Reproduction in Flowering Plants Name:____________________________ Date:_________________
advertisement

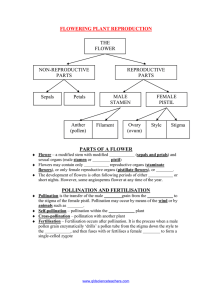
Name:____________________________ Date:_________________ Reproduction in Flowering Plants 1. Reproduction is the goal of every living thing a. What does evolution claim the goal of every organism is? b. What are 2 ways plants reproduce? i. Sexual reproduction – 1. Advantages to sexual reproduction a. b. 2. Disadvantages to sexual reproduction a. b. ii. Asexual reproduction 1. Advantages to asexual reproduction a. b. 2. Disadvantages to asexual reproduction a. b. 2. Reproduction in flowering plants a. Flowers – i. A perfect flower contains 4 parts: 1. 2. 3. 4. ii. sepals 1. Location: 2. Structure: 3. Function: iii. Petals Per:_____ 1. Location: 2. Structure: 3. Function: iv. stamens (Male structure of the flower) 1. Location: 2. Structure: made of 2 parts i. Filamentii. Anther3. Function: v. carpals (female structure of a flower) 1. Location: 2. Structure: made of 3 parts a. Stigma – b. Style – c. Ovary – 3. Pollination and fertilization a. Pollen Grain – i. How many sperm cells does pollen contain ii. What is pollen designed to do b. Pollination c. Pollination leads to sexual reproduction (whether it is self-pollination or cross-pollination) i. Cross-pollination – ii. Why is cross pollination a good thing? iii. Self-pollination – iv. Why is self pollination a bad thing? v. Some plants have mechanisms for preventing self pollination 1. flowers have only stamen and other flowers have only a carpel 2. Release pollens before or after the stigma of that flower is receptive to pollen. 3. genes that prevent self-pollination d. Fertilization- i. After the pollen grain lands on the stigma it grows a pollen tube, two sperms from the pollen grain travel through the pollen tube to get to the ovule. 4. Co-evolution of Flower Plants and Animal Pollinators a. Co-evolution - when two species are so closely related to each other when species changes, the second species will change in response. b. What organisms co-evolved with plants? i. Flowers attract animals in a variety of ways: 1. 2. 3. 5. Wind Pollinated Flowers a. Flower are not big, bright, colorful, scented, or filled with nectar b. Wind-pollinated plants produce huge quantities of pollen to insure that at least some of it lands on a female plant 6. Seed Dispersal a. After fertilization . . . i. The ovule develops a seed ii. The ovary develops into a fruit iii. Fruit b. Seeds from a plant can be dispersed in a number of ways i. 4 ways that seeds are dispersed by animals 1. 2. 3. 4. ii. Seed Dormancy 1. Dormancy – a. Advantages of Seed Dormancy: i. ii. b. What factors end seed dormancy? i. ii. 7. Seed Germination a. Germination – b. What do all seeds need to germinate? c. What happens when water is placed on a seed? d. What is the first part of a plant to emerge from the seed? 8. Asexual Reproduction (reproduction without seeds) a. Not all plants need seeds to reproduce i. Cuttings – ii. Grafting –