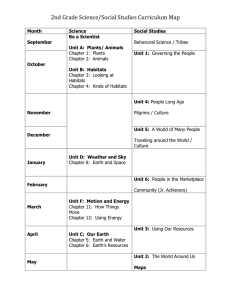
WESTLAKE EARLY CHILDHOOD PROGRAM 2015-2016 STANDARDS WORKED ON DAILY SOCIAL &
advertisement

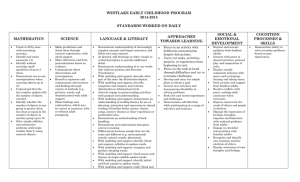
WESTLAKE EARLY CHILDHOOD PROGRAM 2015-2016 STANDARDS WORKED ON DAILY MATHEMATICS Count to 20 by ones with increasing accuracy. Identify and name numerals 1-9. Identify without counting small quantities of up to 3 items. Demonstrate one-to-one correspondence when counting objects up to 10. Understand that the last number spoken tells the number of objects counted. Identify whether the number of objects in one group is greater than, less than or equal to the number of objects in another group up to 10. Solve simple addition and subtraction problems with totals smaller than 8, using concrete objects. SCIENCE Make predictions and check them through concrete experiences, with adult support. Make inferences and form generalizations based on evidence. Communicate about observations and investigations. Record or represent and communicate observations and findings through variety of methods (e.g. pictures, words, and dramatization) with adult support. Share findings and explanations, which may be correct or incorrect, with or without adult prompting. Demonstrate understanding of increasingly complex concepts and longer sentences, and follow two-step requests. As desired, add drawings or other visuals to verbal description to provide additional detail. Demonstrate understanding of or use words that indicate position and direction (Vocabulary). With modeling and support, describe what part of the story the illustration depicts. With modeling and support, describe, categorize and compare and contrast information in informational text. Actively engage in group reading activities with purpose and understanding. With modeling and support, demonstrate an understanding of reading fluency by use of phrasing, intonation and expression in shared reading of familiar books, poems, chants, songs, nursery rhymes or other repetitious or predictable texts. Demonstrate an understanding of book handling. Demonstrate and understands that print conveys meaning. Differentiate between sounds that are the same and different (e.g. environmental sounds, animal sounds, phonemes). With modeling and support, identify, blend and segment syllables in spoken words. With modeling and support, recognize and produce rhyming words. With modeling and support, blend onsets and rhymes in single-syllable spoken words. With modeling and support, identify initial and final sounds in spoken words. With modeling and support, orally blend and SOCIAL & EMOTIONAL DEVELOPMENT APPROACHES TOWARDS LEARNING LANGUAGE & LITERACY Focus on an activity with deliberate concentration despite distractions. Carry out tasks, activities, projects, or experiences from beginning to end. Focus on the task at hand through difficulties and try to overcome challenges. Develop and carry out simple plans to obtain a goal. Invents new activities and demonstrates flexibility in solving problems. Seek new and varied experiences and challenges. Demonstrates self-direction while participating in a range of activities and routines. Request and accepts guidance from familiar adults. Interact with peers in shared activities, pretend play and cooperation of roles. Display socially competent behavior with peers such as helping, sharing and taking turns. Seek security and support from familiar adults. Resolve conflicts with peers, seeking adult assistance when necessary. Express concern for the needs of others and people in distress. Manage the expression of feelings, thoughts, impulses and behaviors with minimal guidance from adults. Engage in extended conversations with familiar adults. Recognize and identify own emotions and the emotions of others. Display awareness of own thoughts and feelings. COGNITION PROCESSES & SKILLS Demonstrate ability to solve everyday problems based on past experiences. segment familiar compound words. With modeling and support, demonstrate a beginning understanding of the connections between letters and sounds. With modeling and support, recognize and “read” familiar words or environmental print. With modeling and support, recognize and name some upper and lower case letters in addition to those in first name. With modeling and support, use a combination of drawing, dictating and emergent writing to express knowledge or share information about a topic of interest. With modeling and support from adults, begin to discuss and respond to questions from others about the writing/ drawing. With modeling and support, participate in shared research and writing projects using a variety of resources to gather information or to answer a question. With modeling and support, speak clearly and understandably to express ideas, feelings and needs. Demonstrate a beginning understanding