Department of Modern Languages – Initial Preparation Annual Program Report Academic Year 2012‐13
advertisement
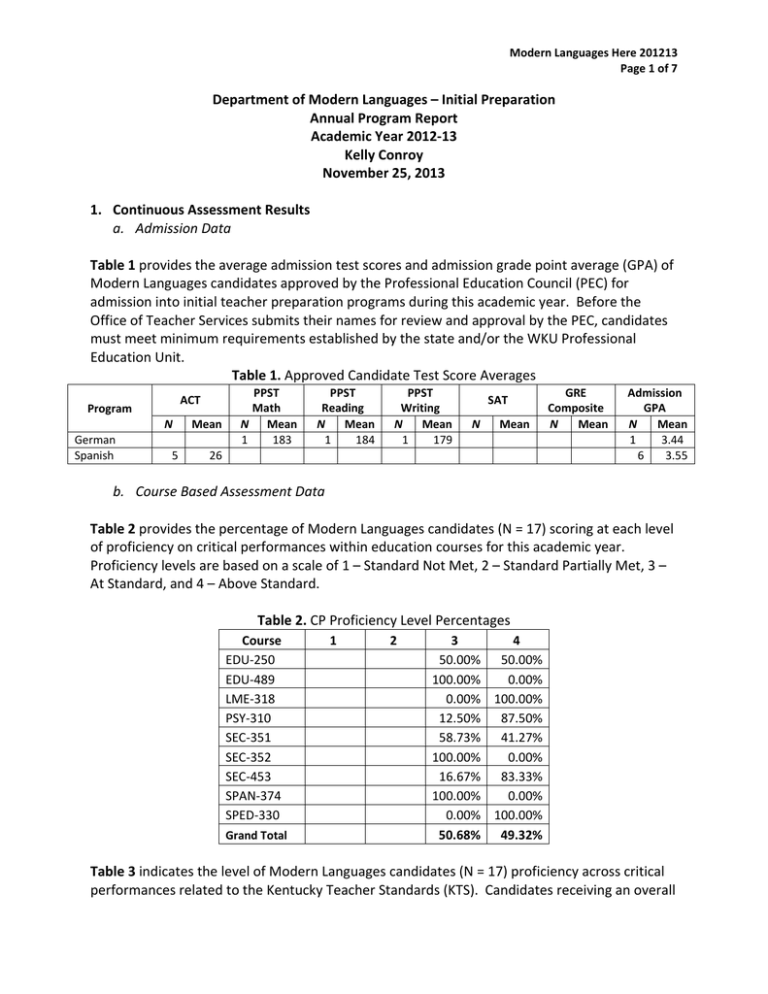
Modern Languages Here 201213 Page 1 of 7 Department of Modern Languages – Initial Preparation Annual Program Report Academic Year 2012‐13 Kelly Conroy November 25, 2013 1. Continuous Assessment Results a. Admission Data Table 1 provides the average admission test scores and admission grade point average (GPA) of Modern Languages candidates approved by the Professional Education Council (PEC) for admission into initial teacher preparation programs during this academic year. Before the Office of Teacher Services submits their names for review and approval by the PEC, candidates must meet minimum requirements established by the state and/or the WKU Professional Education Unit. Table 1. Approved Candidate Test Score Averages Program German Spanish ACT N Mean 5 26 PPST Math N Mean 1 183 PPST Reading N Mean 1 184 PPST Writing N Mean 1 179 SAT N Mean GRE Composite N Mean Admission GPA N Mean 1 3.44 6 3.55 b. Course Based Assessment Data Table 2 provides the percentage of Modern Languages candidates (N = 17) scoring at each level of proficiency on critical performances within education courses for this academic year. Proficiency levels are based on a scale of 1 – Standard Not Met, 2 – Standard Partially Met, 3 – At Standard, and 4 – Above Standard. Table 2. CP Proficiency Level Percentages Course EDU‐250 EDU‐489 LME‐318 PSY‐310 SEC‐351 SEC‐352 SEC‐453 SPAN‐374 SPED‐330 1 2 Grand Total 3 4 50.00% 50.00% 100.00% 0.00% 0.00% 100.00% 12.50% 87.50% 58.73% 41.27% 100.00% 0.00% 16.67% 83.33% 100.00% 0.00% 0.00% 100.00% 50.68% 49.32% Table 3 indicates the level of Modern Languages candidates (N = 17) proficiency across critical performances related to the Kentucky Teacher Standards (KTS). Candidates receiving an overall Modern Languages Here 201213 Page 2 of 7 rating of 3 or 4 on a CP are considered to have demonstrated proficiency on the standards associated with the CP. Compared to the unit‐wide results, Modern Languages candidates are typically performing above average. Table 3. Percent of Modern Languages Candidates Scoring Proficient on CPs by KTS Program Modern Languages Unit‐Wide 1 2 3 100% 100% 100% 97% 97% 97% Kentucky Teacher Standards 4 5 6 7 100% 98% 100% 97% 100% 97% 100% 97% 8 9 100% 100% 98% 97% 10 100% 99% *KTS Key: 1 – Content Knowledge, 2 – Designs/Plans Instruction, 3 – Maintains Learning Climate, 4 – Implements/ Manages Instruction, 5 – Assessment/Evaluation, 6 – Technology, 7 – Reflection, 8 – Collaboration, 9 – Professional Development, 10 – Leadership Table 4 indicates the number of Modern Languages candidates (N = 0) who have scored 2 or lower (below proficiency) on critical performances during this academic year. Modern Languages had zero students who scored below proficient. Table 4. Modern Languages Candidates Scoring Below Proficient on CPs Student ID Score 1 2 Student Count 0 Grand Total c. Clinical Experiences Data Modern Languages uses the following courses and experiences to evaluate candidate dispositions: EDU 250 and EDU 490. The program has identified the following courses and experiences where candidates report the diversity of their field experiences: EDU 250, EDU 490, and SEC 351. SEC 351 has been designated as the experience where candidates must work in settings at or above the average 11% diversity of the schools in the 30+ counties that represent our service area. Table 5 reports how Modern Languages Education candidates performed on dispositions as they entered and progressed through their program (N = 15) and during their student teaching experience (N = 2). Students are considered “proficient” who average a 3 or higher on each disposition category. Modern Languages Here 201213 Page 3 of 7 Table 5. Modern Languages Proficiency Rates on Unit‐Wide Dispositions Period a. Prior to Student Teaching b. During Student Teaching Values Learning WKU Professional Education Dispositions Values Personal Values Values Values Integrity Diversity Collaboration Professionalism 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% Over this academic year, Modern Languages Education candidates (N =13) reported demographic information on 20 field placements with an average of 18.8% ethnically diverse students, 47.4% students on free/reduced lunch, and 9.3% student with disabilities (based on National