Research Efforts on Improving Neonatal Survival Background:
advertisement

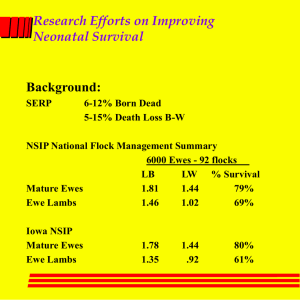
Research Efforts on Improving Neonatal Survival Background: SERP 6-12% Born Dead 5-15% Death Loss B-W NSIP National Flock Management Summary 6000 Ewes - 92 flocks LB LW % Survival Mature Ewes 1.81 1.44 79% Ewe Lambs 1.46 1.02 69% Iowa NSIP Mature Ewes Ewe Lambs 1.78 1.35 1.44 .92 80% 61% In Summary We are losing 15-30% of our production potential. .2 - .3 lambs per ewe after lambing .2 - .3 fetus per ewe in early gestation ISWPB Evaluation of Common Shepherd Practices Vitamin ADE Vitamin B Complex Strong Lamb Lamb & Kid Kare Probiotics Youngs & Hummel ISU Teaching Farm 1990 & 1991 Twin Lambs - one treated 1/2 cc Injacom one control Injacom 50,000 IU A 5,000 IU D 10 IU E Survival averaged 90% Preweaning gain not affected No response on Survival Vitamin B Complex Morrical & McClain 1991 128 Crossbred Lambs Treated Lambs Received -3 cc B-Complex at birth and 3 weeks of age B-Complex Results Birth Wt. 21 day Wt C T 10.9 10.9 23.7 24.1 4 Actually died 10 were pulled for AR WW Survival 40.1 39.7 92% 87% Influence of Subclinical Mastitis Ahmad, Timms and Morrical 1988-1990 McNay Research Farm 4-Corner Polypay and ISU Teaching Farm 1988 - 196 Ewes and 392 Halves Sampled at Birth and Weaning No. Infected No. Halves Infected Lambing 25% 17% Weaning 22% 14% McNay only 1989 1990 Lambing Weaning No. Infected 25% 15% No. Halves 17% 8% No. Infected Halves 13% 9% 16% 9% Coagulase Negative Staph-90% of infections Impact of Infection on Lamb Performance Uninfected Infected 1988 .71 1989 .69a 1990 .68 .67 .62b .65 Uninfected Infected at W Infected at L Infected at L & W 1989 .71 .66 .58 .54 Control of Subclinical Mastitis Treated at Weaning and Resampled 60 days postweaning Treatments Dry Cow Infusion Cefa-Dri 1/2 tube per half - 5 ml Benzathine Penicillin Results Infected Cured 1989 Trt. Cont. 9 15 6 (67%) 5 (33%) 1990 Trt. Cont. 20 15 18 (90%) 7 (47%) Did not prevent new infections at next lambing Summary Subclinical Mastitis 50% of infections occur postweaning 50% of infections occur prelambing Dry cow and injectable are equally effective Birth Weight from Ewes Fed Varying Levels of Energy TDN Single Twin Triplet 2.35 11.2 10.6 2.85 13.3 11.4 2.8 13.2 11.2 9.4 3.6 13.2 10.6 9.4 10.5 11.7 11.7 7.7 8.5 9.4 Singles Twins Triplets 3.2 3.8 4.4 Note these are raw means 1992 Lamb Survival Work McNay Sheep Flock Dan Morrical and Arnold McClain Winter Lambing Ewes and Offspring Randomly allocated within 24 hrs of age Treatments Lamb and Kid Kare Fastrack Probiotic Paste Results Trial 1 - Naturally Reared Lambs N ADG B-W Deaths Orphaned Control 33 .63 1 1 LKK 33 .59 1 0 FT 33 .61 1 1 No effect on Performance or Survival Trial 2 - Orphan Reared N ADG 0-21 ADG 21-42 Deaths Control 6 .42 .41 0 LKK 6 .39 .38 0 FT 6 .36 .34 0 Conclusion to All Previous Work Post Lambing Treatments were not successful in increasing lamb survival Current work Youngs et al. - ISU Teaching Evaluation of Vitamin A & E on OR, Embryo and Fetal Survival Morrical et al. Vitamin A & E Teaching Important observations a single injection of E maintains serum E levels for 6 days younger ewes have higher embryo losses Vitamin A may increase OR Vitamin E injections and lamb survival Protocol 2 X 2 factorial 1994 & 1995 Ewes during late gestation 900 IU or 0 E per week 90 or 10 PPM Se mineral Ewes were fed by fetal number Results of Vitamin E & Se No effect of mineral source on ADG or survival Vitamin E improved pre-weaning ADG 5-10% improved livability one year more important in multiples more important for young and old ewes Current work Evaluating feeding Vitamin E in both late gestation and lactation Regional project with Indiana, Kentucky and Iowa