Jargon Chapter Processing Food and
advertisement

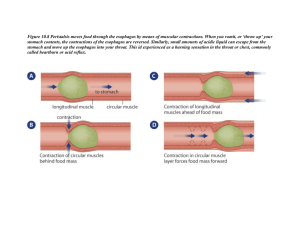
One ATP Sandwich With extra phosphate Comin’ up Chapter Processing Food and Nutrition Chapter 21 Processing Food and Nutrition Objectives: 1. Understand the concepts of digestion 2. Identify the anatomical parts 3. Describe the function of the noted parts 4. Describe the changes in processing food through the animal kingdom with a focus on vertebrates Jargon Elimination: Getting rid of digestive waste (called egestion in lower critters) Excretion: Getting rid of metabolic waste (function of kidneys and lungs) What Is The Diversity Of Digestive Systems In NonHuman Animals • Intracellular digestion in a sponge Digestion: 1. Break apart food into component molecules “Degrade macromolecules into simpler compounds” 2. Rearrange these molecules 3. Use now or later Wa te r, une a te n food, a nd wa s te s a re e x pe lle d through the la rge ope ning a t one e nd of the s ponge Wa s te produc ts a re e x pe lle d by e x oc y tos is H2O H2O (a) Tube s ponge s The food v a c uole m e rge s with a ly s os om e c olla r c e ll H2O c a rry ing food pa rtic le s e nte rs the pore s H2O H2O Food pa rtic le s a re filte re d from the wa te r by the c olla r (b) A s im ple s ponge Food e nters the c olla r c e ll by pha goc y tosis , form ing a food v a c uole food v a c uole (c) Colla r c e ll ly s os om e with dige s tiv e e nz y m e s Fig. 21-6 Animals? • • • Annelids, mollusks, arthropods, and vertebrates are examples of animals with tube shaped gut. Extrace l l u l ar d i ge sti o n Di ge sti o n i n a sac • Lots of functions Soil with food par ticles is ingested pre y Indigestible r em nants ar e expelled intestine (a) Hy dra with pre y Te nta cle s with s tinging c ells c apture the pre y a nd ca rry it into the m outh anus m outh Gla nd c ells s ec rete dige s tiv e enzy me s into the dige s tive s ac and be gin e x tra ce l ular dige s tion m outh phar ynx pre y Nutritiv e ce l s e ngulf food pa rtic les and c om ple te diges tion within food v ac uoles esophagus cr op gizzar d dige s tiv e sac (b) Food proc e ss ing in Hydra Food is gr ound up in the gizzar d Fig. 21-7 Evolution of Digestion • Complete digestion • Gut runs from mouth to anus - food moves in one direction • Digestion occurs outside the cells: Extracellular digestion - Food absorbed by epithelial cells in gut Generic Digestive Parts Structures that take in food Holding tank (some have crop) Pulverizer (gizzards in birds and reptiles) Place to expose food to enzymes Place to absorb nutrients Refuse area (where elimination stuff is stored) Fig. 21-8 Complete Gut Digestion Functions: 1. Movement 2. Secretion 3. Digestion 4. Absorption Salivary glands: Secr ete lubr icating fluid and star ch-digesting enzym es Pharynx: Shar ed digestive and r espir ator y passage 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Food is digested and absor bed in the intestine Oral cavity. tongue, teeth: Gr ind food, m ix with saliva Epiglottis: Dir ects food down the esophagus Esophagus: Tr anspor ts food to the stom ach Stomach: Br eaks down food and begins pr otein digestion Liver: Secr etes bile (also has m any non-digestive functions) Gallbladder: Stor es bile fr om the liver Pancreas: Secr etes buffer s and sever al digestive enzym es Large intestine: Absor bs vitam ins, m iner als, and water ; houses bacter ia; pr oduces feces Small intestine: Food is digested and absor bed Rectum: Stor es feces Fig. 21-9 Vertebrate Digestive Tract The Swallowing Thing Mouth - Mastication 1. Capture and crush food Teeth! Why chew? 2. Lubrication and Enzyme (Amylase) Saliva • Bolus is formed in mouth 1. With tongue, move food to back of mouth Pressure against pharynx closes epiglottis against larynx (lungs), sealing airway 2. Pharynx to esophagus (connects to stomach) 3. Peristaltic movement down esophagus Digestion in the Stomach Salivary glands: Secr ete lubr icating fluid and star ch-digesting enzym es Pharynx: Shar ed digestive and r espir ator y passage Oral cavity. tongue, teeth: Gr ind food, m ix with saliva • Enters through Sphincter muscle • Bolus enters stomach and mixes with digestive juices = chyme • 3 layers of muscle – mechanical digestion • Stomach used for: Storage and digestion Very little absorption occurs in stomach Epiglottis: Dir ects food down the esophagus Esophagus: Tr anspor ts food to the stom ach Stomach: Br eaks down food and begins pr otein digestion Liver: Secr etes bile (also has m any non-digestive functions) Gallbladder: Stor es bile fr om the liver Pancreas: Secr etes