Center for Education Statistics and Kentucky Department of Education). Table 6 reveals the percentages of field experiences with various characteristics. Note that candidates could choose all the characteristics that applied for any given experience. Table 6. Percentages of Field Experience by Category Types Working with Student With Special Needs % Candidates working with Students with Physical Impairments % Candidates working with Students with Learning Disabilities % Candidates working with Students with Moderate/Severe Disabilities % Candidates working with Students with Emotional/Behavioral Disorders % Candidates working with Gifted Students % Candidates working with English Language Learners % Candidates working with Students with Visual Impairments % Candidates working with Students with Hearing Impairments % Candidates working with Students with Speech/Language Delays % Candidates working with Students with Development Delays % Candidates working with Students with Autism Spectrum Disorder % Candidates working with Students with Other Impairments Working with Diverse Students % Candidates working with African American Students % Candidates working with Native American/American Indian Students % Candidates working with Latino/Hispanic Students % Candidates working with Asian Students % Candidates working with Students with Special Needs (Aggregate) % Candidates working with Diverse Students (Aggregate) 0% 40% 25% 15% 60% 65% 10% 0% 5% 10% 5% 0% 100% 40% 90% 65% 95% 100% Overall, as can be seen in Table 6, in 100% of their field experiences Modern Languages Education candidates reported working with at least one student with special needs and in 100% of their field experiences candidates reported working with at least one student from a diverse ethnic group. Modern Languages Here 201213 Page 4 of 7 d. Culminating Assessment Data As Component 4 of the WKU Professional Education Unit Continuous Assessment Plan (CAP) strategy, all initial preparation candidates complete a culminating assessment of professional and pedagogical knowledge and skills, the Teacher Work Sample (TWS). This assessment is also used to demonstrate candidates’ ability to impact P‐12 student learning. In particular, candidate performances on Assessment Planning and Analysis of Student Learning have been identified as key indicators of candidates’ ability related to student learning. Although in spring 2008 the Professional Education Council agreed that candidates who score a holistic score of at least “2 – Developing” are able to exit the program, for program evaluation purposes our goal is that at least 80% of program candidates will achieve “3 – Proficient” or higher. No data were reported for Modern Languages candidates. Because the faculty also scores TWS at the indicator level, we are able to use these scores to ascertain candidate success in meeting each component of the TWS. For program evaluation purposes, candidates are considered successful who average at least 2.5 on a three point scale (1 – Not Met, 2 – Partially Met, and 3 – Met) on indicators aligned to a standard. Table 8 depicts the percentage of Modern Languages candidates who averaged at least 2.5 on the indicators for each TWS Factor: CF – Contextual Factors, LG – Learning Goals, DFI – Design for Instruction, ASL – Analysis of Student Learning, and ROT – Reflection on Teaching. No data were reported. Table 8. Initial Preparation TWS Proficiency Rates of Modern Languages Education Candidates Program Modern Languages Unit‐Wide CF LG DFI ASL ROT NDR 89% NDR 91% NDR 85% NDR 91% NDR 88% Because the TWS indicators have been aligned to Kentucky Teacher Standards, we can use these scores to ascertain candidate success in meeting each standard related to the TWS. Table 9 reports these scores as they relate to Kentucky Teacher Standards. No data reported Additionally, all candidates are assessed during their student teaching experience using the Student Teaching Evaluation form. Table 10 reports the percentages of Modern Languages student teachers (N = 2) successful on each standard. For program evaluation purposes, candidates are considered successful who average at least 2.5 on a three point scale (1 – Not Met, 2 – Partially Met, and 3 – Met) on indicators aligned to a standard. Modern Languages Here 201213 Page 5 of 7 Table 10. Modern Languages Proficiency Rates by Kentucky Teacher Standards Program Modern Languages Unit‐Wide 