CASE STUDY OBJECTIVES: The students will be able to:
advertisement

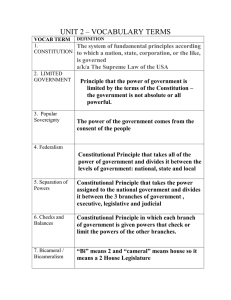
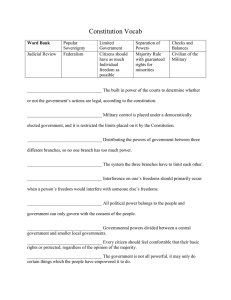
MR. HALEY AMERICAN GOVERNMENT NAME______________________________ CASE STUDY OBJECTIVES: The students will be able to: Explain the concept of American Federalism Analyze contemporary issues under federalism principles Explain the role of the US Supreme Court as the Umpire of Federalism PART I – INSTRUCTIONS: You are to give your opinion to the following statements. Mark each statement with “yes” or “no”. You are to go on your instincts as each of these statements involves some aspect of Federalism. HINT: Federalism is a constitutional principle in which the power of government is divided between the levels of government with each level having direct authority over the people. 1. Does the federal government have the power to enact a law that would result in the creation of a national drinking age of 21 years? 2. Does the federal government have the power to make the possession of a gun on school grounds a federal crime? 3. Does one state have the power to amend its state constitution to place a limit on the number of terms that a member of the US House and US Senate from that same state may serve? 4. Does one state have the power to make the use of marijuana legal for recreational or for medical purposes when there is a federal law which makes marijuana illegal? 5. Does the federal government have the power to tell private business owners that they cannot discriminate against people on the basis of race, sex, national origin or religious beliefs? 6. Does the federal government have the power to pass a law which gives women who were victims of domestic abuse the right to sue those responsible in federal court? 7. Does a state government have the power to pass a law which limits a women’s right to make private medical decisions about her body? 8. Does a state have the right to pass a law banning a specific medical procedure for an abortion? 9. Does a state or city have the right to pass a law banning the sale and possession of guns? 10. Does the federal government have the right to pass a law that limits how much money private groups or organizations can spend on an election campaign? INSTRUCTIONS – PART 2 – Collaborative Exercise 1. 2. 3. 4. Divide the students into small groups of 2 or 3. Assign each group one case study to review and complete using the federalism analysis Each group completes the analysis through the last question in class. Then for homework, the students check their opinions against that of the US Supreme Court using oyez.org 5. Then the next day, each group reports back on their case study issue. Engage the class in a discussion of each topic with the end result being that the students understand that ultimately the USSC tells us what the Constitution and Federalism mean and that they can see the connection to the importance of ideology and the judicial nomination power of a President. 6. As the case study reports proceed, the class fills in the final chart so that they know the law in each case. MR. HALEY AMERICAN GOVERNMENT NAMES____________________________ CASE STUDY ANALYSIS INSTRUCTIONS PART 2: Working in teams of two, you are to analyze one of the questions above and decide whether such a law would be constitutional. In essence you are going to be acting as a Justice on the US Supreme Court exercising the power of Judicial Review. Use the analysis set out below. Federalism Case Analysis – Follow the steps below when looking at your case study. Facts: Whether the US Congress had the power to make a law creating a national bank? Step 1 – Is there an express power set out in Article 1 giving Congress this power? If yes, then the law is constitutional. If no, then proceed to step 2. Step 2 – Is it proper under Article I, Section 8, Clause 18, the Necessary and Proper (Elastic) Clause which says that Congress can do everything necessary and proper to carry out its express powers? In order to fit under these Implied Powers, the law must be reasonably connected to some express power. List any express powers that might come into play. Is the need for a national bank reasonably connected to these express powers? If the Federal Bank is legal, can a state government tax the federal bank like any other business operating within its borders? McCulloch v Maryland 1819 Facts of the Case In 1816, Congress chartered The Second Bank of the United States. In 1818, the state of Maryland passed legislation to impose taxes on the bank. James W. McCulloch, the cashier of the Baltimore branch of the bank, refused to pay the tax. Question The case presented two questions: Did Congress have the authority to establish the federal bank? Did the Maryland law taxing the federal bank unconstitutionally interfere with congressional powers? Decision: 7 votes for McCulloch, 0 vote(s) against Legal provision: US Const. Art 1, Section 8 Clauses 1 and 18 In a unanimous decision, the Court held that 1st - Congress had the power to incorporate the bank - Chief Justice Marshall noted that Congress possessed unenumerated (IMPLIED) powers not explicitly outlined in the Constitution. The case turned on the interpretation of Article I, Section 8, Clause 18 “The Necessary and Proper Clause” (a/k/a