UNIT 3: PROPERTY LAW
advertisement

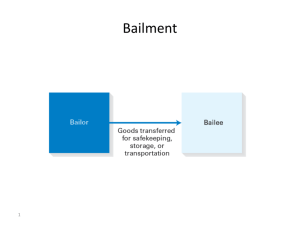
UNIT 3: PROPERTY LAW Property Law Eminent Domain The power to take private property for public use by a state, municipality, or private person or corporation authorized to exercise functions of public character, following the payment of just compensation to the owner of that property. Ex:Widening a road, construction of golf course, condo/shopping complex, etc. Eminent Domain New London condemned 15 non-blighted homes in a middle-class neighborhood as part of an economic development plan that included a state-of-the-art 90,000-square-foot research and office facility that would be occupied by pharmaceutical giant Pfizer, Inc. the economic development plan & condemnations were necessary to spur economic development and stimulate a sagging economy. U.S. Supreme Court in Kelo v. City of New London gave the city its seal of approval and held that the Fifth Amendment of the United States Constitution permits municipalities to condemn non-blighted private property for the valid public purpose of economic development. Other cases: Norwood, OH – p. 267 Property Defined as anything subject to ownership. 2 types: Real Property: land, buildings, anything permanently affixed Sometimes called realty Personal Property: everything else; can be tangible or intangible What’s Your Verdict, page 268 Intellectual property: Defined as intangible property created by intellect & includes: 1. Copyrights: protects work of authors, artists & composers. Owned by creator for lifetime + 70 years Ex: songs, books, computer programs, architectural plans Copyright Infringement is unauthorized copying, sale, display or performance of a protected work Fair use: limited use, ex: quoting a paragraph from another book, one line in a song Intellectual property: 2. Trademarks -unique word, mark, symbol or device that identifies a product of a business -EX: 3. Service marks -unique word, mark or symbol that identifies a service EX: NBC’s three tone chime -both protected indefinitely as long as there is continuous use and the mark is in the public eye 4. Intellectual Property 4. Patents: exclusive right to make, use, import, sell and offer a product or process. -Ex: business methods, chemical patents, software patents - Valid for 20 years 5. Trade Secrets: valuable information to the owner that they attempt to keep secret. -Ex: Coke’s secret formula, Sales customer list How Property is Acquired & Held Constructive Delivery: symbol of the gift given as substitute Example: keys to a car Accession: right of an owner to property based on an increase Example: crops & animals born for a farmer. Lost property: owner doesn’t know when/where possession was lost Mislaid property: placed intentionally then forgotten Occupancy: acquiring abandoned or discarded property Page 275 caption & Question of Ethics 2 basic ways to hold property in Severalty: sole ownership Co-ownership Joint tenancy: equal ownership & right of survivorship Tenancy in common: shares unequal & no right of survivorship Tenancy by entireties: married couples have joint ownership Community property: all property acquired by husband & wife is community property with each spouse having 50% ownership Chapter 15 Assessment Page 280: #1-14 Page 282: #32-39 Chapter 16 - Bailments physical possession of personal property is transferred from one person (the 'bailor') to another person (the 'bailee') who later returns the property or delivers it to a third party. Bailment is distinguished from a contract of sale or a gift of property, as it only involves the transfer of possession and not its ownership. Examples: giving car to valet, storing goods in a warehouse Actual bailments: bailee receive & accepts goods themselves Constructive bailments: bailee receives symbol of the personal property (keys to car) Bailment duties Gratuitous Bailment only one party benefits, generally the bailee must provide extraordinary care, strictly liable for damages ex: stay in someone’s FL vacation home for free Mutual Benefit Bailment: both parties benefit bailee must provide ordinary care, liable if negligent Involuntary Bailment: without consent of bailee benefits only bailor Provide minimal care Ex: caring for a lost dog, items delivered to the wrong house Must the bailment contract be in writing? What’s Your Verdict – p. 289 Chapter 16 Assessment Page 294: #1-12 Page 296: #20-31 Chapter 17 –Ownership & Transfer of Real Property Right to air space above land: ownership power extends to the upper atmosphere Ex: skyscrapers, tall trees. Mineral rights: ownership extends