of the structure and function of print. With modeling and support identify own name in print. Demonstrate a beginning understanding of the structure and function of print With modeling and support follows typical patterns for communicating with others (e.g., listen to others, takes turns talking and speaks about the topic or text being discussed). Physical Well Being & Motor Development Use non-locomotor skills with control, balance, and coordination, such as bending, stretching, and twisting during play. Participate in active play exhibiting strength and stamina. Demonstrate emerging responsibility for eating. Demonstrate coordination in using objects during active play (riding tricycle, catching ball). Coordinate the use of hands, fingers, and wrists to manipulate objects and perform tasks requiring precise movements. Demonstrate loco-motor skills with control, coordination, balance, and active play. Dress with minimal or no caregiver assistance. Complete personal care tasks with increasing responsibility. Demonstrate increasingly complex oral motor skills such as drinking threw a straw, blowing bubbles, or repeating a tongue twister. Social Studies Demonstrate cooperative behaviors and fairness to others during interactions with peers & adults. Demonstrate an awareness of the outcomes of choices Engage in problem solving to resolve social conflicts with adult support. Processes & Skills Demonstrates understanding that symbols carry meaning and use symbols to understand thinking THEME & STANDARDS CALENDAR KEY: SS – Social Studies LL – Language & Literacy S – Science M – Mathematics APT – Approaches Toward Learning SE: Social & Emotional Development P/M: Physical Well Being & Motor Development PS: Processes & Skills WEEK OF THEME August 31September 3 Back to School I am Special LTR/NUM TRANSDICIPLINARY THEMES Who We Are STANDARDS SE: Identify the diversity in human characteristics and how people are similar & different. SE: Compare own characteristics with those of others. P/M: Identify the consequences of unsafe behavior with adult guidance and support. P/M: Demonstrate emerging ability to follow transportation & pedestrian safety rules with adult models & support. P/M: Identify and follow basic safety rules with guidance and support. P/M: Demonstrate emerging ability to follow emergency routine with adult modeling and support. P/M: Demonstrate basic understanding that eating a variety of foods helps the body grow and be healthy. SE: Express a range of emotions in socially acceptable ways. SE: Recognize and identify own emotions and the emotions of others. SS: Demonstrate an awareness of the outcomes of choices. SS: Understand that rules play an important role in promoting safety and protecting fairness. SS: Demonstrate cooperative behaviors and fairness to others during interactions with peers & adults. LL: With modeling and support, identify own name in print. LL: Demonstrates an understanding of basic conventions of print in English, Spanish, & other western languages. LL: With modeling and support describe familiar people, places, things, & experiences. LL: With modeling and support follows typical patterns for communicating with others (e.g., listen to others, takes turns talking and speaks about the topic or text being discussed). ATL: Use prior knowledge and information to assess, inform, and plan for future actions and learning. ATL: Demonstrates self-direction while participating in a range of activities and routines. S: Use observable information (touch, see, hear, smell, taste) to categorize objects and materials, based on different criteria. ACTVITIES RESOURCES Invite parents, family members, and/or members of the community to read stories from their own culture in class. What people, places, audio-visual materials, related literature, music, art, computer software, etc, will be available? Child-led play; taking on different characters in role plays. Ongoing opportunities for promoting language development through storytelling and re-telling; telling a sequence of events from their own life. Puzzles, poems, songs, finger plays, photographs, role play costumes and food items, story props, Asking questions during story time: for example, why do you think she said/did that? How does she feel? What is going to happen next? Is the story the same or different? Children can write and/or narrate a story or event to their teacher to include in their journal. How will the classroom environment, local environment, and/or the community be used to facilitate the inquiry? Change of classroom centers, library books, file folder games/games, music, art/craft activities, large group activities, photographs, drawings. September 810 3 days Back to School I am Special September 1417 5 Senses L Who We Are September 2124 5 Senses F Who We Are September 28October 1 Feelings Emotions