Getting lambs off to a fast start Dan Morrical Iowa State University
advertisement

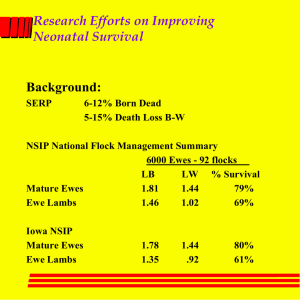
Getting lambs off to a fast start Dan Morrical Iowa State University Lamb losses and Profit Baby lamb losses 10-25 % per year most of the losses are before 72 hrs without records you do not know Lamb Mortality Study, Rook 1986/3600 P 22% S/H 17% P 12% 1987/5200 S/D 17% S/H 25% O 28% A 9% O 27% S/D 22% S/H 14% A 21% P 14% S/D 24% O 25% 1988/7000 A 23% McNay Death Loss by Seasons 1995 Winter Lambs 251/lambs/124 ewes Spring Lambs 151 lambs/74 ewes S/D 41% O/U 9% P 0% S/H 50% A O/U 10% 10% P S/H 20% 20% S/D 40% Fall 148 Lambs/ 81 ewes P 13%O/U 0% S/H 13% S/D 74% Goals of Late Gestation Ration 1. Healthy, vigorous ewes 2. In condition for heavy milking 3. Healthy, vigorous lambs of moderate size. 4. High vitamin E status Results - Serum E ewes Con E-G E-L E-GL Pretreatment 1.27 1.26 Pre-lambing 1.51a 1.91b Post-lambinga .93a 1.13b Mid-lactation .97a .95a 1.28b 1.37b Milk e at 3 days 10.8 15.1 a,b Row means with different superscripts differ (p<.05). Results - Serum E lambs 3 days Con E-G E-L E-GL 1.08 1.08 28 days .41 .38 1.33 1.33 Birth Weight on Livability Best 11.4 pounds VPI 1 pound increase in birth weight = 4% in death loss Texas A & M Birth Weight & Feedlot Performance Birth Weight Small Medium Large 8.5 8.6-13.3 13.4 Wt. gain/ day of age .69 .75 .82 Feed eff. 4.8 4.3 3.8 U. of Kentucky So what is the right birth weight? •Depends on: ewe size type of birth •Singles 7% of dam wt. •Twins 6.5% of dam wt. •Triplets 5.5% of dam wt. •175 ewe single 12-13 twin 11-11.5 triplet 9-10 Goal of Lambing Season Management “Maximize Lamb Livability” Starts before lambing What you do can not raise number born Causes of Death Starvation Poor ewe condition Weak ewe or lamb Plugged teats Mastitis Mis-mothering Poor suckling Prevention: Weak or Starved Adequate ewe nutrition (i.e. good condition) Energy level of diet Crossbreeding Exercise Weaning management Prevention: Weak or Starved Pre-lambing shearing Observation Condition score Dryer environment Lamb indoors Easier nursing Intake Trouble Shooting-Use the Thermometer Normal temp. - 101° - 102°F Elevated temp.-above 103°F (think infection) Cold Lambs - mild hypothermia 99°-102°F - severe hypothermia below 99°F Mild Hypothermia 99°-102°F 1) Remove and dry 2) Supplement warm dry heat (100°-103°F max. temp.) 3) Tube feed 120-200 ml colostrum (20 mls/lb.) 4) Return when rectal temperature is normal (1-3 hours) 5) Assure future nutrition Elevated Temperatureabove 103°F - or animals showing clinical signs - assume infectious process - probably pneumonia, joint ill or liver abscess - LA200 1/2cc/10 lb. under the skin given daily for 4-5 days - Long acting penicillin 1cc/10-20 lb. under the skin given daily for 4-5 days - Assure nutrition and hydration Severe Hypothermiabelow 99°F *Under 6 hours old remove and dry supplement heat warm dry moving air 100-103°F tube feed 120-200 ml colostrum return when temperature normal 1-3 hours assure future nutrition Severe Hypothermiabelow 99°F *Over 6 hours old remove and dry supplement heat with warm dry moving air 100103°F max tube feed 120-200 ml colostrum CAUTION inject 40 ml of 20% dextrose into body cavity 1 inch beside and 1 inch behind navel, 20 ga 1 inch needle return when rectal temp. normal 1-3 hours assure future nutrition Solution - Observation Paint brand Cubicles & lambing jugs Shear pre-lambing Stomach tube Proper feeding at lambing & weaning Selenium status Stillborns/dystocia Symptoms of dystocia yellow fleece causes - Fat ewes, Poor hybrid vigor Was it truly born dead? check lungs and feet Stillborns Two types -infectious -hypoxia (observation) Solutions Condition score Observation Intercom, Feed video camera antibiotics Vaccinate against vibrio, EAE BoSe ?????? Assist after 30 minutes in labor Abortion Diseases Iowa Camphylobacter (vibrio) Enzootic abortion in ewes (EAE) Toxoplasmosis Solutions Vaccinate vibrio/EAE Closed flock Late gestation feed antibiotics (5 mg/lb. if abortion occurs) Sanitation Isolation Pray Pneumonia Causes Poorly ventilated buildings Inadequate space Wet bedding Solution ft.2 area for ewes with lambs Sulfa water treatment Open up barn Use more bedding Pre-lambing shearing 20 Antibiotics 60-65 mg/day 6 weeks prior to lambing Results 65-73% in lamb losses Univ. of Wyoming S.D. State univ. Intestinal Disorders Causes Wet bedding Stress SolutionsLime jugs Adequate colostrum (esp. Ecoli) Vaccinate ewes CI. perfringens C & D toxoid Increase space and bedding Relieve stress Equipment & Supplies Colostrum Lamb Reviver i.e. stomach tube Thermometer Head Snare Ropes or dog choke collars Equipment...cont. Lubricant Cubicles Gloves Intercom Bonding Pens Equipment...cont. Grafting Stanchion Hot box / incubator Towels Biologicals Lambing Problems How Do You Know? 1 - Length of labor 2 - Position of feet Toes up okay Toes down backwards Tail first backwards One foot first Nose first Newborn Management 1 - Colostrum intake - minimum 2 ounces/8 pounds - ideal 10% of BW first 24 hrs. 2 - Clip - Dip - Strip castrate early 3 - Lambing Jugs 4 x 6, 5 x 6 4 - Observe often 5 - Check for inverted eyelids Weaning Wean early 60 days or less Dry up ewes prior to weaning Remove protein Remove energy Remove water ?