Energizing Energy Efficiency – Management Course
advertisement

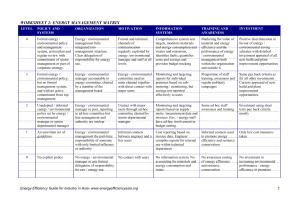
Energizing Energy Efficiency – Management Course Energy Efficiency Methodology, Workshop Exercise A – Meeting with Top Management Explanation of the Energy Management Matrix The Energy Management Matrix (“Matrix”) is shown in the next page. It can give an insight into the way a company manages its energy. The Matrix includes six energy management components: Policy & systems: does the company have policies and management systems for energy/ environment? Organization: are there organizational structures in place to facilitate energy/ environmental management? Motivation: are staff encouraged to improve energy/resource efficiency? Information systems: are information systems effective to measure and communicate energy/ environmental performance? Training & Awareness: are staff sufficiently trained and aware to be able to improve energy/ resource efficiency? Investment: is energy/ environment considered explicitly when investment decisions are made? For each component the company will be at level 0 (lowest), 1, 2, 3 or 4 (highest level). At the meeting with top management of a company (task 1a of the methodology), the assessor/auditor has to find out where on the Matrix this company is by asking questions for each component. Based on the answers a bullet is put in the right level, and a line is drawn to connect the bullets. The results of the Matrix can be used for: Task 1b: forming a team (maybe the team can be based on an existing energy / environmental committee) Task 1c: pre-assessment (after filling out the matrix you should know who to get information from and what information is available) Task 1e: preparing assessment proposal for top management approval (the results of the Energy Management Matrix will have an influence on the approach, the team, time planning and budget) Task 3b: identifying options (options to improve energy management at the company fall under “improved process management” options) Energizing Cleaner Production – Training Package 1 WORKSHEET 2: ENERGY MANAGEMENT MATRIX1 LEVEL 1 POLICY AND SYSTEMS ORGANIZATION MOTIVATION INFORMATION SYSTEMS TRAINING AND AWARENESS INVESTMENT 4 Formal energy / environmental policy and management system, action plan and regular review with commitment of senior management or part of corporate strategy. Energy / environmental management fully integrated into management structure. Clear delegation of responsibility for energy use. Formal and informal channels of communication regularly exploited by energy /environmental manager and staff at all levels Comprehensive system sets targets, monitors materials and energy consumption and wastes and emissions, identifies faults, quantifies costs and savings and provides budget tracking Marketing the value of material and energy efficiency and the performance of energy / environmental management both within the organisation and outside it. Positive discrimination in favour of energy / environmental saving schemes with detailed investment appraisal of all new build and plant improvement opportunities 3 Formal energy / environmental policy, but no formal management system, and with no active commitment from top management Energy / environmental manager accountable to energy committee, chaired by a member of the management board Energy / environmental committee used as main channel together with direct contact with major users Monitoring and targeting reports for individual premises based on submetering / monitoring, but savings not reported effectively to users Programme of staff training, awareness and regular publicity campaigns Same pay back criteria as for all other investments. Cursory appraisal of new build and plant improvement opportunities. 2 Unadopted / informal energy / environmental policy set by energy / environmental manager or senior departmental manager Energy / environmental manager in post, reporting to ad-hoc committee but line management and authority are unclear Contact with major users through ad-hoc committee chaired by senior departmental manager Monitoring and targeting reports based on supply meter /measurement data and invoices. Env. / energy staff have ad-hoc involvement in budget setting. Some ad hoc staff awareness and training Investment using short term pay back criteria mostly 1 An unwritten set of guidelines Energy / environmental management the part-time responsibility of someone with only limited influence or authority Informal contacts between engineer and a few users Cost reporting based on invoice data. Engineer compiles reports for internal use within technical department Informal contacts used to promote energy efficiency and resource conservation Only low cost measures taken 0 No explicit policy No energy / environmental manager or any formal delegation of responsibility for env / energy use. No contact with users No information system. No accounting for materials and energy consumption and waste No awareness raising of energy efficiency and resource conservation No investment in increasing environmental performance / energy efficiency in premises Modified from BRESCU (Building Research Energy Conservation Support Unit) and the Sustainable Energy Authority of Victoria, Australia, www.seav.vic.gov.au Energizing Cleaner Production – Training Package 1 Workshop exercise - AUDITOR This workshop exercise is a role play. One person is the auditor and 1 person is the company’s managing director. Below is the information for the auditor. You are the auditor and have a meeting with the company’s managing director. You have to determine how well the company manages energy by filling out the Energy Management Matrix. During the meeting, introduce yourself, and explain that you want to get an understanding of the company’s systems and processes that are in place to manage energy before you start with the energy assessment. Then you have to ask questions for each Matrix category. Suggested questions are included below, but you can also make up your own questions. Based on the managing director’s answers you can put a bullet in the