The Elastic Clause). Chief Justice John Marshall pointed out that while the word “bank” did not appear in Congress’s enumerated powers, the creation of a bank was a means of executing its listed powers: “Although, among the enumerated powers of government, we do not find the word ‘bank,’…we find the great powers to lay and collect taxes; to borrow money; to regulate commerce…” The ruling’s description of what kind of actions can be justly implied, however, restricts the scope of the Necessary and Proper Clause to those laws that are “within the scope of the constitution, and all means which are appropriate, which are plainly adapted to that end, which are not prohibited, but consist with the letter and spirit of the constitution…” 2nd - Maryland could not tax instruments of the national government employed in the execution of constitutional powers. CJ Marshall also held that while the states retained the power of taxation, "the constitution and the laws made in pursuance thereof are supreme. . .they control the constitution and laws of the respective states, and cannot be controlled by them." Marshall said “The power to tax is the power to destroy” so this would violate Article VI the Supremacy Clause. McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) State Taxes, National Supremacy Excerpts from the Court Decision 1. ". . . Although, among the enumerated powers of government, we do not find the word "bank" or "incorporation," we find the great powers to lay and collect taxes; to borrow money; to regulate commerce; to declare and conduct a war; and to raise and support armies and navies . . . But it may with great reason be contended, that a government, entrusted with such ample powers . . . must also be entrusted with ample means for their execution. The power being given, it is the interest of the nation to facilitate its execution. . . . " —Chief Justice John Marshall 2. “But the constitution of the United States has not left the right of congress to employ the necessary means, for the execution of the powers conferred on the government, to general reasoning. To its enumeration of powers is added, that of making "all laws which shall be necessary and proper, for carrying into execution the foregoing powers, and all other powers vested by this constitution, in the government of the United States, or in any department thereof." 3. “. . . Let the end be legitimate, let it be within the scope of the constitution, and all means which are appropriate, which are plainly adapted to that end, which are not prohibited, but consist with the letter and spirit of the constitution, are constitutional. . . “ 4. “. . . This great principle is, that the constitution and the laws made in pursuance thereof are supreme; that they control the constitution and laws of the respective states, and cannot be controlled by them. “ 5. “. . . That the power to tax involves the power to destroy. . . . If the states may tax one instrument, employed by the government in the execution of its powers, they may tax any and every other instrument. They may tax the mail; they may tax the mint; they may tax patent-rights; they may tax the papers of the custom-house; they may tax judicial process; they may tax all the means employed by the government, to an excess which would defeat all the ends of government. This was not intended by the American people. They did not design to make their government dependent on the states. . . “ Use the following list of express powers for the national government contained in Article I Section 8 and Article VI, the Supremacy Clause of the US Constitution. Article I Section 8. The Congress shall have power to lay and collect taxes, to pay the debts and provide for the common defense and general welfare of the United States; To borrow money on the credit of the United States; To regulate commerce with foreign nations, and among the several states, and with the Indian tribes; To coin money, regulate the value thereof, and of foreign coin, and fix the standard of weights and measures; To raise and support armies, but no appropriation of money to that use shall be for a longer term than two years; To provide and maintain a navy; To make all laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into execution the foregoing powers, and all other powers vested by this Constitution in the government of the United States, or in any department or officer thereof. Article VI - This Constitution, and the laws of the United States which shall be made in pursuance thereof; and all treaties made, or which shall be made, under the authority of the United States, shall be the supreme law of the land; and the judges in every state shall be bound thereby, anything in the Constitution or laws of any State to the contrary notwithstanding. NAMES___________________________________________________________________ CASE STUDY 1 – Whether the US Congress can pass a law which says that any state that does not raise the drinking age to 21 years will lose 5% of their federal highway funds? (Please note that this 5% loss of funds would total millions of dollars) Federalism Case Study Analysis 1. What are the goals of this federal law? Answers Improve safety on our roadways by reducing the number or people who may legally drink alcohol and who then might drive while under the influence. Protect our young people from the evils of alcohol 2. Is there an express power saying that Congress could create a national drinking age? 3. Are there any express powers that exist which might be reasonably connected to reducing the number of people who are allowed to drink alcohol? List any that you think might apply. (Necessary and Proper Clause) 4. Is the issue of a drinking age qualification something that has been historically viewed as a state reserved power? 