GLOSSARY OF LITERARY TERMS FORESHADOWING FLASHBACK
advertisement

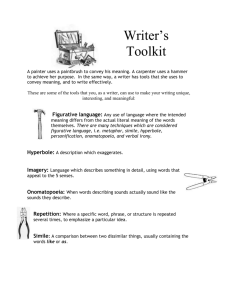
GLOSSARY OF LITERARY TERMS FORESHADOWING Hints or clues about what will happen in the plot FLASHBACK Information is presented about the past to fill in gaps, provide information about characters, etc. A flashback interrupts the normal sequence of events in the story to tell about something that happened in the past. INTERIOR MONOLOGUE the inner thoughts of a character. Often set off by italics in a story DRAMATIC IRONY The reader knows more about a situation or the outcome than a character . SITUATIONAL IRONY When the opposite of what you expect happens. Example: If a fire station burns down VERBAL RONY Using a word or phrase to mean the opposite of its normal meaning. Example: Calling a small house a mansion. SUSPENSE is a feeling of uncertainty and anxiety about the outcome of certain actions. Refers to a reader’s reaction. Created by irony, foreshadowing, short sentence, vivid verbs, leaving information out, etc. SYMBOL A person, place, thing or event that is used to represent something else. The object stands for or represents an idea or concept. Example: The crucifix represents the suffering and death of Jesus POETIC OR LITERARY DEVICES ALLITERATION is the recurrence of initial consonant sounds ex. What a special sunny day! ALLUSION is a reference to a famous person or event. Adds meaning to a story or helps the reader understand a character’s personality. Ex. He was greedy like Midas. HYPERBOLE an exaggeration, making something more than it is for effect Example: He exploded with anger. He had a thousand excuses for being late. IMAGERY When an author creates a picture with words Example: The bright red balloon drifted through the light blue sky METAPHOR An indirect comparison between two unlike things not using like or as Figurative Language used to suggest a common quality is shared by the two objects. Example: My dog Cookie is a rat; Heart of stone; I am the bread of life. ONOMATOPOEIA a word that sounds like its meaning; the pronunciation imitates the sound the word describes Example: “Buzz”, “Slam” “Pop”, “Crunch”, “Sizzle”, “Bang” OXYMORON a paradox reduced to two words; two contradicting terms coined together to create meaning ex. Old news; soft rock; act naturally; found missing; butt head PATHETIC FALLACY When the weather reflects the mood of a story or the situation of a character Example: Rain or cloudy weather during a funeral of a hero PERSONIFICATION When an inanimate object (non living thing) or something in nature is given human qualities or abilities Example: The wind whispered in her ear. The boat began to crack and moan. PUN a play on words that are usually synonyms or homophones or the word used is out of context ex. Kath and Mouse – play on a game – Kath toys with Helen like a cat would a mouse ex. The man who survived both pepper spray and mustard gas is now well seasoned ex. Did you hear about the guy whose whole left side was cut off? He's all right now. ex. When the smog lifts in Los Angeles, U C L A. ex. It was an emotional wedding. Even the cake was in tiers RHETORICAL QUESTION Any question asked for a purpose other than to obtain the information the question asks. The answer is already known or implied Example: “Are you serious?” SIMILE A direct comparison between two unlike things using like or as Figurative language implies there is relationship between the two objects. Example: My dog Cookie looks like a little rat when she is wet. UNDERSTATEMENT Opposite of hyperbole, making something less than it is Example: The bullet wound is just a scratch