buffer s and sever al digestive enzym es Large intestine: Absor bs vitam ins, m iner als, and water ; houses bacter ia; pr oduces feces Small intestine : Food is digested and absor bed Rectum: Stor es feces Fig. 21-9 Digestion in the Stomach Digestion in the Stomach • Parietal cells secrete Hydrochloric acid • Chief cells secrete Pepsinogen LET’S DIGRESS FOR A MOMENT!! Hydrochloric Acid: - kills bacteria - converts Pepsinogen to enzyme Pepsin (breaks apart proteins) Puking and throat burn!!!!!!!!!!!! Protection from Acid? • Tightly packed epithelial cells • Mucus for lubricates and protects • Chyme remains in stomach ~ 2 hours - leaves stomach through pyloric sphincter Peptic Ulcer: Too much HCl, or too little mucus – or – Bacterium Helicobacter pylori Pancreatic Juice • Contains water, bicarbonate, and digestive enzymes Salivary glands: Secr ete lubr icating fluid and star ch-digesting enzym es Accessory digestive organs Oral cavity. tongue, teeth: Gr ind food, m ix with saliva Pharynx: Shar ed digestive and r espir ator y passage • Digestive enzymes include amylase for starch, trypsin for proteins, and lipase for fats, deoxyribonuclease ??? Epiglottis: Dir ects food down the esophagus Liver weighs 3 lbs. below diaphragm - Makes bile Stomach: Br eaks down food and begins pr otein digestion Esophagus: Tr anspor ts food to the stom ach Liver: Secr etes bile (also has m any non-digestive functions) Gallbladder: Stor es bile fr om the liver Gallbladder Pancreas: Secr etes buffer s and sever al digestive enzym es Small intestine: Food is digested and absor bed Large intestine : Absor bs vitam ins, m iner als, and water ; houses bacter ia; pr oduces feces Rectum: Stor es feces Fig. 21-9 On to the Small Intestine Salivary glands: Secr ete lubr icating fluid and star ch-digesting enzym es (5-6 meters long – 18 Ft!) Oral cavity. tongue, teeth: Gr ind food, m ix with saliva Pharynx: Shar ed digestive and r espir ator y passage 3 regions: 1) Duodenum – 10 inches 2) Jejunum - 8 feet 3) Illium – 12 feet Epiglottis: Dir ects food down the esophagus Stomach: Br eaks down food and begins pr otein digestion Esophagus: Tr anspor ts food to the stom ach Liver: Secr etes bile (also has m any non-digestive functions) Most Digestion and absorption occurs here Bile from liver added (fats) Enzymes from pancreas added (fats, peptides, carbs) Small intestine has characteristics that enhance surface area! - Folding of lining, Villi and Microvilli Gallbladder: Stor es bile fr om the liver Pancreas: Secr etes buffer s and sever al digestive enzym es Small intestine : Food is digested and absor bed Large intestine: Absor bs vitam ins, m iner als, and water ; houses bacter ia; pr oduces feces Rectum: Stor es feces Fig. 21-9 • The small intestine lacteal fold of intestinal lining microvilli villi capillaries intestinal gland (a) Small intestine 18-73 (b) A fold of the intestinal lining (c) A villus arteriole lymph vessel venule (d) Cells of a villus • Chyme remains in small intestine from 3 to 10 hours • Nutrients move to liver (Fat to cardiovascular system!) Fig. 21-12 Summary of digestion Carbohydrates: Mouth, Stomach, Small Intestine Proteins: Stomach, Small Intestine Lipids (fats): Small Intestine Nucleic Acids: Small intestine Last, but not Least,,, The Large Intestine •Little nutritional absorption occurs here! Parts: Cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, anus • Elimination of w aste •Absorption of w ater and sodium 5 -6 feet long Salivary glands: Secr ete lubr icating fluid and star ch-digesting enzym es Pharynx: Shar ed digestive and r espir ator y passage Oral cavity. tongue, teeth: Gr ind food, m ix with saliva Epiglottis: Dir ects food down the esophagus Esophagus: Tr anspor ts food to the stom ach Stomach: Br eaks down food and begins pr otein digestion Liver: Secr etes bile (also has m any non-digestive functions) Gallbladder: Stor es bile fr om the liver •Production of vitamin K and some B vitamins (bacteria) Pancreas: Secr etes buffer s and sever al digestive enzym es •Chyme can stay in Large Int for a few hours up to days. Large intestine : Absor bs vitam ins, m iner als, and water ; houses bacter ia; pr oduces feces Small intestine : Food is digested and absor bed Rectum: Stor es feces Fig. 21-9 Herbivores have special adaptations? Why? Cellulose!! • Teeth adaptations: Premolars and molars - High crowned - Broad flat occlusal surfaces • Coprophagy • Reingesting feces Why? - Cecum (houses bacterial microorgs.) Stomach adaptations: - bacteria micro-organisms - dry and gelatenous pellets - increased vitamins B and K