Pertemuan 26 Proses dan Threads pada Sistem Operasi Windows Matakuliah
advertisement

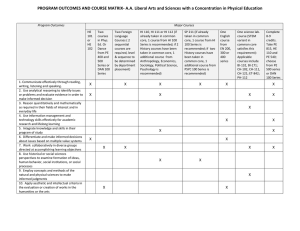
Matakuliah Tahun Versi/Revisi : T0316/sistem Operasi : 2005 :5 Pertemuan 26 Proses dan Threads pada Sistem Operasi Windows 1 Learning Outcomes Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa akan mampu : • membandingkan sistem operasi Linux dan Windows 2000 (C4) 2 Outline Materi • • • • • • • • • Proses dan threads pada windows 2000 Komunikasi inter proses Penjadwalan Proses booting pada windows 2000 Pengaturan memory Pengaturan I/O Device driver Sistem file pada windows 2000 Securiti pada windows 2000 3 Processes and Threads (1) Basic concepts used for CPU and resource management 4 Job • Sekumpulan proses • Share quota dan resource limit – Jumlah proses – CPU time – dll 5 Process • Container for resources – Created via Win32 call • CreateProcess (Win32 API function di dalam library kernel32.dll) • NTCreateprocess (system call) – Minimal satu thread – Serangkaian handles – Access token for security information – 4 GB adress space 6 Thread • Entity scheduled by kernel • Created via Win32 call – Created using CreateThread (Win32 API function di dalam library kernel32.dll) – NTCreateThread (system call) • State: ready, running, block • Normal vs daemod threads (in user and kernel space, respectively) • Thread switching – (between user and kernel mode) • Dapat memiliki beberapa fibers 7 Fiber • • • • • Lightweight thread Lightweight pseudo-parallelism Scheduled in user space faster Tidak termasuk executive object Melalui Win32 API tanpa system call 8 Komunikasi antar process • Threads komunikasi lewat – Pipes – Named pipes (dengan network) – Mailslot • only on Windows 2000 • One-way, un-guaranteed delivery, allow broadcast – Socket connect processes on different machine • Similar to pipe – Remote procedure calls – Shared files 9 Komunikasi (2) • Synchronization mechanism – Semaphore – Mutexes – Critical sections – Events • Set or cleared • Eg. Set waiting threads are released 10 Penjadwalan • Scheduler diaktifkan ketika – Threads terhalang (blocked) misal oleh semaphore – Thread memberi signal (misal up on semaphore) pada suatu object – Quantum habis – Operasi IO selesai – Batas waktu menunggu habis 11 Emulasi MS-DOS • Run as many MSDOS programs as prossible • NT vitual DOS machine ntvdm – Monitor MSDOS program and carry out its system calls • Trampoline – Emulation to bounce back MSDOS IO request 12 MS-DOS Emulation How old MS-DOS programs are run under Windows 2000 13 Booting Windows 2000 • Processes starting up during boot phase • Those above the line are always started • Those below are examples of services which could be started 14 Process Booting • Baca master boot record sektor pertama dari disk pertama • Assembly language program • Baca partition table • Cari boot sector sektor pertama dalam partisi yang berisi bootable OS • Baca root directory • Cari dan execute file ntldr (nt loader) • Baca file boot.ini • Baca files hal.dll, ntoskrnl.exe, bootvid.dll (video driver) 15 Process Booting (2) • First user process session manager (smss.exe) • Aktifkan win32 environment subsytem (crss.exe) • Baca registry hives • Login daemon winlogon.exe • Authentication manager lsass.exe • Services.exe parent process of all services 16 Pengaturan Memory • Memory Virtual – Proses 32 bit virtual address (4GB virtual address space) – Upper 2GB untuk OS, shareable – 4KB page size (Pentium), atau 8/16KB (Itanium) – Demand paged – States dari virtual page • Free, reserved, committed 17 Pengaturan Memory (2) • Memory manager – Berkaitan dengan proses, bukan thread (scheduler) – Virtual Address Descriptor (VAD) • Contains list of range of address mapped, backing store file and offset, protection code • Balance Set Manager – Kernel daemon thread – Kontrol ketersediaan free pages 18 Pengaturan Memory (3) • Working set manager – Thread yang mengatur working set bagi proses – Berdasarkan parameter min dan max size of working set – Local allocation strategy • Win32 API – To allocate, free, protect and query Virtual Address Space (VAS) – Pengaturan memory-mapped files 19 Pengaturan Physical Memory • Page lists – Standby page list – Modified (dirty) page list – Free list – Zeroed page list • Page frame databases – Banyaknya entries banyaknya pages dalam RAM – Index menurut physical page frame # 20 Pengaturan Input/Output • Plug and Play Manager – Enumerable bus allows request to the slot for self identification of devices – Mengalokasikan H/W resource (eg interrupt level) – Memilih driver yang sesuai – Load ke memory & create driver object • Win32 API – Utama pada window management – Management of text colour, size, width, typeface – clipboard 21 Pengaturan IO (2) • Device Drivers – Windows driver model • • • • • • • IO request dengan format standar Object based Support plug-and-play Support power management Configurable Reentrant Portable – Stacked drivers request must pass a sequence of drivers – Filter drivers perform transformation on the data 22 File System • Support FAT-16, FAT-32, dan NTFS • NTFS – 64 bit disk address – Long file name (255 chars) – Volume (partition) terdiri dari • Files, directories, bitmaps, and data structures – Block (cluster) size 512 bytes hingga 64 KB compromised 4 KB – Master File Table (MFT) • Each describe one file/directoriy 23 File System (2) • Win32 API – File create, delete, open, close, read, write, etc – Mutual exclusion lock file, unlock file – Directory create, remove, find first file, etc • NTFS File name Lookup – Dimulai dari root object manager name space – Directory \?? • Contains the disk letter (eg. A, C, D …) • ?? read first in ASCII – Support hard link – Support symbolic links (reparse point) 24 File System (3) • NTFS File Compression – Transparent file compression – Compressed mode compress blocks as written and uncompress as read – Run compression algorithm • NTFS File Encryption – Option to encrypt files – Done by EFS (Encrypting File Standard) driver • A variant of DES (Data Encryption Standard) – Generates a random 128 bit file key 25 File System Structure (1) The NTFS master file table 26 File System Structure (2) The attributes used in MFT records 27 File System Structure (3) An MFT record for a three-run, nine-block file 28 File Name Lookup Steps in looking up the file C:\maria\web.htm 29 File Compression (a) An example of a 48-block file being compressed to 32 blocks 30 (b) The MFT record for the file after compression Security • Mewarisi security dari Win NT • Identifikasi user dan group dengan Security ID (SID) • Access token for each process – DACL (Discretionary Access Control List) • contains who may use the object – ACE (Access Control Elements) • Access or deny – Security Descriptor • Header + DACL + one or more ACEs • Win32 API – Berbasis security descriptor – Menggunakan security dan SAM (Security Account Manager) keys di dalam registry 31 Caching • Cache manager • Untuk keperluan kinerja sistem • Menyimpan blok-blok file yang baru digunakan untuk kegunaan berikutnya • Berdasarkan virtual block (bukan physical block) • Diacu (referenced) dengan (file, offset) • Sebesar 256 KB VAS dipetakan (mapped) ke file 32 Caching in Windows 2000 The path through the cache to the hardware 33