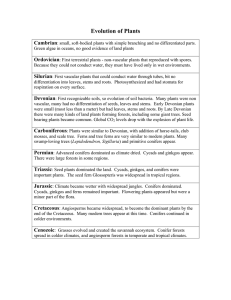
The Geologic History of New York State The Acadian Orogeny Devonian Strata
advertisement
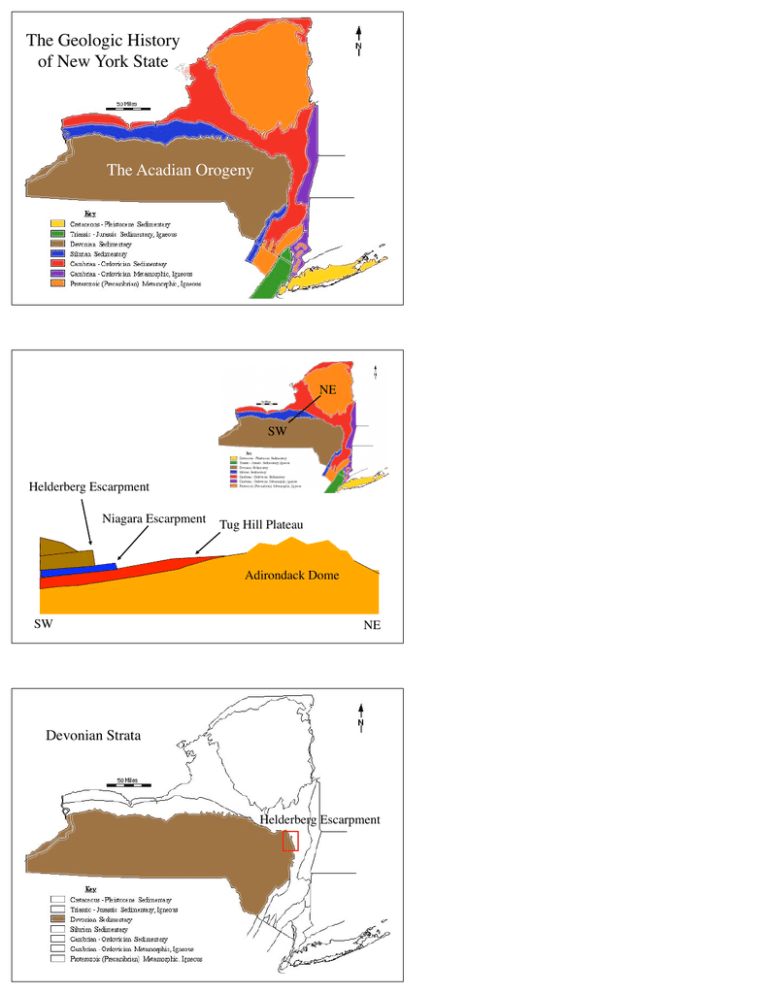
The Geologic History of New York State The Acadian Orogeny NE SW Helderberg Escarpment Niagara Escarpment Tug Hill Plateau Adirondack Dome SW NE Devonian Strata Helderberg Escarpment Helderberg Escarpment John Boyd Thatcher State Park Lower Devonian - Coeymans Fm. Limestone Lower Devonian - Manlius Fm. Limestone Upper Silurian - Rondout Fm. Dolostone Algal mat laminae - tidal flat deposits in the Manlius limestone Lower Devonian Coeymans Limestone Lower Devonian coral reefs Onondaga limestone, Leroy, NY Devonian seascape Middle Devonian Hamilton Group Shales and Siltstones Middle Devonian Hamilton Group Shales and Siltstones Middle Devonian Hamilton Group Brachiopod and Nautiloid Middle Devonian Hamilton Group Pelecypod Middle Devonian Hamilton Group Trilobite Devonian Strata Catskill Mts. Catskill Mountains horizontal strata Catskill Group River channel sandstone Flood plain redbeds Upper Devonian Evolution of seed plants, trees, and forests Gilboa fossil forest tree stumps, Catskills Wattieza attached to Eospermatopteris Devonian Strata Letchworth Gorge Letchworth Gorge, western New York Upper Devonian sandstones, siltstones, and shales Letchworth Gorge Western New York regression Simplified mid-Paleozoic Stratigraphy of New York Upper Devonian Terrestrial Active Margin Nearshore Middle Devonian transgression Catskill Group Hamilton Group Basin Lower Devonian Silurian Shallow Water Coeymans - Onondaga Manlius - Limestones Tidal Flat Rondout Carbonates Passive Margin Acadian Orogeny • Middle - Upper Devonian • Collision of N.Am with Avalonia (continental fragment associated with Baltica (northern Europe). • Rising Acadian Mountains to the east create a deepening foreland basin in New York. • Erosion of the Acadian Mountains fills in the basin with a thick sequence of clastic sediments. • Catskill Clastic Wedge Middle Devonian 390 Ma Devonian Strata A’ A Catskill clastic wedge - a filled-in foreland basin A’ A Evidence for the Acadian Orogeny • Deposition of shale, siltstone, sandstone, conglomerate - Catskill Delta. • Devonian-age metamorphism in New England and Virginia. • Regions of pre-Devonian rock in New England with European fossils (exotic, accreted terrains). 