UNIT 2: Metabolic Processes Chapter 3: An Introduction to Metabolism
advertisement

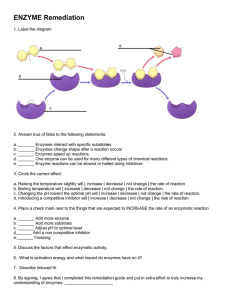
UNIT 2: Metabolic Processes Chapter 3: An Introduction to Metabolism 3.3: Enzymes and Activation Energy pg. 124 - 165 pg. 146 - 150 Enzymes enable chemical reactions to proceed more readily by reducing the amount of activation energy that the reactants must overcome, enzymes lower the energy required for the reaction to occur. Just because a reaction can proceed on it own, does not mean that it will proceed. Enzymes as Catalysts Enzymes are biological catalysts that are mostly proteins. Some RNA molecules can also act as enzymes. Maud Menten, was one of the first scientists to determine the fundamental role of enzymes, she determined a mathematical equation to measure the rates of enzymes and explain enzyme kinetics. An enzyme binds with reactant molecules; speed up the rate of the reaction, and then is released unchanged to support the reaction again. The enzyme lowers the potential energy of the transition state for the reaction, causing the reaction to occur faster, and more often. An enzyme has one or more binding sites that bind to specific type reactant substrate, than the chemical reaction can occur. These catalyzed reactions are reversible. You can recognize an enzyme and its substrate by its name. The root of its name is often based on the substrate or type of chemical reaction and usually ends in the suffix –ase. The enzyme maltase catalyzes a reaction involving maltose. Other names indicate the type of reaction that the enzymes catalyze, such as; carboxylase. maltase Maltose + water ↔ glucose + glucose Activation Energy as a Barrier to Chemical Reactions In a typical reaction the bonds of the reactants must break before the products can form. The reactant possesses activation energy (Ea) barrier that must be overcome for the reaction to occur. Once the activation energy barrier has been reached, reactant bonds are broken, the reaction may move forward. The reactants must meet at an appropriate geometrical position and collide with other reactants for the chemical reaction to produce its products and form new bonds. Transition state must be reached before new bonds and new products can form. Figure 2: Catalyzed reactions, molecules must overcome the activation energy barrier for the reaction to proceed. pg. 147 What provides this activation energy? The motion of the molecules themselves, an increase in temperature, or enzymes will allow reactions to occur. An increase in temperature is a problem for biological reaction, because it is harmful to the cell, destroying DNA and proteins. Lowering Activation Energy with Enzymes Enzymes increase the rate of reactions by lowering the activation energy required to start the reaction. When the enzyme lowers the activation energy barrier, more reactant molecules can reach the transition state at a faster rate. Figure 4: Enzymes lower the Activation Energy of both, a) exergonic reactions and b) endergonic reactions. The enzymes do not affect the ∆G, pg. 148 The enzyme reduces the activation energy require for a reaction to occur by attaching to substrates, and bring these molecules closer together. The enzymes also expose some substrates to altered charged environments. The active site of some enzymes may contain ionic groups (positive/negative) that attract or repel parts of the substrate. This can stress bonds of the substrates. Enzymes can also change the shape of the substrate which can weaken the bonds, reducing the amount of energy required for the reaction to occur. This mechanism of enzyme-substrate interaction is called the Induced-Fit model. Figure 5: Induced-Fit Model, a) Enzymes can bring both substrates into contact by binding them to specific sites. This allows them to collide more easily so that bonds can be broken more quickly and new bonds can form. b) Enzymes can distort or bend the shape of a substrate, which weakens the chemical bond. pg. 149 Enzyme can become non-functioning if they are heated. An increase in temperature will denature the protein molecule, changing its shape, making it unable to interact with the reactants.