Unit E: Electrical Applications Chapter 12: Static and Current Electricity
advertisement

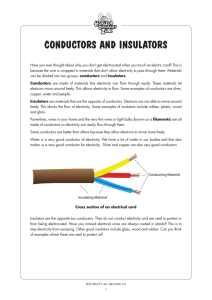
Unit E: Electrical Applications Chapter 12: Static and Current Electricity 12.8: Moving Charges pg. 484 Key Concepts: 1. Electricity describes how electrons move from one place to another. 2. Current electricity is generated by moving electrons is a closed path. Conductors Conductor: a material that transmits thermal energy or electrical energy easily. A conductor is a material that allows electrons to travel freely through it, like copper wire in the electrical wiring in your house. Metals (aluminum, silver, and gold) are excellent conductors of electricity. Pure water is a poor conductor of electricity, but water with minerals dissolved in it is an excellent conductor. Insulators Insulator: is a material that resists or blocks the flow of electrons through it. Insulators (plastic, glass, rubber, air, and wood) are materials that have more tightly bound electrons and resist losing them. Insulators are used to prevent conductors from transferring charges, and are used to protect us from dangerous effects of electricity flowing through conductors. Wires with plastic coating are insulated. Conductivity Conductivity: a measure of a material’s ability to conduct electricity. Selecting what is an insulator or conductor is based on a range of conductivity. The relative ability to conduct electricity and allow electrons to flow through it is conductivity, different materials fall along a range of conductivity. Least conductive material is an insulator and the greatest conductive material is a conductor. Figure 4: Insulators and conductors actually fall along a range based on increasing levels of conductivity Current Electricity Electric Current: is the flow of electricity through a conductor in a closed circuit. Direct Current (DC): is an electric current in which the flow of electrons travels in one direction only. Electronic devices run on electricity, but can not use static electricity. Electricity must flow from an energy source through conducting wires and back again. This must be a closed circuit or path way, the electricity goes from the source and back again. Batteries Figure 5: A dry cell battery converts the chemical energy generated by reactions between chemicals inside it into electrical energy. In a battery, chemical reactions release electrons as they move internally from positive to negative terminals. The electrons need to move from the negative terminal to the positive terminal, but the only way to do this is to flow a path back, but can not return the way it came. The flow of electrons in one direction is known as direct current (DC). The wires and devices resist electron flow through them. The Grid Alternating Current (AC): is an electric current that repeatedly reverses direction. Electric current travels to your house through the electrical energy distribution grid, (power grid). Energy is produced by the generator, when an energy source (fossil fuel, nuclear, or hydro) turns a turbine, causing the generator to turn. The spinning coils of the generator between magnets, produces an alternating current (AC). The electricity flows in wires in one direction and then reverses and goes in the other direction. Alternating current is used to supply electricity to our homes and electronic devices. Alternating current must travels to a transformer so it can be transmitted over long distances. Figure 6: the grid consists of a generating plant with its electric generator, the substation, transmission lines, transformers at the substation, and the poles leading electrical wires into your home. Check Your Learning: Questions 1 – 6, pg. 488 Wrap Up: - Electrical conductors are materials that allow electrons to flow through them easily. - Insulators are materials that resist or block the flow of electrons. - Conductivity is a measure of a material’s ability to conduct electricity. - Electric current is the flow of electrons through a conductor. - Direct current is current that flows through a conductor in one direction only. - Alternating current is current that repeatedly reverses direction. - Electric current travels over transmission lines from a generating plant to our home by the electrical energy distribution grid.