Web Science Tea Discussion Topic: Feb 29, 08 Milena Mihail
advertisement

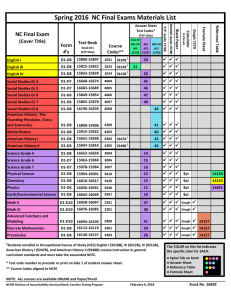
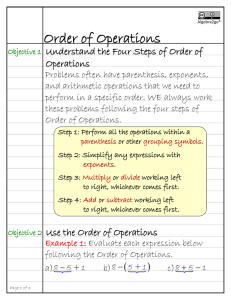
Web Discussion Science Topic: Tea Feb 29, 08 Milena Mihail mihail@cc.gatech.edu 1 Elsewhere : What is Web Science ? Our grassroots discussions : Includes some intersection of comp sci, economics, social sci. Our non grassroots discussions : Super-Duper Data Center, ala Jeanette Wing Should revisit this point, in view of NSF-Google-IBM ? NSF : CDI Yahoo: Raghavan WWW06 Brachman GT talk Microsoft: New Cambridge Lab Jennifer Chayes Chris Klaus GT talk Parenthesis: MSN SemGrail 07 What is Web Science ? The study of the WWW, broadly defined. By virtue of the pervasiveness of the object of study. Systems-like science (like chemistry or biology). As opposed to “computer science” which is the study of “computation”, biology is the study of “life” from the cell to evolution to animals…. Should be studied in terms of its descriptive/predictive/explanatory/prescriptive analytic value. Parenthesis: MSN SemGrail 07 Why should there be Web Science ? Encourage collaboration across different areas. Something between the union and intersection of several areas. Need to establish common vocabulary, goals, problems. “Understanding the elephant versus the tail trunk”. Educate students for industry. Encourage academia to understand the study of the Web as a discipline. Parenthesis: MSN SemGrail 07 Themes cutting across subareas of Web science Long Tails / Economics / Culture Fractal Nature, multi-scale Dynamics, emergent systems, social networks Requires new analytics (eg what are right logics, probabilistic and approximation metrics) Humans and machines interact and interactions registered. New dimension in social sciences. Transformed way we think about information (analogy to introduction of printing press). Democracy of information, producers and consumers of information coincide. (in this spirit) What is Web Science ? Outline: Our grassroots discussions : Wide Range of intersection Models Includes some of Canonical Example: Modeling comp sci, economics, social sci.Small World Phenomenon Model Parameters/Metrics and their Relevance Models : Structural Explanatory (Optimization or Incentive Driven) Hybrid Which question are you (am I) trying to answer? Range of Models (nice pictures with some meaning) Internet (general) Routing Internet AS Level Routing Level few long links in a flat world Sparse Power Law Graphs with very different assortativity Range of Models (nice pictures with some meaning) Patent / co-author network in Boston area notice bottleneck bad cut Flickr social network from Flickr search keyword “graph” notice no botlleneck bad cut ( Range of Flickr Pictures - meaning ? ) Technology Platforms Local Facebook Friendship Graph A Wep Page Organization 4 Color Theorem Range of Models Biological Networks with unclear meaning, but make front page of Nature/Science/PNAS Range of Models (nice pictures with no meaning) Range of Mathematical Models Rick Durrett, Cornell, Probabilist n Canonical Example: Modeling the Small World Phenomenon Clustering and Small Diameter Milgram’s Experiment 60’s : Even though relationships are highly clustered, most people are pairwise reachable via short paths, “Six Degrees of Separation” (for fun, see also Facebook group) Strogatz&Watt’s Model 80’s: In a clustered graph of size n, a few random links decrease the diameter to logn. Kleinberg 90’s: Navigability ! These short paths can be found efficiently with local search! Kleinberg’s navigability model Theorem: Are there natural network models which are navigable The onlyand value have, for eg, which power-law degree distributions ? the network is navigable is r =2. Are there natural models where the threshold is not sharp ? 14 Model Parameters/Metrics (as a function of n) and their Relevance Important to have FLEXIBLE network models eg in Prediction / Simulation economics engineering Average degree and Degree distribution Evolving toward monopolies/oligopolies? Clustering coefficient (small dense subgraphs) Assortativity Diameter Expansion/Conductance (bottlenecks) Can it be searched, crawled efficiently? Can pagerank be computer efficiently? Can it route with low congestion? Does it support efficient info retrieval? How does information/technology spread? Eigenvalues, eigenvectors (quantify bottlenecks and find groups efficiently) Structural / Macroscopic Models Random graphs with desirable graph properties, thought to be aggregating all microscopic primitives Example 1: Power Law Random Graph Given Choose random perfect matching over Example 2: Growth & Preferential Attachment One vertex at a time New vertex attaches to existing vertices Example 2, generalization towards flexibility: Some evolutionary random graph models may also capture more factors, e.g, geography, and hence varying conductance. Explanatory / Microscopic Models / Optimization Driven Example: HOT, evolutionary, new node attaches by minimizing cost and maximizing quality of service Point: Optimization primitives can yield power law distributions. Explanatory / Microscopic Models / Incentive Driven Example: A Network Formation Game How fast can such a stable configuration be reached? Hybrid Models RANDOM DOT PRODUCT GRAPH MODEL Example 1: Example 2: SUMMARY It is important to identify critical metrics and parameters ie, how they impact network performance. It is important to develop models where critical parameters vary and flexible network models. It is important to identify network primitives related to optimization and incentives. It is important to develop mechanisms that affect such primitives. 24 HOW ABOUT YOU ? WHICH QUESTIONS DO YOU WANT TO ANSWER ?