Unit Five: Lesson 2: Graphs of Polynomial Functions
advertisement

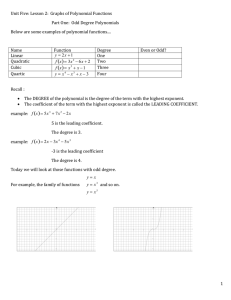
Unit Five: Lesson 2: Graphs of Polynomial Functions Part Two: Even Degree Polynomials Today we will look at functions with even degree. y x2 y x 4 and so on. For example, the family of functions y x6 For each of the following quartic functions, use the graphing calculator to sketch a neat graph. a) y x 4 2x 2 3 d) y x 4 4 x 3 4 x 2 5 b) y x 4 4 x 3 2x 2 12x e) y 3x 4 28x 3 90x 2 108x 28 c) of two of the graphs on one grid. Be sure to label them. Use the grids below. Put a maximum y x 4 2x3 x 2 2x f) y x 4 7 x 3 11x 2 7 x 12 1 2 Using the graphs you just completed, state the x-intercepts and the end behaviour in the table below. Function a) y x 4 2x 2 3 b) y x 4 4 x 3 2x 2 12x c) y x 4 2 x 3 x 2 2 x d) y x 4 4 x 3 4 x 2 5 e) y 3x 4 28x 3 90x 2 108x 28 f) y x 4 7 x 3 11x 2 7 x 12 x-intercepts End Behaviour on the right as x End Behaviour on the left as x Answer the following questions: 1. When the leading coefficient is negative, how does the graph change compared to when the leading coefficient is positive? ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. When the leading coefficient is positive, the quartic graphs extend FROM quadrant number __________ to quadrant number __________________. 3. When the leading coefficient is negative, the quartic graphs extend FROM quadrant number __________ to quadrant number __________________. 3