Limiting Factors and Carrying Capacity •What is carrying capacity? DO NOW WEDNESDAY
advertisement

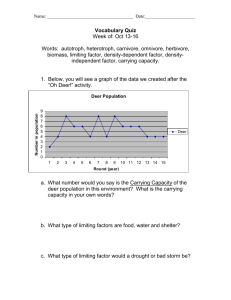
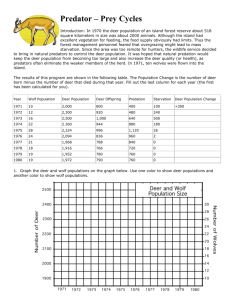
Limiting Factors and Carrying Capacity DO NOW WEDNESDAY •Explain what limiting factors are. Give some examples. •What is carrying capacity? Objective: How a Predator-Prey Population Changes Over Time Key Words: Natural Resources, Limiting Factors, Carrying Capacity Scenario •In 1970 the deer population of an island forest reserve about 518 square kilometers in size was about 2000 animals. Although the island had excellent vegetation for feeding, the food supply obviously had limits. Thus the forest management personnel feared that overgrazing might lead to mass starvation. Since the area was too remote for hunters, the wildlife service decided to bring in natural predators to control the deer population. It was hoped that natural predation would keep the deer population from becoming too large and also increase the deer quality (or health), as predators often eliminate the weaker members of the herd. •In 1971, ten wolves were flown into the island. Objective: How a Predator-Prey Population Changes Over Time Key Words: Natural Resources, Limiting Factors, Carrying Capacity Results of the program • The results of this program are shown in the following table. Data Table Trials (years) 1971 1972 1973 1974 1975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980 Number of Deer 2,000 2,300 2,500 2,360 2,224 2,094 1,968 1,916 1,952 1,972 10 12 16 22 28 24 21 18 19 19 Number of Wolves 1. Graph the deer and wolf populations on the graph below in a graph line. Use one color to show deer population and another color to show wolf population. Objective: How a Predator-Prey Population Changes Over Time Key Words: Natural Resources, Limiting Factors, Carrying Capacity Deer and Wolf Populations from 1971 to 1980 Conclusions 2. How did the deer and wolf populations change over time? • Deer and wolf populations first increased, then decreased, and then became stable. Objective: How a Predator-Prey Population Changes Over Time Key Words: Natural Resources, Limiting Factors, Carrying Capacity Deer and Wolf Populations from 1971 to 1980 d. Discussion 3. Once the wolves were introduced, what is the carrying capacity for deer and wolves in the ecosystem? • Deer’s carrying capacity is 1960. Wolf’s carrying capacity is 19. 4. What do you think would have happened to the deer on the island if the wolves had NOT been introduced? • Initially, deer’s population would increase because there would be no predators . Then, deer’s population would decrease, because deer would have used up all of the resources and then starve to death. Objective: How a Predator-Prey Population Changes Over Time Key Words: Natural Resources, Limiting Factors, Carrying Capacity Deer and Wolf Populations from 1971 to 1980 d. Discussion 5. What limiting factors affect deer population? • Water, food, shelter, predators, diseases, and climate. 6. What limiting factors affect wolf population? • Water, food, shelter, diseases, and climate. Objective: How a Predator-Prey Population Changes Over Time Key Words: Natural Resources, Limiting Factors, Carrying Capacity Deer and Wolf Populations from 1971 to 1980 Less wolves Deer and wolf Less deer populations More deer depend on each other. More wolves d. Discussion 7. How would you describe the relationship between the deer and wolf population? • Deer and wolf populations depend on each other. • Both show the same pattern: increase and decrease, then become stable. Objective: How a Predator-Prey Population Changes Over Time Key Words: Natural Resources, Limiting Factors, Carrying Capacity Deer and Wolf Populations from 1971 to 1980 d. Discussion 8. Would you agree or disagree with the following statement. “Predators and prey exist in a balance.” Explain. • Agree, because… • Or disagree, because… Objective: How a Predator-Prey Population Changes Over Time Key Words: Natural Resources, Limiting Factors, Carrying Capacity Deer and Wolf Populations from 1971 to 1980 d. Discussion 9. What are the advantages of having a population of predators and prey in an ecosystem? • It increases biodiversity and makes the ecosystem more stable. • Predators keep the deer population from becoming too large and prevent mass starvation. • Predators increase the deer health, as predators often eliminate the weaker members of the herd. Objective: How a Predator-Prey Population Changes Over Time Key Words: Natural Resources, Limiting Factors, Carrying Capacity 10. In certain areas of the United States, the populations of wolves and other predators have decreased. As a result, deer populations in these areas have increased. Describe one way that an increase in the deer population can be harmful to humans. •They transmit diseases to humans, i.e. Lyme disease. •They cause automobile accidents. •They eat crops.