Sound Devices ENG1DP - Efpatridis
advertisement

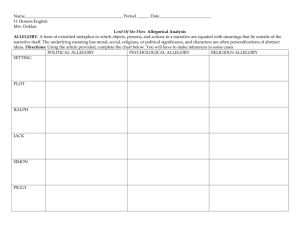
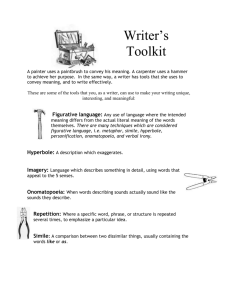
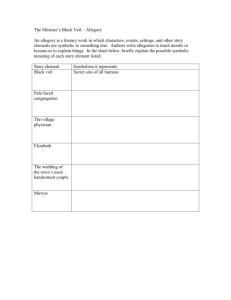
Sound Devices ENG1DP - Efpatridis Alliteration: the recurrence of initial consonant sounds (bubbling brook) Assonance: similar vowel sounds repeated in successive or proximate words ex. A city that is set on a hill cannot be hid. Consonance: similar consonant sounds repeated in successive words; especially evident at the end of words ex. I gave little thought to what he had brought. Onomatopoeia: the use of words whose pronunciation imitates the sound the word describes (buzz imitates the sound of an insect) This is a figure of speech uses words to imitate sounds: boom bang hiss, vroom, etc. Literary Terms and Figurative Language Allegory: often within a story, there is a secondary story running parallel or within the existing story. The characters and events are symbols or symbolic of human life or for a political or historical situation. Writers use allegory to add different layers of meanings to their works. Allegory makes their stories and characters multidimensional, so that they stand for something larger in meaning than what they literally stand for. Allegory allows writers to put forward their moral and political point of views. A careful study of an allegorical piece of writing can give us an insight into its writer’s mind as how he views the world and how he wishes the world to be. Allusion: a short, informal reference to a famous person (real or fictional), place, time period or historical event (He’s the team’s Hercules) Analogy: a comparison between two things, similar in several respects, for the purpose of explaining or clarifying something unfamiliar or difficult by showing its similarity to something familiar; while similar to a simile, an analogy is often more concrete and practical, rather than artistic, and is more developed. Ex. "If you want my final opinion on the mystery of life and all that, I can give it to you in a nutshell. The universe is like a safe to which there is a combination. But the combination is locked up in the safe." Epiphany: a sudden moment of realization Flashback: a break in the storyline to introduce what has taken place in the past to fill in gaps Foreshadowing: hints of what will occur in the future in the storyline Hyperbole: the counterpart of understatement, deliberately exaggerates conditions for emphasis and/or effect; not to be overused, the hyperbole can effectively grab attention is used sparingly (I’m starving; waiting forever) Imagery: descriptive language that evokes a sensory experience i.e. The coach was showered with freezing-cold Gatorade (sight, touch) that ran into his mouth and greeted him with sweetness (sight, touch, taste) Irony: the expression of meaning by using language that normally signifies the opposite i) dramatic – the reader has information that the characters do not ii) verbal – what is said has the opposite meaning or effect iii) situational – the opposite of what is expected happens Metaphor: a comparison between two unlike things, asserting that one thing is another; frequently invoking the to be verb (you are the light of my life; she is a beautiful flower) Mood (Atmosphere): is the emotional colouring given to a text. It is created through the author’s choice of setting, characters, diction, themes, description, imagery, and detail included in the story. It is the emotional impression left on the reader or feeling aroused in a reader by the events of the story and author’s style of writing. Oxymoron: a paradox reduced to two words for effect and/or emphasis (deafening silence; cruel kindness; inertly strong) This figure of speech uses contradictory terms. Paradox: a statement seemingly opposed to common sense that may have some truth in it (poor little rich girl) It is a contradictory assertion. Pathetic Fallacy: nature and weather are used to reflect the mood of the story or characters’ disposition ie. It was a dark and stormy night and the winds destroyed the shelter. Personification: giving human characteristics to inanimate objects (the water hose danced across the lawn; the tree stretched its arms into the sky) Pun: a play on words created for humorous effect; when a word has more than one possible meaning (A father says to a mother while at the beach with his son and daughter: At least the sun is bright could refer to the “sun” or the “son”; I used to be a ballerina but I found it too-too difficult.) Created by exploiting ambiguities and innuendoes. Simile: a comparison between two unlike things using like, as or than to emphasize a similarity (her eyes shone like diamonds) Suspense: is a feeling of uncertainty generated by the author through the use of short sentences, foreshadowing, vivid verbs, withholding information, repetition, dramatic irony, and/or understatement Symbol: an object or concrete idea that stands for or represents something else. Symbols can be natural, colours, religious, cultural, universal or global, or personal. (heart for love; four leaf clover for luck) Symbolism: the use of symbols in literature to suggest other ideas Understatement: deliberately expressing an idea as less important than it actually is, either for ironic emphasis or for politeness and tact; especially useful when dealing with a disagreement (with a speaker or an audience), because the statement may carry the same point with less offense (Tiger Woods has talent as a golfer.)