matrix under each category and connect the bullets to draw a line. Suggested questions are: Policy & systems Is there a formal energy / environmental policy? (ask for a copy) Is there a formal energy / environmental management system (ask to see copy of manual, ISO 14001 certificate) What role does top management play? Organization Is there a person or department responsible for energy / environmental management? (ask for name, title and department, and if this person reports to management) Is there an official committee that deals with energy / environmental issues? (ask name of committee, who is in it, if a management representative is in this committee, are meeting minutes prepared). What role does top management play? Motivation How are staff motivated to come up with new ideas for energy / environmental improvements? (ask what type of communication like meetings, newsletters, notice boards; who communicates with staff; which staff are covered) Does the company give rewards or recognise staff for good ideas? (ask how) What role does top management play? Information systems What energy / environmental data are collected? (ask if this covers: energy, greenhouse gas emissions, materials, water, waste, other emissions; ask if it covers quantities, costs, savings) How are data collected (from supplier invoices meters or measured by the company) and at what level (at plant level or for each department / production process also) and how often (daily, monthly, quarterly, annually)? Energizing Cleaner Production – Training Package 1 - What information is reported to top management (how, by whom and how often, e.g. Monthly Management Report, ask for a copy!) and what does management do with this information (e.g. set targets, determine future energy consumption, give feedback to departments)? Training and awareness Is there training for staff on energy / environmental management and conservation? (ask who is trained, what the training is about, who gives the training) Is there awareness raising for staff on energy / environmental management and conservation? (ask how awareness is raised, what the awareness is about, for which staff, who does the awareness raising) Is there marketing of the importance and results of energy and environmental management outside the organization? (ask to whom, how often, how this is done, does this include energy and greenhouse gas emissions) Investment What is the process for evaluating and approving projects? (ask who needs to approve, are there any standard forms or procedures, how long this takes, if it needs to coincide with budgeting process) What criteria are used for the evaluation of any projects (e.g. impact on safety, labour and product quality, investment costs, savings, payback period, ease of implementation etc)? Are energy and greenhouse gas emissions considered in all project evaluations? What are the minimum criteria that a project (including an energy project) must meet? (ask maximum investment, maximum pay back period e.g. 2 years, so that you know if you can look at all options later, or maybe just as low cost options with a short payback period) Have there been projects that were not implemented? (ask why!) Energizing Cleaner Production – Training Package 2 Workshop exercise – COMPANY’S MANAGING DIRECTOR (1) This workshop exercise is a role play. One person is the auditor and 1 person is the company’s managing director. Below is the information for the managing director of a multinational company. You are the company’s Managing Director and have a meeting with an auditor who wants to carry out an energy assessment of your plant. You don’t know what he will be asking, but your answers should be based on the information about your company provided below. Your plant is based in a developing country and part of a multinational from Europe and employs 570 staff. Head office has been making environmental management a priority over the last years and wants you to do more in this area. So far you have a written environmental policy that also covers energy and that was signed by yourself. You also have appointed an Environmental Manager who is part of the Production Management Team and reports directly to you. This committee is responsible for informing senior management about production aspects, including environmental performance, through meeting minutes and the monthly Management Reports. However, you rely on departmental team meetings for improvement suggestions. All environmental and energy improvement options have to go through the regular decision-making process, require approval by the Senior Management Team and are treated the same as other investments. One important criterion is that the payback period is less than 2 years, except for options that cost less than US$5000. For example, a proposal to install a new crusher was rejected because the investment costs were too high and the payback period was almost 5 years. You are implementing an environmental management system in accordance with ISO 14001 because this is required by head office, but this will not be ready until early next year. The existing information system already includes the collection and reporting in the Management Report of key environmental and energy data and costs. These data are monitored for each department, such as fuel and electricity consumption, water usage, but no data is gathered for waste and emissions. There are also targets for each parameter and energy use is now a selection criterion for all investment decisions. There is an extensive training program for senior management but it is left to the department heads to organize training for staff if needed and the department heads should also make staff aware of the importance of energy and environmental management, although at this stage this is rather informal and infrequent. Communication is limited to within the company and you report to head office and local authorities only what is strictly necessary. You are simply too busy to communicate with anybody else. Energizing Cleaner Production – Training Package 3 Workshop exercise – COMPANY’S MANAGING DIRECTOR (2) This workshop