Energy & Matter
advertisement

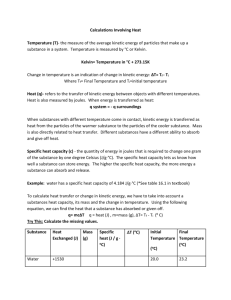
Energy & Matter Name ___________________________ 2.1, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 Period_______Date ________________ 1. Energy (2.1) A. Energy: The capacity to do ____________ or produce ______________. 1. 7 types of energy: 2. Kinetic Energy: Energy of _______________ Ex. 3. Potential Energy: _______________Energy; Determined by ___________________. Ex. 4. Energy can be __________________ from a system to its surroundings. Ex) 5. Energy absorbing changes are called ___________________. If energy is released the change is called ________________________. B. Measuring Energy: 1. Common Unit: _____________ The amount of _________needed to raise ____g of water ___oC. (One calorie = 1g°C) 2. SI Unit for energy: _____________(J) C. Law of Conservation of Energy (2.1): Energy is neither _________________ nor _______________, it just changes ______________. D. Temperature (2.1): 1. Energy can be transferred in the form of _______________. 2. Temperature is a measurement of heat or _________________ _______________. 3.Common Temperatures: Farenheit (F) Celsius (°C) Kelvin (K) Background Information Boiling Point of Water Body Temperature Room Temperature Freezing Point of Water Absolute Zero 1 °F C K Boiling point of Water Body Temperature Room Temperature Freezing Point of water 4. Kelvin: °C = K K = C + 273 C = K – 273 5. The zero point on the Kelvin scale is called __________________ _____________. (-273°C) 6. All motion of particles ______________! Therefore the __________________ energy is zero. 2. Matter (1.2): A. Matter is anything that has _____________ and takes up __________________. 1. Volume: Amount of _________________ an object takes up. 2. Mass: Quantity of _________________ in a substance. ________________ everywhere. 3. Weight: Force produced by _________________ acting on a mass. This is ____________ In different locations. B. Properties of Matter (1.2): 1. Physical: 2. Chemical: 2 C. States of Matter (1.1): State Solid Liquid Gas Shape Volume Movement Structure D. Kinetic Theory of Matter (2.1) 1. ________________ possess the greatest amount of kinetic energy. 2. Two factors that determine the state of matter of a substance: _______________________ and the ___________________________________. 3. These two factors contribute to the ___________________ between the particles. 4. Substances _____________ _______________ when they overcome these attractions. 5. The overall _______________ ______________ (temperature) will remain constant until the entire substance has completely changed phase. 6. Heating/Cooling Curve for water: Heat Energy → E. Changes in Matter (2.1): 1. Physical Changes: a. Do NOT change the ___________________ of the substance. b. Often change what the __________________ looks like. c. Examples: 3 2. Chemical Changes: a. Alter the ______________________ of the substance. b. The new substance has _______________ ______________ than the original substance. c. Examples of Chemical Changes: d. Signs that a chemical change has occurred: 1. 2. 3. 4. 4 F. Law of Conservation of Matter (2.2): Matter is neither _________________ or ______________ it just changes ________________. G. Classification of Matter (1.3) 1. Pure substances: Substances that have a _________________ set of ___________________ and ___________________ properties. a. Elements: The smallest part of an element is an _______________. 1. Cannot be separated into ___________________ ___________________. 2. Represented by _______________ that have ____ or _____ letters. 3. Examples: Atomic Number: 1 H H Hydrogen Hydrogen 1.008 1.008 Element Symbol: Element Name Atomic Mass: b. Compounds 1. Made up of _____ or more kinds of atoms _________________ combined in a fixed proportion. 2. Represented by ______________________. 3. Examples: 2. Mixtures: a. Heterogeneous Mixture: Visibly _____________________ throughout. Ex) b. Homogeneous Mixture: The ________________ throughout. Ex) 5 H. Separating Mixtures (1.3): 1. Heterogeneous Mixtures can be separated by: a. Filtration- Material remaining on the filter paper is called the _________________________. The ____________________ goes through the filter paper. 2. Homogeneous Mixtures: a. Distillation- separates ________________ (and 1 solid) by differences in __________________ ___________________. The remaining material is called the ____________________. The material that goes through is called the ______________________. 6 b. Crystallization- ______________________ the liquid and the solid will ___________________. Ex) c. Chromatography- Used ______________________ pigments and ink by differences in _______________________ on a strip of paper. Ex) 3. Compounds: a. Electrolysis- decomposes a compound into its _____________________. Ex) 7