Structure of Cdc42 in complex with the GTPase-binding
advertisement
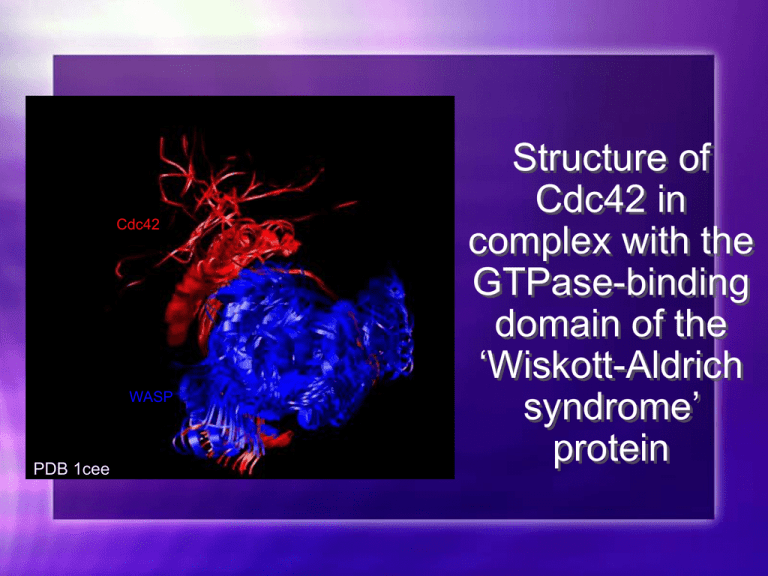
Cdc42 WASP PDB 1cee Structure of Cdc42 in complex with the GTPase-binding domain of the ‘Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome’ protein List Finish Breast Cancer Talk Look up Drugs affecting WAS and structures Conclusion/ WAS Write whole speech PRACTICE PRACTICE PRACTICe Tuesday, 10-12 Eagleton Institute of Politics 1-4:30 I have 3 1/2 hours Overview Introduction Function Structure Disease Treatment Conclusion Introduction CDC42 is a member of a small family of GTPases. Through the action of GTPases, GTP (an essential for signal transduction with G-proteins) is converted to GDP (guanosine diphosphate). GTP-binding proteins together control the assembly, organization, and disassembly of the actin cytoskeleton in response to extracellular signals in eukaryotic cells. The Cdc42 proteins bind to effector proteins Diseases such as the Wiskott- Aldrich Syndrome or certain forms of cancer,such as breast cancer are thought to arise due to derangement or mutations of the Cdc42. Function “Cdc42 acts as a molecular switch in signaling pathways that regulate cytoskeletal architecture, gene expression, and progression of the cell cycle. The switch transmits different signals through the GTP-dependent binding to effector proteins containing a Cdc42/Rac interactive binding (CRIB) motif” Function Regulators of the actin cytoskeleton Control motility of mammalian cells Transduce signals from extracellular stimuli to intracellular signal transduction pathways. Signaling Pathway Involving Cdc42 Cdc42 Re Cdc42 GDP GTPase Cycle Cdc42 GTP Effectors WASP Regulates Actin cytoskeleton Cell morphology Cell migration Cell growth Cell survival Gene expression Structure (By NMR Spectroscopy) Structure of the Cdc42 complex binding through GTP-dependent binding to effector proteins containing a Cdc42/Rac interactive-binding (CRIB) motif. Chain A : GTP-binding Rho-like Protein Chain B is the Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein Fifty-five known interactions The CDC42/Rac- binding domain is between amino acids 201-321 on WASP. Chain B: WASP CRIB Motif Chain A: Cdc42 PDB 1cee C Switch I Switch II N ß3 ß2 CRIB C N PDB 1cee Structure Cdc42 residues Phe37, Asn39 and Ala41, near the C terminus of switch I, form main-chain hydrogen bonds to WASP residues Val250, Val247/Ser 248 and Lys 245. These interactions position the Asp38 side chain of Cdc42 near WASP residues His246 and His249. There is a hydrogen bond from the Asp 38 to eiter His 246 or His249 ring. C Switch I Switch II N ß3 ß2 CRIB C N PDB 1cee I276 V36 L67 A274 V260 D38 F271 F37 H249 Y40 I21 L70 L270 L267 F56 T25 H246 PDB 1cee WASP H249 D38 F56 Hydrogen B Y40 I21 Cdc42 H246 Structure Hydrophobic interactions anchor WASP residues 232-238 to the Cdc42 B2/B3 hairpin and alpha 5 helix. Interaction of the WASP GBD N terminus and the Cdc42 B2/ B3 hairpin and alpha5 helix. C Switch I Switch II N ß3 ß2 CRIB C N Y51 I46 I238 D237 I233 I173 L177 L174 K235 Y51 I46 I173 L177 Hydrogen Bonds D237 K235 E174 PDB 1cee Gene Sequence Binding Preference Rac Cdc42 WASP N-WASP ACK PAK65 STE20 MRCKb 230 192 502 67 329 1577 KKKISKADIGAPSΡ GFKHVS HVGWDPQNGFDVNNLDPDLRSLFSRAG IS KKRLTKADIGTPS-- NFQHIG HVGWDPNTGFDLNN LDPELKNLFDMCGIS VAGLSAQDISQPLQNSFI HTGHGDS DPRHCWGFP-DRIDE LY LGNPMDPP KKEKERP EISLPS-- DFEHTI HVGF DAVTG-EFTGMPEQ WARLLQTSN IT SSITTA LRISTPY-- NAKHIH HVGVDSKT GE-YTG LPEEWEKLLTSS G IS DPELRSKMISNPTΡ NFN HVAHMG---PGD GMQV LMDLPLSVRPQPRRK ISXPX---XFXHXXH -277 -239 -550 -113 -375 -1620 + + - CRIB motif Cdc42 Rac1 RhoA Ι SEYVPTV FDNYAVTVMIGG...AGQEDYDRLRPLSYPQT...VFDEAILAALEΙ ...GEYIPTVFDNYSANVMVDG...AGQEDYDRLRPLSYPQT...VFDEAIRAVLC... ...EVYVPTVFENY VADIEVDG...AGQEDYDRLRPLSYPDT...VFEMATRAALQ... 30 Switch I 48 59 Switch II 75 168 178 + + + + + + Wiskott- Aldrich Syndrome Rare X-lined recessive disorder that affects cell morphology and signal transduction in hematopoietic cells Function of WASP is to serve as a bridge between signaling and movement of the actin filaments in the cytoskeleton. Researchers identified many different mutations that interfere with the protein binding to Cdc42, which is involved in regulation of the actin cytoskeleton of lymphocytes. The actin cytoskeleton is responsible for cellular functions such as growth, endocytosis, exocytosis, and cytokinesis. Interaction Show surface depiction of interaction Look for mutated ones Drugs used and structures Treatment WAS is treated with a variety of therapeutic agents including antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, chemotherapeutic agents, immunoglobulins, and corticosteroids. Examples: Prednisone, Methylprednisolone, fluocinolone, and immune globulin. Conclusion References Questions/Comments?