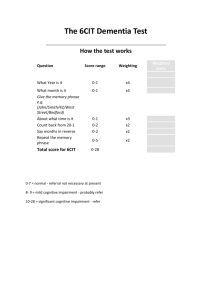
1. Chapter 8 Mental Retardation (Cognitive or Intellectual Disabilities)
advertisement

1. Chapter 8 Mental Retardation (Cognitive or Intellectual Disabilities) 2. Mental Retardation Issues Normalization “dignity of risk” Sub areas of retardation Mild retardation vs. Moderate/Severe How their educational needs can best be met General Education Curriculum 3. Mentally Impaired Federal Definition Mental retardation means significantly subaverage general intellectual functioning, existing concurrently with deficits in adaptive behavior and manifested during the developmental period that adversely affects a child's education performance. 4. MI-Cognitive Impairment MI Rule Revision-2002 R340.1705 Cognitive Impairment; Determination Rule 5 1. Cognitive impairment shall be manifested during the developmental period and be determined through the demonstration of all of the following characteristics 5. Cognitive Impairment (Cont) a. Development at a rate at or below approximately 2 standard deviations below the mean as determined thru intellectual assessment b. Scores approximately within the lowest 6 percentiles on a standardized test in reading and arithmetic. This requirement will not apply if the student is not of an age, grade, or mental age appropriate for formal or standardized achievement tests. 6. Cognitive Impairment (Cont) c. Lack of development primarily in the cognitive domain d. Impairment of adaptive behavior e. Adversely affects a students educational performance 2. A determination of impairment shall be based upon comprehensive evaluation by a multidisciplinary team, which shall include a psychologist 7. AAMR AAMR (2002) Mental Retardation is a disability characterized by significant limitations both in intellectual functioning and in adaptive behavior as expressed in conceptual, social, and practical adaptive skills (systems of support). This disability originates before age 18. 8. Measurement Adaptive Behavior “What everyone uses to function is daily life” (Figure 8.2 p. 282) Conceptual, Social, and Practical Adaptive Behavior Testing observation Scale 9. Systems of Support Figure 8.3 p. 283 Person’s Capabilities and Adaptive Skills Risk/Protective Factors Participation in Life Environments Intensity of need for support Source of support evaluation of support 10. Future Mild (old MI regulations (EMI) possible independent or semi-dependent living Hold a job with guidance Maintain good social relationships Contribute to society Moderate (old MI regulations TMI) Marked developmental delays Some degree of independence in self-care semi-dependent or dependent living hold a job with lots of supervision total dependence survival skills 11. Supports Natural supports Nonpaid supports Generic supports Specialized supports 12. Causes and Prevention Mental Retardation is caused by many factors, some known and some unknown Most common Down syndrome Fragile x Fetal alcohol syndrome 13. Groups Socioeconomic and environmental factors Injuries Infections and toxins Biological 14. AAMR, 2002 Prenatal Perinatal Postnatal 15. Prevention For pregnant women For children For society (Table 8.2 p.290) 16. History Late 1700s Marc-Gaspard Itard Mid 19th Century Residential Centers First in the U.S. 1848 Perkins Inst. For the Blind By 1917 all but 4 states on institutions Late 1960’s Deinstitutionalization 17. Educational Goals Functional Curriculum (focus on life skills) Self care - daily living skills Independent living Communication / Social Vocational Domestic / Community Leisure Community Based Instruction Self-Determination 18. Educational Goals Applied behavior analysis Task analysis Repeated opportunities Transfer of knowledge to real world - generalization Cue cards or guided notes Feedback Simulations Sequencing Short term vs long term 19. Transition Quality of Life Supported Employment Independent Living Collaboration 20. Educational Goals Placements LRE Integrated into regular schools and classrooms Resource rooms Self contained classroom Institutions 21. Educational Goals Inclusion benefits drawback Middle / High school 18 years old Friends 22. Trends Laws have given these individuals lots of benefits Make life as normal as possible student family sibling Transition and training programs Change public attitudes Medical advancements Genetic Counseling Technology 23. Future Needs Families / Siblings Dealing with the CI issue Dealing with the dependence issue Life long care Special needs Guilt 24. Families Dads Moms Grandparents Siblings