from the land’s surface to the center of the earth. Doctrine of capture: person who extracts is granted ownership Limitations on ownership Easements: the right to use the real property of another without possessing it Restrictive covenants: promise made between buyer & seller about use of the land Zoning ordinances: city or county regulation on the location of residences, business & industrial areas Spot zoning (treatment of a single property differently than other similar properties) generally prohibited unless there is a variance granted by a city or county Transfer of Ownership Grantor (party who transfers ownership powers) & grantee (party who receives ownership powers). Deed: legal document used to transfer ownership of real property. Conveyance: When ownership is granted by a deed Adverse possession: person publicly possesses the land of another private person for years Leasing Real Property Lease: one party receives temporary possession of another’s real property Rent payment is given as consideration Landlord is lessor, tennat is lessee Eviction: landlord removes tenant from the real property Subletting: tenant leases all or part of the property to a third party Page 314: #1-11 & Page 317: #32-37 Chapter 18 – Insurance Contractual agreement that protects against financial loss Life, health, auto, home, business Policy: written contract of insurance. Face value: maximum amount that could be paid for injury Premium: consideration paid by the insured (party covered/protected) to the insurer (State Farm, Geico, All State, etc.) Indemnify: insurer makes good on and covers the loss to the suffering party (insured) Types of Insurance Life: Term-written for a certain number of years Whole-for as long as the insured lives or 100 years; aka ordinary or straight life Fire: protects damage caused by fire and smoke Casualty: 1. Automobile: -Collision moving car(s) collides -Comprehensive (vandalism, theft, weather) -No-fault insurance: all parties in automobile accident are indemnified by their own insurance company, regardless of fault 2. Burglary, robbery, theft & larceny: protects personal property 3. Liability: if parties suffer injury or loss from negligence 4. Disability: hospital bills, loss of income. “if you get hurt and miss work it won’t hurt to miss work.” Property & Casualty Insurance Property Insurance: Fire, theft, act of God Casualty Insurance: losses from accident, chance or negligence Insurable interest: your potential to sustain a loss Endorsements: attachments to policies for additional needs; aka riders Example – page 325 Coinsurance: fire insurance policy clause, requires policyholder to maintain coverage equal to a percentage of the value of the property. Page 336 #1-12 Page 338 #26-31 Chapter 19Property Distribution upon Death Decedent: person who dies Estate: property of the deceased (personal & real) Testator: maker of a will Executor: appointed to carry out the will’s directions Testate: dying with a will Intestate: person who dies without a will Administrator appointed by the court to take charge of intestate’s property Very costly on beneficiary & adds large estate tax costs Living will: directives to physicians for life support issues Requirements of a will Testamentary intent: no duress or undue influence in signing the will 2. Testamentary capacity: maker must know property involved & who stands to benefit upon their death. 3. Writing: will must be in writing, signed and witnessed by two adults. Codicil: formal, written, witnessed amendment -usually the result of marriage, birth or divorce Holographic will: written & signed by decedent, no witness. Recognized by some states Nuncupative (nun-coo-pa-tive) will: an oral will, must be witnessed 1. Distribution of a will After proof of death is established the executor of the estate has four responsibilities: 1. Organizing & appraising assets, collecting debts owed to the estate 2. Public notice of the estate & filing claims against it 3. Paying valid claims against the estate 4. Distributing remaining money according to the will -Statutory period for filing claims is generally 6 months -Law Brief, page 345. If a person dies without a will… Trusts The transfer of some or all property to another party with direction from a third party Settler: Creator of the trust. Aka trustor or donor Trustee: legal entity that has title & direction to the property Beneficiary: party for whom the trust has been created Child, grandchild Trusts (cont’d) Inter vivos trust: Created during the settlor’s lifetime Latin for between the living Testamentary: Created after the settlor’s death