E Who We Are H Who We Are T How the World Works October 5-8 October 12-14 3 days Clifford Goes to Dog School Nutrition Healthy Body Chicka Chicka Down on the Farm Rumble in the Jungle Who We Are S: Recognize examples of organisms that are similar to each other and of the same kind. S: Recognize some elements of the natural environment and understand that these change over time. S: Demonstrate an understanding that living things change over time. S: Identify the habitats of people and familiar animals and plants in their environment, and begin to realize that living things have their habitats in different environments. S: Develop understanding for the relationship between humans and nature, recognizing the difference between helpful and harmful actions towards the natural environment. SS: Explore the concept of responsible consumption and conservation of resources. SS: Recognize that people have wants and must make choices because resources and materials are limiting. M: Describe and compare objects using measurable attributes; length, size, capacity, and weight. M: Order objects by measurable attributes. M: Collect data by categories to answer simple questions. M: Measure length and volume (capacity) using nonstandard or standard measurement tools. ATL: Pose questions to seek explanations about phenomena of interest. LL: Sort common objects into categories to gain a sense of the concepts the categories represent (vocabulary). October19-22 Down on the Farm I How the World Works U How the World Works C How the World Works O How We Express Ourselves The Letters Are Lost October 26-29 November 2-5 3 days Fall Halloween The Night Before Preschool Fall Clifford Goes to Dog School November 912 Authors Chicka Chicka SE: Engage in extended conversations with familiar adults. M: Demonstrate an understanding of the relative positions of objects with terms such as in, on, under, up, down, inside, outside, above, below, beside, between, in front of, behind, & next to. LL: Identify real life connections between words and there use (vocabulary). LL: Identify characters and major events in a story. LL: Demonstrate understanding of frequently occurring verbs and adjectives by relating them to their opposites (Vocabulary) LL: Retell or reenact familiar stories. LL: With modeling and support begin to demonstrate letter formation in “writing”. LL: With modeling and support name the author & illustrator of a story and what each person does for a book. LL: Use language to communicate in a variety of ways with other to share observations, ideas, and experiences: problem solves, reason, predict, and seek new information. LL: With modeling and support discuss some similarities and differences between two texts on the same topic. LL: Ask and answer questions, and comment about characters and major event in familiar stories. LL: With Modeling and support determine the meanings of unknown/ concepts using the context of conversations, pictures that accompany text, or concrete objects. LL: With modeling and support use a combination of drawing dictating and emergent writing to express an idea or opinion about an experience or book. LL: With modeling and support prints letters of own name and other meaningful words with mock letters and some actual letters. LL: With modeling and support begin to use the conventions of standard English. LL: With Modeling and support begin to demonstrate and understanding of the differences between fantasy and reality. ATL: Express interest in and show appreciation for the creative work of others. PS: Demonstrates understanding that symbols carry meaning and use symbols to understand thinking. PS: Participates cooperatively in complex pretend play, involving assigned roles and overall plan. November 1619 Authors Q How We Express Ourselves Rumble in the Jungle November 23 & 24 2 days November 30December 3 Authors How We Express Ourselves The Letters are Lost Authors G How We Express Ourselves The Night Before Preschool December 710 Nursery Rhymes S How We Express Ourselves J How We Express Ourselves D How We Express Ourselves P How the World Works If You Give A Moose A Muffin December 1417 Nursery Rhymes The Mitten January 4-7 Music Appreciation The Way I Feel January 11-14 Winter Hibernation Giggle Giggle Quack S: Recognize examples of organisms that are similar to each other and of the same kind. S: Recognize some elements of the natural environment and understand that these change over time. S: Demonstrate an understanding that living things change over time. S: Identify the habitats of people and familiar animals and plants in their environment, and begin to realize that living things have their habitats in different environments. S: Develop understanding for the relationship between humans and nature, recognizing the difference between helpful and harmful actions towards