UNIT 2: Metabolic Processes 5.6: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: A Comparison
advertisement

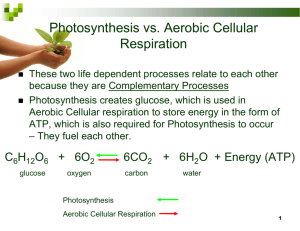
UNIT 2: Metabolic Processes Chapter 5: Photosynthesis: The Energy of Life pg. 210 - 240 5.6: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: A Comparison pg. 237 – 240 Aerobic cellular respiration and photosynthesis are two main chemical processes that are essential to most of the life on Earth. These reactions are complementary, as the products of one reaction are the reactants of the other reaction. Photosynthesis: occurs in the Chloroplast sunlight energy + water + carbon dioxide → glucose + water + oxygen Cellular Respiration: occurs in the cytosol and Mitochondrion glucose + water + oxygen → ATP + water + carbon dioxide Figure 1: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration, Photosynthesis and aerobic cellular respiration are complementary – they use each other products. The NAD+ that are reduced to NADH in the cytosol and during pyruvate oxidation are also regenerated by the transfer of their hydrogens and high energy electrons to the electron transport chain. For simplicity, H+, ADP, and Pi are not shown in this diagram. pg. 237 Chemical Steps and Reaction Processes Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration have an electron transport chain, and ATP synthase complexes. Photosynthesis uses NADP+ and NADPH to carry electrons to produce glucose, while cellular respiration uses NAD+ and NADH to produce ATP. The chloroplast and the mitochondrion organelles are similar in structure. Both have two membranes and fluid filed spaces, containing proton gradients. The Calvin cycle (carbon fixation) and citric acid cycle, (carbon releasing) are complementary. Both the chloroplast and mitochondrion have their own DNA (replicate their DNA) and reproduce on their own. Figure 2: Comparing Chloroplast and Mitochondrion, Comparison of Chemiosmosis in mitochondria and in chloroplasts, a) In mitochondria, the proton gradient is established by pumping hydrogens out of an internal space (matrix), b) chloroplasts, the proton gradient is established by pumping hydrogens into an internal space )the thylakoid lumens). pg. 238 Comparison of Animals and Plants Table 1: compare Plant and Animal, pg. 239 Chapter 5: Summary pg. 244 Chapter 5: Self-Quiz pg. 245 Chapter 5: Review pg. 246 – 251 Unit 2: Self – Quiz pg. 254 – 255 Unit 2: Review pg. 256 - 263