World War II
advertisement

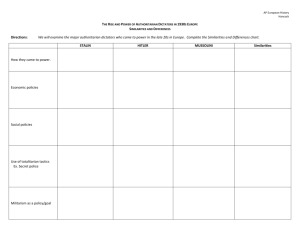
World War II Basic Details about the War 1939-1945 Two major fronts to the war Europe (Germany and Italy vs. Allies) Pacific (U.S. vs. Japan) Most devastating war in human history Over 15 million soldiers die Over 25 million soldiers wounded Approximately 12 million deaths in the Holocaust Close to 50 million civilian deaths Entire cities reduced to rubble Objective: Students will be able to discuss major causes of World War II Causes of World War II Major Causes of the war Economic Problems, which facilitate the rise of dictators (Slides 6-15) Treaty of Versailles (slides 17-18) Appeasement (19-22) Causes of World War II Economic Problems: Recovery from World War I resulted in weak economies Great Depression caused major economic problems Germany among the hardest hit by depression Great Depression began with the U.S. Stock Market Crash in 1929 D.Q….If the Great Depression began in the United States, why did it have such a huge impact in Europe????? Causes of World War II Rise of Dictators: Strong, often charismatic, leaders begin to rise to power D.Q….What role did the poor economy play in the rise of dictators????? Dictators emerge in: Italy (Benito Mussolini) Soviet Union/USSR (Josef Stalin) Spain (Francisco Franco) Germany (Adolf Hitler) Causes of World War II Activity: Research and present information about one of the major dictators. Information to include: 3 Interesting “fun” facts about this person Brief summary of how he rose to power 3 Important Government Policies implemented by this person Causes of World War II Dictators: Benito Mussolini Causes of World War II Important Details about Mussolini…… Causes of World War II Dictators: Josef Stalin Causes of World War II Details about Josef Stalin… Causes of World War II Dictators: Francisco Franco Causes of World War II Details about Francisco Franco… Causes of World War II Dictators: Adolf Hitler Causes of World War II Details about Hitler… Causes of World War II Treaty of Versailles: Review of major provisions in the treaty: War Guilt Clause Reparations German loss of land Disarmament of Germany League of Nations D.Q….How does the Treaty of Versailles lead to another war????? Causes of World War II Appeasement: The policy of allowing someone to have his/her way to avoid conflict In the 1930’s, Germany began to become increasingly aggressive and began to violate terms of the Treaty of Versailles. Examples of German defiance/aggression: Creation of the Luftwaffe (German Air Force) Occupation of the Rhineland (DMZ between Germany and France) Annexation of Austria Annexation of Sudetenland in Czechoslovakia D.Q…..Why did Germany want these territories????? Causes of World War II Munich Conference: September, 1938 Allies become worried about German actions Call a conference to discuss German aggression Allies agree to “appease” Hitler and let him keep all of the territory with a promise that he would not try to expand any further Allies agree to avoid war unless Germany attacked another state….especially Poland Objective: Students will be able to identify and discuss major events from World War II. War Begins Hitler continued to prepare for war. Had no intentions of honoring the Munich Agreement. August, 1939: Hitler and Stalin sign the Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact Agree not to attack each other Agree to split Poland D.Q…..Why would Hitler and Stalin sign this agreement? What does Hitler gain? What was Hitler hoping to avoid by signing this agreement? What does Stalin gain? War Begins September 1, 1939: World War II begins with the German invasion of Poland German War Strategy Blitzkrieg: “lightning warfare” Germans use massive coordinated attacks to quickly defeat the enemy VERY Successful! Poland defeated in less than a month Germany then begins a path of conquest across Western Europe France Falls! June, 1940: France surrenders to Nazi control French government (Third Republic) destroyed and a puppet government, called the Vichy Government, established Battle of Britain By late-1940, England remained as the only major Allied Power fighting against the Axis Powers (Germany, Italy, Japan) Germany began air raids against Great Britain in what is knows as the Battle of Britain. Bombing campaigns continue for months without British surrender British Prime Minister Winston Churchill vows “We will never surrender” D.Q….Why were German attempts to defeat the British unsuccessful? What advantage did the British have that Germany was unable to overcome? World War II Expands Having solidified his control over the western half of the continent, Hitler turned his eyes east. Summer, 1941: Operation Barbarossa Hitler violates the NonAggression Pact with Soviet Union and invades World War II Expands U.S. had tried to remain neutral and avoid involvement Began to send supplies to the Allies, but refused to commit troops D.Q…..How does this policy compare to the U.S. policy during WWI? U.S. eventually has no choice but to join the war Relations between Japan and the U.S. had been deteriorating since the early 1930’s due to Japanese aggression in Asia. Japan invaded Manchuria, China in 1931 U.S. implemented trade sanctions (restrictions) against Japan to show our dissatisfaction World War II Expands December 7, 1941: Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W5Iw UMCmxD8 The Tide of War Turns Axis Powers enjoyed success in the early stages of the war. However, the tide of war starts to turn in the favor of the Allies. Turning Point in the European War: Battle of Stalingrad https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oJ3bzg-Tvt4 Turning Point in the Pacific War: Battle of Midway Allies also have success in liberating North Africa, and eventually make their way into Italy. The Tide of War Turns Operation Torch in North Africa Allies defeat German forces, led by Erwin Rommel (The Desert Fox) D.Q….Why was North Africa such an important location for the Allied War strategy? The Tide of War Turns In 1943, Allies were able to move into Italy. July, 1943: Mussolini deposed and arrested German forces rescue him September, 1943: Italy’s surrender announced Allies move up the Italian peninsula, pushing the Axis Powers back The Tide of War Turns Allies begin to plan the invasion of Western Europe, which would ultimately lead to the liberation of France. June 6, 1944: D-Day (Operation Neptune/Operation Overlord) Massive amphibious attack on the beaches of Normandy (Western France) D-Day campaign gave Allies a strong foothold in Western Europe Over 2 million men participated in this campaign Paris Liberated in August, 1944 D.Q…..Why was Western France such a strategic location for the Allied attach? What does “amphibious attack” mean? Why would the Allies need to use such a large number of troops in this mission? https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=QHvqS2kk1rs Victory in Europe! With Allies advancing from the west, south, and east, Germans are forced into retreat. Last big attempt to defeat Allies was known as the Battle of the Bulge failed April 28, 1945: Mussolini captured and killed April 30, 1945: Hitler committed suicide May 8, 1945: Germany surrenders to end WWII in Europe Victory in Europe Day (V-E Day) Why would Hitler choose to commit suicide? Wrapping up the War with Japan Island Hopping: the U.S. war strategy in the Pacific Allows U.S. to get closer to the main islands of Japan Numerous important battles Iwo Jima Okinawa Why were Iwo Jima and Okinawa so important to both the Japanese and American war strategies? Wrapping up the War with Japan April 12, 1945: U.S. President, Franklin D. Roosevelt, dies Vice President, Harry Truman, takes over and learns of a new weapon Manhattan Project: plan to build the atomic bomb U.S. has two options for ending the war with Japan Invade the Japanese mainland OR Use the newly developed Atomic Bomb to force Japanese surrender D.Q….What are the PROS and CONS of each option listed above? If you were President, which option would you have chosen? Using the bomb August 6, 1945: U.S. drops atomic bomb on Hiroshima, Japan August 9, 1945: U.S. drops a second atomic bomb on Nagasaki, Japan D.Q….What was the immediate impact of the atomic bombs? What was the long-term impact of the atomic bombs? The War is Finally Over! September 2, 1945: Victory in Japan announced (V-J Day) World War II was officially over!