exercise is in the form of a role play. One person is the auditor and one person is the company’s managing director. Below is the information for the managing director of a small/medium family-owned business. You are the company’s Managing Director and have a meeting with an auditor who wants to carry out an energy assessment of your plant. You don’t know what he will be asking, but your answers should be based on the information about your company provided below. Your plant is a family-owned business since five generations located in a developing country with about 80 staff. As competition is fierce you have to be focused on reducing costs all the time, and energy is a large proportion of your production costs. Therefore all staff know the senior management’s policy to reduce energy, although this was never formally put in writing. You are proud of your staff as they are very motivated to help reduce costs wherever they can. Staff are made aware of this during the monthly meetings that all staff and senior management attend, during team meetings and even during casual conversations between management and staff because you often walk through the plant. Suggestions to reduce energy and costs are raised frequently by staff even though it is not clear who should follow up on these. But you have implemented many options already. One month ago a staff member suggested turning off the fans inside the factory when the temperature was below 25oC and you rewarded him with a dinner voucher. Energy management is part of every staff’s task, although the Production Engineer takes a bigger role in energy management which has been included as one of his tasks in his job description. All staff receive training on a regular basis and this also covers energy and environmental issues because this is part of production. The existing information system collects key environmental and energy data and costs. These data are monitored for each department, such as fuel and electricity consumption, water usage, but no data is gathered for waste and emissions. There are also targets for each parameter although these are not written down. The data are included in monthly Production Reports of which management gets a copy for their information. Local authorities get information only when they ask for it so no one outside the company really knows about past efforts to improve energy and resource efficiency. As a relatively small family business it is more difficult to raise funds for investments in the plant. Therefore investments in options to improve energy efficiency have to pay themselves back quickly, preferably within one year. A consultant suggested to install Variable Speed Drives on the fans but this was simply too expensive and you are not sure if it actually would result in the high electricity savings that the consultant promised. This is different for investments to expand production because the demand for your product is high. Energizing Cleaner Production – Training Package 4 WORKSHEET 2: ENERGY MANAGEMENT MATRIX LEVEL POLICY AND SYSTEMS ORGANIZATION MOTIVATION INFORMATION SYSTEMS TRAINING AND AWARENESS INVESTMENT Formal energy / environmental policy and management system, action plan and regular review with commitment of senior management or part of corporate strategy. Energy / environmental management fully integrated into management structure. Clear delegation of responsibility for energy use. Formal and informal channels of communication regularly exploited by energy /environmental manager and staff at all levels Comprehensive system sets targets, monitors materials and energy consumption and wastes and emissions, identifies faults, quantifies costs and savings and provides budget tracking Marketing the value of material and energy efficiency and the performance of energy / environmental management both within the organisation and outside it. Positive discrimination in favour of energy / environmental saving schemes with detailed investment appraisal of all new build and plant improvement opportunities 3 Formal energy / environmental policy, but no formal management system, and with no active commitment from top management Energy / environmental manager accountable to energy committee, chaired by a member of the management board Energy / environmental committee used as main channel together with direct contact with major users Monitoring and targeting reports for individual premises based on submetering / monitoring, but savings not reported effectively to users Programme of staff training, awareness and regular publicity campaigns Same pay back criteria as for all other investments. Cursory appraisal of new build and plant improvement opportunities. 2 Unadopted / informal energy / environmental policy set by energy / environmental manager or senior departmental manager Energy / environmental manager in post, reporting to ad-hoc committee but line management and authority are unclear Contact with major users through ad-hoc committee chaired by senior departmental manager Monitoring and targeting reports based on supply meter /measurement data and invoices. Env. / energy staff have ad-hoc involvement in budget setting. Some ad hoc staff awareness and training Investment using short term pay back criteria mostly 1 An unwritten set of guidelines Energy / environmental management the part-time responsibility of someone with only limited influence or authority Informal contacts between engineer and a few users Cost reporting based on invoice data. Engineer compiles reports for internal use within technical department Informal contacts used to promote energy efficiency and resource conservation Only low cost measures taken 0 No explicit policy No energy / environmental manager or any formal delegation of responsibility for env / energy use. No contact with users No information system. No accounting for materials and energy consumption and waste No awareness raising of energy efficiency and resource conservation No investment in increasing environmental performance / energy efficiency in premises 4 Multinational Family owned Energizing Cleaner Production – Training Package 5