Spread & Power of Asian Culture Post-Class: Ch12-13 Study Guide NAME: ____________________________
advertisement

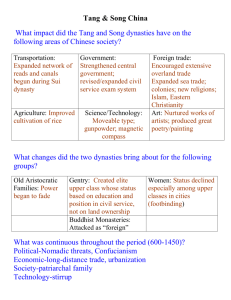
Post-Class: Ch12-13 Study Guide NAME: ____________________________ Spread & Power of Asian Culture (Ch. 12-13) ...is about the flowering of Chinese civilization at its pinnacle and spread of its culture to greater East Asia between 600 CE and 1450. Overarching Ideas: Humans need to adapt to environments has necessitated technological innovation. Cultures spread through syncretism. Economic conditions and religion are key components in legitimizing or undermining government. Ever intensifying trade is a powerful force for social and political change. Social inequality is source of conflict yet ever-present in civilizations. Objectives: 1. Explain the political, economic, and social development of the Tang and Song dynasties. 2. Compare the strengths of the Tang and Song empires. 3. Debate the significance of China’s internal development versus its international influence. 4. Explain the effects of Confucianism in East Asia. 5. Compare the degree of sinification in Korea, Japan, and Vietnam. 6. Compare feudalism in Europe and Japan. Key Concepts: Explain the definition, role, and significance of… Sui Tang Song Buddhism Neo-Confucianism Scholar-gentry Junks Flying Money Footbinding Tribute System Sinification Trung sisters Taika Reforms The Tale of Genji Bafuku Daimyo Samurai Bushido Shinto China & East Asia Key Places: Locate on the map… Mongolia Manchuria Himalaya Huang He River Yangtze River Silk Road Tang Grand Canal Song Southern Song Korea Vietnam Red River Japan Heian Kanto Plain China Guided Timeline: China 600 589618 618907 690-705 = 840s = 1000 9601279 1127 = 12791368 1450 13681644 Post-Class: Ch12-13 Study Guide NAME: ____________________________ East Asia Guided Timeline: China Korea Vietnam Japan 313-618 600 Sui 589-618 39CE = 618-668 111 BCE939 CE Tang 618-907 604-784 710-784 = 668-918 7941185 1000 Song 9601279 9181392 9391500 12791368 1450 Ming 13681644 11851600 13921910 646 = Post-Class: Ch12-13 Study Guide NAME: ____________________________