1 2 3 Kentucky Teacher Standards 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 97% 91% 87% 90% 86% 93% 89% 92% 96% 97% e. Exit and Follow Up Data Table 11 delineates the Educational Testing Services reports of the pass rates on the Praxis II content exams of candidates who completed the program in the 2011‐12 academic year (the most recent year with complete data). The last column allows for pass rate comparison of our candidates to our 2010‐11 results. No data reported Table 12. Average Scores on Teacher Standards Questions No data reported Respondents were also able to provide comments. Table 13 presents Modern Languages respondent comments. Table 13. Modern Languages Respondent Comments My only real complaint is the disconnected format of the program. As a Spanish major, my content classes Never interconnected with my education courses. This definitely needs to change in the future. Modern Languages Here 201213 Page 6 of 7 2. The following are guiding questions designed to focus discussion relative to the data and to help develop the narrative for the annual program report. Based on the reported data, MLE candidates are meeting or exceeding preparation requirements. In particular, MLE candidates have excelled at disposition proficiency rates and in working with special needs and/or diverse students in their field work. In table 13, a respondent indicates some dissatisfaction with the cohesion of the program. The respondent indicates language content courses did not relate to any education courses. This is of concern to the Modern Languages faculty. The department is working to address concerns like these are addressed, in part with the addition of a Foreign Language Pedagogy specialist who began in fall 2013. This position now assists with coordinating communication between the School of Education and Modern Languages, and will teach foreign language methods courses for MLE students. Faculty in the Department of Modern Languages reviewed the results of this report and as compared to reports from 2010‐11 and 2011‐12. Total numbers of students participating in the MLE program are relatively small. The data in most tables over the three‐year range do not show significant trends that require specific changes, with the exception of comments in Table 13, as addressed above. The annual program report should include: 3 (a) summary of findings related to the guiding questions above: MLE candidates continue to do well on their performance assessments and take advantage of opportunities to work in diverse/special needs field placements. The Department of Modern Languages continues to work to grow the numbers of MLE students and to address concerns about program articulation. 3 (b) summary of results related to students performance on the Kentucky Teacher Standards (KTS) and other key conceptual values a. Admission Data: Table 1 shows that mean admission test scores (ACT) and admission grade point averages (GPA) for the Modern Languages Education candidates tracked for the time period were well above minimum requirements established by the state and/or the WKU Professional Education Unit. b. Course Based Assessment Data: 100% of Modern Languages Education candidates scored a 3 or a 4 on a 4 point scale for all CPs. Modern Languages Here 201213 Page 7 of 7 c. The percent of MLE candidates scoring proficient on CPs by KTS is slightly higher on average than in last year’s report than unit‐wide percentages. Overall, the number of students in this cohort is down slightly compared to last year with numbers more closely reflecting those of 2010‐11 and 2009‐10. The department will continue to monitor the cohort numbers. d. Clinical Experiences Data: Unit‐wide disposition scores are high. The percentages of diversity and special needs experiences by MLE candidates are high. f. Exit and Follow Up Data: Candidates give feedback that indicates they feel a need for greater articulation across content and education courses. 3 (c) recommended changes and plan for disseminating the report This report is being shared among the ML faculty, and discussed at a faculty meeting. Data in the report can and will be used to inform (a) the types of in‐house professional development offered to faculty, (b), the advising of teacher candidates in the department, and (c) the types of outreach and professional development experiences offered as part of courses or extracurricular activities.


