™ Examination of Protein Folding Using Sivvu
advertisement
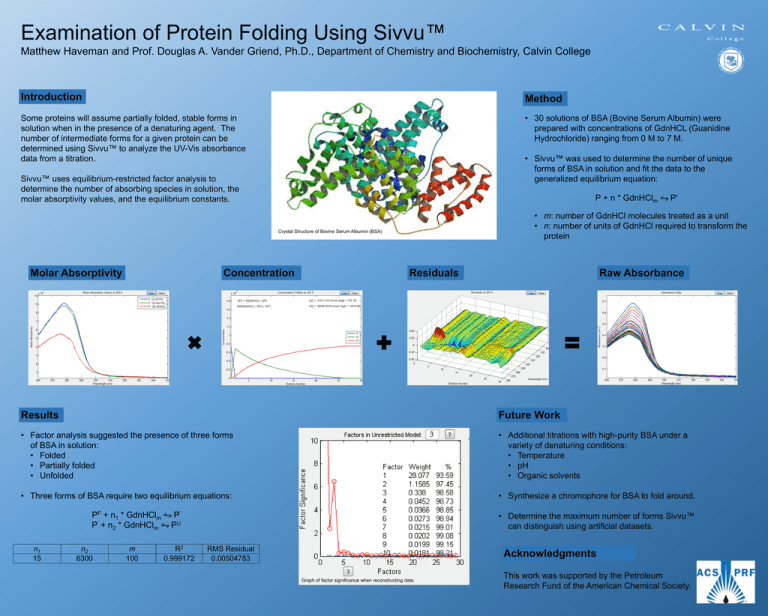
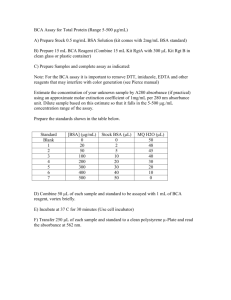
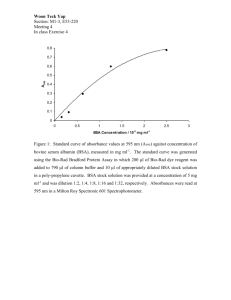
Examination of Protein Folding Using Sivvu™ Matthew Haveman and Prof. Douglas A. Vander Griend, Ph.D., Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Calvin College Introduction Method Some proteins will assume partially folded, stable forms in solution when in the presence of a denaturing agent. The number of intermediate forms for a given protein can be determined using Sivvu™ to analyze the UV-Vis absorbance data from a titration. • 30 solutions of BSA (Bovine Serum Albumin) were prepared with concentrations of GdnHCL (Guanidine Hydrochloride) ranging from 0 M to 7 M. • Sivvu™ was used to determine the number of unique forms of BSA in solution and fit the data to the generalized equilibrium equation: Sivvu™ uses equilibrium-restricted factor analysis to determine the number of absorbing species in solution, the molar absorptivity values, and the equilibrium constants. P + n * GdnHClm • m: number of GdnHCl molecules treated as a unit • n: number of units of GdnHCl required to transform the protein Crystal Structure of Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) Molar Absorptivity Concentration P’ Residuals Raw Absorbance Results Future Work • Factor analysis suggested the presence of three forms of BSA in solution: • Folded • Partially folded • Unfolded • Additional titrations with high-purity BSA under a variety of denaturing conditions: • Temperature • pH • Organic solvents • Three forms of BSA require two equilibrium equations: • Synthesize a chromophore for BSA to fold around. PF + n1 * GdnHClm P’ + n2 * GdnHClm n1 15 n2 6300 m 100 P’ PU R2 0.999172 • Determine the maximum number of forms Sivvu™ can distinguish using artificial datasets. RMS Residual 0.00504783 Acknowledgments Graph of factor significance when reconstructing data. This work was supported by the Petroleum Research Fund of the American Chemical Society.