Bailments, Personal Property, Real Propety
advertisement

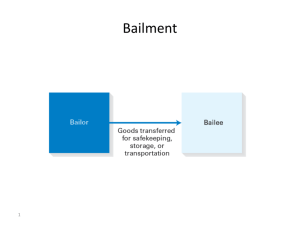
REAL AND PERSONAL PROPERTY OBJECTIVE 09.02 COMPARE THE LEGAL RIGHTS OF ACQUISITION, TRANSFERAL AND RENTING/LEASING OF REAL OR PERSONAL PROPERTY. BAILMENTS Bailment An agreement created by the temporary delivery of personal property by the owner to someone agreeing that the property will be returned to the owner. Bailee - temporary possession property Bailor – owner of property Ex: autos parked in a garage Mutual Benefit Bailments Both parties receive benefit Duty of ordinary care on the bailee Results from a contract - consideration exchanged Most bailments are mutual benefit Bailment by Necessity Implied by law, a customer must give up possession of property. Ex: When you leave your clothes temporarily in the dressing room while you try on a new outfit Other Bailments Gratuitous Bailment Free of charge Only one party benefits Extraordinary bailment A common carrier or hotel is strictly liable for damage to bailed goods Rights and Duties of Bailee Rights: Mechanic’s Lien -the right to retain property of another, if not paid for service rendered To expect payment for services rendered Duties: Of reasonable care and protection of goods while in custody of bailee To comply with terms of bailment Rights and Duties of Bailor Rights to have goods protected to receive service as agreed upon to have goods returned in timely manner Duties to pay for service provided to warn of dangers or special care required to pick up goods in a reasonable time Tortious Bailee What is a tortious bailee? A party who wrongfully retains lost property or stolen property A party who wrongfully uses a bailed article for a purpose other than that agreed upon by the parties Ex: Parking valet who takes your nice car on a joy ride REAL AND PERSONAL PROPERTY OBJECTIVE 09.02 COMPARE THE LEGAL RIGHTS OF ACQUISITION, TRANSFERAL AND RENTING/LEASING OF REAL OR PERSONAL PROPERTY. PROPERTY OWNERSHIP Real Property Land and anything permanently attached, including: Buildings, structures, fixtures Water, water rights Minerals on and below the surface of the earth. Trees & crops Air space above the surface Grantor - conveys a deed to real property Grantee – receives the deed Personal Property Anything other than real property, including: Clothing, jewelry, furniture, appliances in a home Automobiles, ATVs, lawnmowers Equipment & machinery used in business Copyrights, patents, trademarks Software, stocks, loans, mutual funds Must be delivered in order to transfer ownership. Tangible or Intangible. Intellectual Property Includes copyrights, patents, trademarks and trade secrets Is an original work fixed in a tangible medium of expression. Examples: literature, computer software, musical scores and lyrics, choreography, dramatic works, unique product or process, symbols or word that identify a product, commercially valuable information that is kept secret Methods to Acquire Property Purchase contract – earn money and use it to buy Gift – includes intent, delivery and acceptance Intellectual labor – creation of property Inheritance – wills and trusts Accession – farm animals naturally increase Found property – lost or mislaid Occupancy – possession of property that belongs to no one else Types of Deed Quitclaim Transfers a seller’s interest in a property but doesn’t warrant that the seller owns any interest General Warranty Deed Warrants the title Most desirable for the buyer Bargain and Sale Deed Transfers title to property without giving warranties Property Rights Physical rights apply to: Surface (the right to occupy the land, and develop it with buildings, etc.) Subterranean Minerals or Water (rights to remove or conserve) Air (right extends into upper atmosphere-but cannot exclude aircraft from flying over property) Eminent Domain Right to make private property into public if it is for the public good. Ex: Highways are widened Owners are paid the fair market value Limits on Use of Property Restrictive Covenants Deed restrictions Ex: homeowners association Easements for limited use Ex: Gas lines end at my driveway Why buy a home? (Supplemental) Rent Home Equity Equity Home = Zero Ownership = Equity = Value of Home - Principle of Loan, or = Market Value - Debt in Property = Personal Asset Accumulation Why rent an apartment? (Supplemental) No large down payment required No long term commitment to location No upkeep to grounds and property Bad credit, cannot get a loan Not ready to own More freedom to move NEGATIVE: NO ASSET ACCUMULATION