Muscle
advertisement
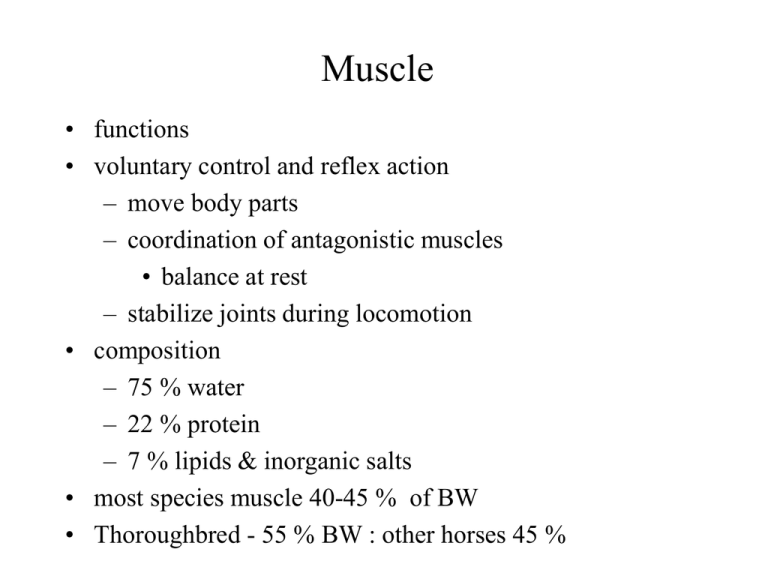
Muscle • functions • voluntary control and reflex action – move body parts – coordination of antagonistic muscles • balance at rest – stabilize joints during locomotion • composition – 75 % water – 22 % protein – 7 % lipids & inorganic salts • most species muscle 40-45 % of BW • Thoroughbred - 55 % BW : other horses 45 % Structure of Muscle • epimysium - outer connective tissue covering, surrounds the entire muscle • fasciculi - bundles of fibers • perimysium - sheath of connective tissue surrounding fasciculi • muscle fiber - inside fasciculi • endomysium - connective tissue surrounding muscle fiber Muscle Fiber • sarcolemma - plasma membrane surrounding muscle fiber – fuses with tendon, which inserts into bone • sarcoplasm - gelatin-like substance between myofibrils, (muscle fibers cytoplasm) – contains dissolved proteins, minerals, fats, and organelles – contains large quantity of stored glycogen – contains myoglobin – transverse tubules • T tubules- extensions of sarcolemma, laterally through muscle fiber – transmit nerve impulse from sarcolemma to each myofibril – pathway for glucose, oxygen and ions from extracellular fluids • sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) -longitudinal network found within muscle fiber – storage site for calcium, for muscle contraction • myofibril - contractile element of skeletal muscle – 100’s - 1000’s in one fiber – sarcomere - subunit of myofibril (striations) – functional unit of myofibril – actin filaments – myosin filaments • actin and myosin - 3000 actin : 1500 myosin / myofibril • myosin – thick filament – double stranded with myosin heads • actin – thin filament contains active site for attachment of myosin head – actin • backbone of filament – tropomyosin • tube shaped protein, twists around actin – troponin • attached to actin and tropomyosin Fiber Action • nerve impulse to nerve endings – release ACh – binds to receptors on sarcolemma – charge transmitted length of muscle fiber • depolarizes membrane (action potential) – impulse travels through T tubules and SR • release stored calcium • calcium binds to troponin • troponin lifts tropomyosin off actin – freeing binding sites – – – – myosin heads attach to actin (ATPase splits ATP) conformational change drag actin and myosin in opposite directions heads release , reattach to a new active site further on actin • end of muscle action – calcium is actively pumped out of sarcoplasm back to SR – requires energy • internal membrane and energy pathways regulate Ca & ATP for contraction – cramping • weak Ca pump • energy exhausted to run Ca pump Fiber Type • contractile and metabolic properties – contractile - speed of contraction – metabolic - ability to use different pathways • contraction – all or nothing – amount of contraction = number of fibers stimulated • twitch - cycle of contraction and relaxation – varies with type of fiber • ST - slow twitch - SO -type I • FT - fast twitch - FOG & FG - type IIA & type IIB • no conversion of type • can utilize either pathway, better adapted to one or another • overall muscle types – ST • appear flatter • Arabian – FT • appear bulky • QH • force = proportional to cross section area – FT more forceful – sacrifice efficiency for force – contractile ability • small animals: 3-5 fold difference • horse: 10 fold difference • muscle biopsy and NMRI • fiber type variation within horse – front legs - less FT than hind legs – deep middle gluteal - less FT & higher ST • structural – superficially - less ST & more FT • speed and force • generally higher % of FT (FOG & FT) – 70-90 % • variation of breeds – QH • higher % FT and glycolytic enzyme activity – Heavy hunter • higher % ST and oxidative enzyme activity – Thoroughbred • relatively high oxidative enzyme activity