the natural environment. SS: Explore the concept of responsible consumption and conservation of resources. SS: Recognize that people have wants and must make choices because resources and materials are limiting. M: Describe and compare objects using measurable attributes; length, size, capacity, and weight. M: Order objects by measurable attributes. M: Collect data by categories to answer simple questions. M: Measure length and volume (capacity) using nonstandard or standard measurement tools. ATL: Pose questions to seek explanations about phenomena of interest. LL: Sort common objects into categories to gain a sense of the concepts the categories represent (vocabulary). January 20 & 21 2 days Winter Hibernation B How the World Works R How the World Works K Where We Are in Place and Time Where’s My Teddy January 2528th Day & Night If You Give a Moose a Muffin February 1-4 Friendship The Mitten S: Compare and contrast objects and events, and begin to describe similarities and differences. S: Begin to identify and use some observation and measuring tools, with adult support. P/M: Use classroom and household tools independently with hand/eye coordination to carry out activities. P/M: Demonstrate spatial awareness in physical activity or movement. PS: Communicate about past events in their life and anticipate familiar routines and experiences. PS: Recreate complex ideas, events/situations with personal adaptations. SS: Engage in problem solving to resolve social conflicts with adult support. SS: Demonstrate an understanding of time in the context of daily experiences. M: Recognize, duplicate, and extend simple patterns using attributes such as color, shape, or size. M: Compare two-dimensional shapes, in different sizes, and orientations, using informal language. M: Sort and classify objects by one or more attributes. LL: With modeling and support, describe, categorize and compare and contrast information in informational text. LL: with modeling and support use a combination of drawing, dictating, and emergent writing to communicate about a personal experience or story and tell about the event in a meaningful sequence. ATL: Develop and carry out simple plans to obtain a goal. ATL: Invents new activities and demonstrates flexibility in solving problems. ATL: Seek new and varied experiences and challenges. ATL: Express individuality life experiences, and what they know and what they are able to do through a variety of media. February 8-11 Friendship A Where We Are in Place and Time M Where We Are in Place and Time N Where We Are in Place and Time V Where We Are in Place and Time Giggle Giggle Quack February 1618 3 days Where We Live The Way I Feel February 2225 Where We Live Where’s My Teddy February 29March 3 Dr. Seuss A Color of His Own March 7-10 Dr. Seuss W Where We Are in Place and Time X How the World Works Y How the World Works Z How the World Works Bunny Cakes March 14-17 Community Workers In the Small, Small Pond March 21-24 Spring break March 25April 1 Community Workers Five Little Monkeys Sitting in a Tree April 4-7 Spring Pond How Do Dinosaurs Go to School? S: Recognize examples of organisms that are similar to each other and of the same kind. S: Recognize some elements of the natural environment and understand that these change over time. S: Demonstrate an understanding that living things change over time. S: Identify the habitats of people and familiar animals and plants in their environment, and begin to realize that living things have their habitats in different environments. S: Develop understanding for the relationship between humans and nature, recognizing the difference between helpful and harmful actions towards the natural environment. SS: Explore the concept of responsible consumption and conservation of resources. SS: Recognize that people have wants and must make choices because resources and materials are limiting. M: Describe and compare objects using measurable attributes; length, size, capacity, and weight. M: Order objects by measurable attributes. M: Collect data by categories to answer simple questions. M: Measure length and volume (capacity) using nonstandard or standard measurement tools. ATL: Pose questions to seek explanations about phenomena of interest. LL: Sort common objects into categories to gain a sense of the concepts the categories represent (vocabulary). April 11-14 Spring Pond 1&2 How the World Works 3&4 How the World Works 5&6 How the World Works 7&8 How the World Works 9 & 10 How the World Works A Color of His Own April 19-21 3 days Zoo Bunny Cakes Earth Day Friday, April 22 April 25-28th Zoo In the Small, Small Pond May 2-5 Ocean Five Little Monkeys Sitting in a Tree May 9-12 Ocean How Do Dinosaurs go to School? May 16-19 Camping How the World Works May 23-26th Camping How the World Works May 31-June 2 2 days & then Ice cream social