Document 14452518
advertisement
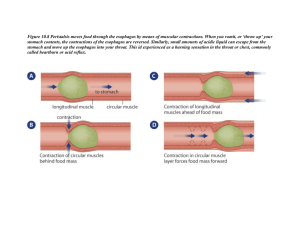
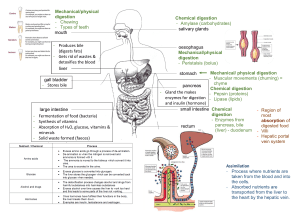
Organ system that takes in food, digests it, and excretes remaining waste Long tube with two openings that is composed of: Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Rectum Anus Not part of the digestive tract, but aid in digestion Liver Gallbladder Pancreas Mechanical Digestion: Physical breakdown of food Chemical Digestion: Break down of food using enzymes (biological catalysts) Begins the process of breaking down food Mechanical Digestion: Uses teeth and tongue Chemical Digestion: Uses enzymes Provides water and enzymes (amylase) to chemically break down and moisten food Produced by epithelial tissue that lines the mouth Tiny flap-like structure that covers the trachea during swallowing to prevent food from entering the respiratory system Muscular tube connecting the mouth to the stomach Food moves through the esophagus involuntarily Peristalsis: Muscle contractions that moves food through the esophagus Holds food and churns it to continue digestion Stomach lining produces digestive enzymes, acid and mucous (protective layer from stomach acid) 6 m long and narrow Site of most digestion and absorption of nutrients Small intestines contain fingerlike projections called villi. Villi increase the surface area so there is more area for the absorption of nutrients. 1.5 m long Absorbs water from indigestible food Remaining solid waste is excreted as feces from the anus Liver: Produces bile Bile: helps to mechanically break down fats in our food Gallbladder: Stores bile produced by the liver Pancreas: Releases enzymes into the small intestine that aid in digestion Produces insulin which helps to regulate our blood glucose levels