5. Is this law Constitutional? Give your reasoning. What was the decision of the US Supreme Court in South Dakota v. Dole (1987) See - http://www.oyez.org/ Yes under the 10th Amendment Reserved Powers, the setting of an age at which people can drink has always been the prerogative of each state. NAMES___________________________________________________________________ CASE STUDY 2 – Does the federal government have the power to make the possession of a gun on school grounds a federal crime? Federalism Case Study Analysis 1. What was the goal of this federal law? 2. Is there an express power saying that Congress could make the possession of a gun on school grounds a federal crime? 3. Are there any express powers that exist which might be reasonably connected to making schools safer? List any that you think might apply. (Necessary and Proper Clause) 4. Is the issue of education and school safety something that has been historically viewed as a state reserved power? 5. Is this law Constitutional? Give your reasoning. 6. What did the US Supreme Court say in the case of United States v Lopez 1995? http://www.oyez.org/ Answers Make schools a safer place for children and for education. Protect our kids. NAMES___________________________________________________________________ CASE STUDY 3 – Does a state government have the power to amend its state constitution to place a limit on the number of terms that a member of the US House of Representatives or US Senate from that state may serve? Federalism Case Study Analysis 1. What was the purpose of this law? 2. Is setting term limits for the federal Congress typically a federal government power? 3. Is the setting of term limits in a state constitution typically a RESERVED state power under the 10th Amendment? 4. Is this law Constitutional? Give your reasoning. 5. What did the US Supreme Court say in U. S. Term Limits v. Thornton 1995? http://www.oyez.org/ Answers Term Limits prevent lifelong politicians and improve our democracy by opening up the political system to a more diverse group of people and will also control an abuse of power that may develop when one person serves too long in government. NAMES___________________________________________________________________ CASE STUDY 4 – Does one state have the power to make the use of marijuana legal for either medical or recreational purposes when there is a federal law which makes marijuana illegal? Federalism Case Study Analysis 1. What is the purpose of the Controlled Substances Act, a federal law which makes marijuana illegal and punishable as a federal crime? 2. What is the purpose of a state law that makes marijuana legal? Answers Protect our citizens from the dangers of drugs Medical benefits for people with severe illnesses and pain. Recreational ? 3. Is there an express power saying that Congress could make the possession of marijuana a federal crime? 4. Are there any express powers that exist which might be reasonably connected to protecting people from the evil weed, marijuana? List any that you think might apply. (Necessary and Proper Clause) 5. Is the issue of medical treatment and private criminal behavior something that has been historically viewed as a state reserved power under the 10th Amendment? 6. Is the federal law constitutional? Is this state law constitutional? Who wins? Give your reasoning. What did the US Supreme Court say in Gonzalez v. Raich (2005) http://www.oyez.org/ NAMES___________________________________________________________________ CASE STUDY 5 – Does the federal government have the power to tell private business owners that they cannot discriminate against people on the basis of race, sex, national origin or religious beliefs? Federalism Case Study Analysis 1. What is the purpose of this federal law (called the Civil Rights Act of 1964)? 2. Is there an express power saying that Congress could prevent private acts of discrimination? 3. Are there any express powers that exist which might be reasonably connected to protecting people from being discriminated against? List any that you think might apply. (Necessary and Proper Clause) 4. Is the issue of private acts of discrimination (private actions that do not cross state lines) something that the state governments control under the 10th Amendment? 5. Is this law Constitutional? Give your reasoning. 6. What did the US Supreme Court say in Heart of Atlanta Motel v US 1964? http://www.oyez.org/ Answers Protect the civil rights of all Americans. Stop discrimination. NAMES___________________________________________________________________ CASE STUDY 6 - Does the federal government have the power to pass the Violence Against Women Act (VAWA) and give females who have been victims of violence (domestic abuse) a right to sue those responsible in federal court? Federalism Case Study Analysis 1. What is the purpose of this federal law VAWA? 2. Is there an express power saying that Congress could prevent private acts of discrimination? 