Sex-Linked Inheritance
advertisement

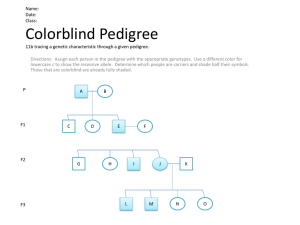
Sex-Linked Inheritance Date ______ Name ___________________ Colorblindness is a recessive trait found on the X chromosome. In this investigation you will model how sex-linked traits, such as colorblindness, are inherited. A woman who is a carrier for colorblindness marries a colorblind man: What is the genotype of the woman and the man? Make a Punnett square to show the all possible outcomes and give the phenotype ratio. Obtain a two paper cups, one that says “mom” and one that says “dad.” Use beans to represent the X and Y chromosomes. The white bean represents the X chromosome and the red bean represents the Y chromosome. A dot on the white bean represents a recessive allele for colorblindness. Randomly pick one bean from each cup to represent how each parent contributes a sex chromosome to a fertilized egg. In your data table, record the color of each bean and the sex of the individual who would carry this pair of chromosomes. Also record how many Xlinked alleles the individual has. Put the beans back in the cups they came from. Repeat this process until you have completed 12 trials. Trial # Sex Chromosomes (XX or XY) Number of Colorblindness Alleles Is the individual colorblind (Yes or No) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Analysis ____________________ What is the actual number of males and females after 12 trials? ___________________ What is the expected number of colorblind males and females for 12 trials? ____________ What is the actual number of colorblind males and females after 12 trials? ____________ 1. What is expected number of males and females for 12 trials? 2. 3. 4. 5. Compare your actual and expected numbers for color males and females. Do they agree or disagree? If they disagree, how much do they disagree? What could you do to get closer to the ______________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ expected results? 6. How would the results be different if the man was not colorblind? Use a Punnett square to support your explanation. Date ______ Sex-Linked Inheritance Name ___________________ Hemophilia is a sex-linked trait. Use the following symbols to answer the questions. XHXH = normal female XHXh = normal female, a “carrier” of the trait XhXh = hemophiliac female XHY = normal male XhY = hemophiliac male 1. Queen Victoria in England was a carrier for hemophilia. Draw a Punnett Square for the cross between her and her husband if her husband did not have hemophilia. a. What is the probability that the couple will have a female with hemophilia? b. If the couple has a male son, what is the probability that he will have hemophilia? 2. If a female has hemophilia, what must be the genotypes of her parents? 3. A homozygous normal female marries a male with hemophilia. What percentage of their sons will have hemophilia? What percent of their daughters will be carriers for hemophilia? 4. A normal male marries a normal female and they have 24 children. They have 12 daughters who are all normal, 6 sons who are normal, and 6 sons who have hemophilia. Explain these results. 5. In humans, normal vision (XC) is dominant to colorblindness (Xc) and is sex-linked. A normalvisioned man, whose father was colorblind, marries a colorblind woman. What are the chances that a son will be colorblind? A daughter? Explain. 6. Hairy ear rims is a trait carried on the Y chromosome. A woman does not have hairy ear rims, and her husband does. a. Draw a Punnett Square for the cross. b. What is the probability of the couple having a child with hairy rims? c. If a woman does not have hairy rims, and her husband does not have hairy ear rims, what is the probability that they will have a child with hairy ear rims?