilowatt-hours does a 60-W incandescent bulb use during a 12-hour period? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 2. How many kilowatt-hours does a 15-W compact fluorescent bulb use during the same period? (Both bulbs provide the same light intensity of 900 lumens.) __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 3.If the utility rate is $0.10 per kW•h, how much does it cost to run each light bulb in questions 1 and 2? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 4. According to the information on their packages, the compact fluorescent bulb lasts 10 000 hours and the incandescent bulb lasts 1350 hours. How much money will you save in electricity charges over the life of each bulb? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 5. If the compact fluorescent bulb costs $30.00 to buy and the incandescent bulb costs $2.00 to buy, which bulb is more economical over the long term? (Hint: To make this comparison, assume 10 000 hours of operation. This will require purchasing more than one incandescent bulb, so you will need to determine how many.) __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 53 Day 20 Power Generation Reading Assignment (pages in SciencePower9) 1. Systems at a Glance Visit http://www.opg.com/power/ to learn about power generation in Ontario. As of December 31, 2006 OPG’s electricity-generating portfolio had a total in-service capacity of 22,000 megawatts (MW)*. This consisted of: operating nuclear units with a capacity of ______________TWh http://www.opg.com fossil-fueled stations with a capacity of ______________TWh hydroelectric power with a capacity of ____________TWh 29 EcoLogoM-certified green power hydroelectric stations with a capacity of 12MWh Green power stations with a capacity of _____________MW List 1 example of a green power station including the location. _____________________________ Hint: check out the map and the other links on nuclear, fossil, hydro. Hydroelectric Power 2. From p395 of SciencePower 9 Most of Canada’s electricity comes from _________ power. Energy from Flowing River Uses water (_________) pressure to generate electrical energy Large ____ cause the water levels to rise above the power plant As the level rises the _________ underneath the water ___________ Water pressure at the bottom of the dam is therefore enormous A channel (called a _____________) directs the water from the bottom of the reservoir to a _________ High pressure of the rapidly flowing water turns the turbines and the turbines turn the generators Generators convert ________ energy (energy from the motion of the turning turbine) into electrical energy High voltage power lines carry the electric energy over many kilometres from the plant to communities http://www.ec.gc.ca/water/en/manage/use/e_hydro.htm 54 3. Visit http://www.opg.com/power/hydro/howitworks.asp for a diagram of hydroelectric power generation. Fill in the blanks about generator portion. In very simple terms, electricity is produced by _________ _______-magnets inside a coil of wire in a __________ to create a ______ of ___________. To keep the electro-magnets spinning, a hydroelectric station uses falling water. Advantages Disadvantages http://www.tva.gov/power/hydroart.htm Fossil Fuels 4. How fossil fuel works (coal fired power plant) http://www.tva.gov/power/coalart.htm Electricity is produced at a coal-fired fossil plant by the process of _________ water in a boiler to produce ________. The steam, under tremendous _________, flows into a __________, which spins a ____________ to produce electricity. Fossil Fuel Power (Coal-fire Generation) Advantages http://www.tva.gov/power/coalart.htm Disadvantages 55 Nuclear Power (CANDU Reactor Generation) Advantages Draw Fig 12. 12 and label Wastes) Disadvantages p. 403 (Nuclear Energy Leaves Radioactive 56 Tidal Energy Advantages Draw Fig 12. 27 and label Disadvantages p. 412 (Tidal Energy) List the sources of electricity in Canada according to their importance: (p. 398) Examples of this source Most 1. 2. 3. 4. Least 5. Internal Combustion gasoline powered generators Define the following terms: (p. 407) RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCE – NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCE – Classify the following sources of energy: (various pp. 394 – 413) solar-cell nuclear gasoline-generator hydroelectric dam tidal wind solar collector gas-fire wind renewable non-renewable 57 Answer the following questions: 1. The one component that is common to almost all forms of power generation is the turbine. a. What is a turbine? (p. 395) b. How is the turbine used to create electricity? (p. 395) 2. Complete the table: (pp. 395, 396, 397, 398, 411, 412) Form of Power What is the original source of the energy? What substance turns the turbines? hydroelectric (dam) coal-fire heat from burning coal steam nuclear wind tidal diesel, gas, and internal combustion (p. 398 Canada’s Energy Resources) pg. 416 (6,7) water 58 - watch video www.teachersdomain.org : energy sources and answer questions below : -renewable. watch video www.teachersdomain.org : alternative energy Independent Research assess some of the social, economic, and environmental implications of the production of electrical energy in Canada from renewable and non_renewable sources (e.g., wind, solar, hydro, coal, oil, natural gas, nuclear) Issue: The operation of wind farms along Lake Huron produces electricity from a renewable source, reducing dependence on non-renewable sources of electricity. However, the wind farms produce noise and visual pollution, affect local animal life, and reduce the amount of land available for agriculture. Questions: What is the price difference between electricity produced from solar power and by coal-burning plants? What effects do coal mining, oil production, wind farms, and hydroelectric dams have on surrounding ecosystems? 59 What types of hazardous substances are used or created in the production of solar power and nuclear power? What types of emissions are produced by coal-burning and hydroelectric power plants? What are the effects of these emissions on human health and the environment? Test Review 422 (1-30)34, 36,38,39,40,41,42 60 Unit 3 Review 1. What is the difference between an insulator and a conductor? Give two examples of each. 2. By adding positive and negative charges, make the first circle positively charge, the second negatively, and third neutral. After you have drawn them determine the overall charge. Overall: Overall: Overall: 1. Complete the charges on this diagram of lightning just before it strikes. ground 2. What is the purpose of a lightning rod? 3. Explain clearly why a balloon rubbed with fabric will produce static electricity but a metal bar rubbed with fabric will not. Include the words charges moving freely, charges building up in one place, insulator, conductor in your explanation. 4. Add positive and negative charges on the following pair of objects. Make sure there is a difference between the charges on each object. Add a spark in the correct direction. 5. Draw the four diagrams that were used to explain induction. Add descriptions in your own words to make it clearer. 61 Electricity Problems 1. If there is a current of 15 amperes in a circuit for 5 minutes, what quantity of electric charge flows through the circuit? 2. 1 MW of power is produced by the Bearskin Lake generating station every Christmas day. How much energy is consumed between 9:00am and 5:00pm on December 25 th? 3. 1.2 x 103C of charge passed through a transformer over a 5 minute period. What is the resistance of the transformer if its potential difference is 240 V. 4. A buzzer plugged into a 110V wall socket has a resistance of 1.25 x 10 2 Ω. Find how many seconds it takes to pass 1C of charge. 5. Draw a circuit that has a bulb attached in series to a 1.5 V cell, an ammeter and a switch. Find the resistance of the bulb if the switch is closed and the ammeter reads 1.2x10 -2 A. 6. What is the equivalent resistance of four resistors (3 Ω, 6 Ω, 9 Ω, and 12 Ω) when: (a) they are attached in series? (b) they are attached in parallel. 7. Three 25 Ω resistors are attached in parallel. There is a cell and an ammeter. (a) Draw the circuit. (b) If the cell offers 6 V of potential difference what is the current on the ammeter? 62 63 D. Power Generation 1. State how the following are important in power generation: (a) turbine (b) generator 2. List three renewable and three non-renewable forms of power generation. Renewable 1. 2. 3. Non-renewable 1. 2. 3. 3. What are the major disadvantages of the following forms of power generation: (a) coal (b) nuclear (c) hydroelectric dam