3. Are there any express powers that exist which might be reasonably connected to protecting people from being discriminated against? List any that you think might apply. (Necessary and Proper Clause) 4. Is the issue of private acts of behavior and violence that occurs solely within the border of one state something that the state governments control under the 10th Amendment? 5. Is this law Constitutional? Give your reasoning. 6. What did the US Supreme Court say in the case of United States v Morrison 1999? http://www.oyez.org/ Answers Protect women from violence and provide them with federal remedies if they are subject to violence NAMES___________________________________________________________________ CASE STUDY 7- Does a state government have the power to pass a law which limits a women’s right to make private medical decisions about her body (specifically that a women has to have informed consent prior to an abortion, a 24 hour waiting period prior to the procedure, parental consent for a minor to get an abortion, and spousal notification prior to an abortion)? Federalism Case Study Analysis 1. What is the purpose of this state law? 2. What did the US Supreme Court say about this “constitutional right” in Roe v Wade? http://www.oyez.org 3. Is the issue of medical supervision and health care something that the state governments control under the 10th Amendment? 4. Is this law Constitutional? Give your reasoning. What did the US Supreme Court say in Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. Casey (1992)? http://www.oyez.org Answers To limit the number of abortions that take place and to provide women with information about options and to protect minor’s from serious medical issues and to protect the life of a fetus NAMES___________________________________________________________________ CASE STUDY 8 – Does a state have the right to pass a law banning a specific medical procedure for an abortion (specifically a procedure known as Partial Birth Abortion)? Federalism Case Study Analysis 1. What is the purpose of this state law? 2. What did the US Supreme Court say about this “constitutional right” in Roe v Wade? http://www.oyez.org 3. Is the issue of medical supervision and health care something that the state governments control under the 10th Amendment? 4. Is this law Constitutional? Give your reasoning. What did the US Supreme Court say in Stenberg v Carhart 1999 and in Gonzalez v. Carhart 2007? http://www.oyez.org Answers To limit the number of abortions that take place and to provide women with information about options and to protect minor’s from serious medical issues and to protect the life of a fetus NAMES___________________________________________________________________ CASE STUDY 9 – Does a state or city have the right to pass a law banning the sale and possession of guns? Federalism Case Study Analysis 1. What is the purpose of laws that ban the sale and possession of guns? 2. Is there an express constitutional right about guns? 3. Is the issue of protecting the health, safety and welfare of its citizens something that the state and city governments control under the 10th Amendment? 4. Is this law Constitutional? Give your reasoning. What did the US Supreme Court say in District of Columbia v. Heller (2008) and in McDonald v City of Chicago (2010) http://www.oyez.org Answers Protection of victims of violent crimes NAMES___________________________________________________________________ CASE STUDY 10 – Does the federal government have the power to pass a federal law that limits the amount of money that private groups or organizations can spend to influence an election? Federalism Case Study Analysis 1. What is the purpose of this federal law? 2. Is there an express constitutional right about donating money to campaigns? 3. Does the federal government have an express power to regulate elections? 4. Is this law Constitutional? Give your reasoning. What did the US Supreme Court say in Citizens United v FEC 2009? http://www.oyez.org Answers To limit the amount of money that a group can spend to influence an election campaign and to protect the integrity of US elections. NAME____________________________________ FEDERALISM CASE STUDY RESULTS CASE STUDY 1. ALCOHOL SUPREME COURT REASONING South Dakota v. Dole (1987) 2. GUNS United States v Lopez 1995 3. TERM LIMITS 4. MARIJUANA U. S. Term Limits v. Thornton 1995 No. The Constitution prohibits States from adopting Congressional qualifications in addition to those enumerated in the Constitution. A state congressional term limits amendment is unconstitutional if it "has the sole purpose of creating additional qualifications indirectly." - Supremacy Clause Article VI Gonzalez v. Raich (2005) 5. CIVIL RIGHTS Heart of Atlanta Motel v US 1964 6. VAWA United States v Morrison 1999 7. ABORTION Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. Casey (1992) 8. PARTIAL BIRTH ABORTION Stenberg v Carhart 1999 and in Gonzalez v. Carhart 2007 9. GUNS 10. CAMPAIGN FINANCE District of Columbia v. Heller (2008) and in McDonald v City of Chicago (2010) Citizens United v FEC 2009