Chapter 3: The Economic Problem – The Problem of Scarcity
advertisement
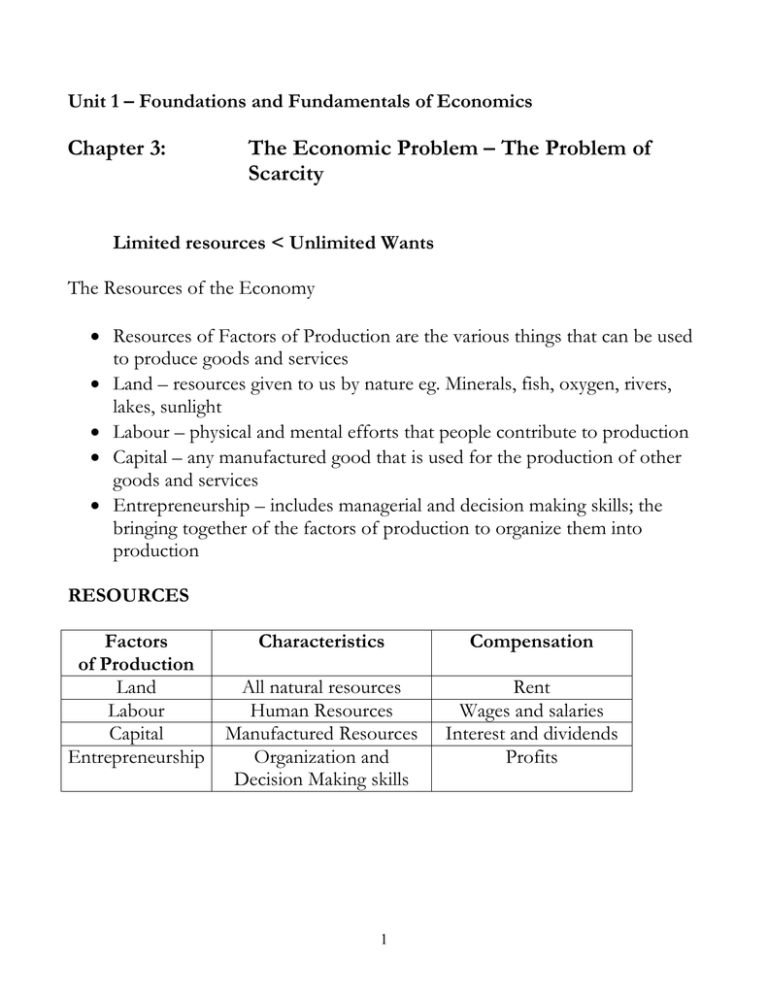
Unit 1 – Foundations and Fundamentals of Economics Chapter 3: The Economic Problem – The Problem of Scarcity Limited resources < Unlimited Wants The Resources of the Economy Resources of Factors of Production are the various things that can be used to produce goods and services Land – resources given to us by nature eg. Minerals, fish, oxygen, rivers, lakes, sunlight Labour – physical and mental efforts that people contribute to production Capital – any manufactured good that is used for the production of other goods and services Entrepreneurship – includes managerial and decision making skills; the bringing together of the factors of production to organize them into production RESOURCES Factors of Production Land Labour Capital Entrepreneurship Characteristics Compensation All natural resources Human Resources Manufactured Resources Organization and Decision Making skills Rent Wages and salaries Interest and dividends Profits 1 SCARCITY, CHOICE and OPPORTUNITY COST Scarcity of resources requires a choice between wants Opportunity cost refers to the alternative that is sacrificed when a choice is made eg. If a city decides to build a school instead of adding a wing to a hospital, then the opportunity cost of the school is the additional hospital facilities that the city would have had instead PRODUCTION POSSIBILITIES the PPC (production possibilities curve) is an economic model that illustrates the economic problem of scarcity Assume that an economy devotes all of its resources to the production of only two goods, houses and automobiles Several possible combinations of houses and automobiles is possible, as illustrated in the production possibilities schedule Possibilities Number of Houses 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 100, 000 200, 000 300, 000 400, 000 500, 000 600, 000 700, 000 800, 000 Number of Automobiles 8, 000, 000 7, 000, 000 6, 000, 000 5, 000, 000 4, 000, 000 3, 000, 000 2, 000, 000 1, 000, 000 0 If the economy uses all of its resources to produce automobiles, it can produce a maximum of 8, 000, 000 automobiles and no houses (possibility 1) 2 If it uses all of its resources to produce houses, then it can produce a maximum of 8, 000, 000 houses and no automobiles (possibility 9) Between these two extreme cases are many possibilities Note that for every 100, 000 houses produced, the economy sacrifices 1 000, 000 automobiles. Thus the opportunity cost of 100 000 houses is 1, 000, 000 automobiles That is, in order to produce one house the economy must sacrifice 10 automobiles In this example the opportunity cost remains constant throughout Houses (00, 000) Automobiles (000, 000) 3