0 Ma Phanerozoic Modern Geologic Time Scale C M P Neogene Tertiary Pleistocene Paleogene Cenozoic Proterozoic Pliocene Miocene Oligocene Eocene Paleocene Cretaceous Mesozoic 2500 Ma Holocene Quat. 540 Ma Jurassic Triassic Archean 3800 Ma Carb. Paleozoic Permian Pennsylvanian Mississippian Devonian Silurian Ordovician Cambrian Ma 0 .01 1.6 5 23 35 57 65 146 208 245 290 323 360 408 439 510 540 Hadean 4600 Ma Quat. = Quaternary Carb. = Carboniferous Acadian Orogeny Passive margin Taconic Orogeny Passive margin Mississippian Period • Few Mississippian age rocks preserved in NY. • Deposition of limestone alternating with nearshore shale and shoreline sandstones across much of eastern North America. • Passive margin conditions after erosion of Acadian mountains. Pennsylvanian Period • Alleghenian Orogeny • Collision of N.Am with Africa. • Part of the assembly of Pangea. • Not preserved in New York State, except for some possible Alleghenian folds in older rock strata. • Age of coal-forming swamps - hot, humid conditions across Europe and Eastern North America. Evidence for the Alleghenian Orogeny • Little evidence in New York. • Foreland basin filled with clastic sediments - Ohio, West Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee. • Folding and thrust faulting of pre-Permian strata from Pennsylvania to Georgia. • Pennsylvanian metamorphism east of folded rock. Coastal Plain Blue Ridge Plateau Miss.-Penn. Sandstone / shale Valley and Ridge Prot. - Miss. folded and thrust faulted sedimentary rock Piedmont Paleozoic metamorphic rock Coastal Plain Blue Ridge Plateau Foreland basin filled with sediments eroded from east. Valley and Ridge Slices of crust shoved westward by collision. Piedmont Deeply buried roots of the Alleghenian mountain range. Folds and thrust fault in Lower Devonian carbonates, Catskill Front Mmmm…. Fresh outcrop…. Carboniferous Sea Level Cycles • High amplitude transgression-regression cycles. • Cyclothems: repeating deposits alternating between marine and terrestrial deposition. • Coal swamps formed during beginning of transgression. • Coals flooded by marine waters. • Thick sandstone layers deposited during regression. coal sideritic silty shales regressive limestone core shale transgressive limestone Middle Pennsylvanian marine interval 0 Ma Phanerozoic Modern Geologic Time Scale C M P Neogene Tertiary Proterozoic Pliocene Miocene Oligocene Eocene Paleocene Cretaceous Mesozoic 2500 Ma Pleistocene Paleogene Cenozoic Grenville Orogeny Holocene Quat. 540 Ma Jurassic Triassic Archean 3800 Ma Carb. Paleozoic Permian Pennsylvanian Mississippian Devonian Silurian Ordovician Cambrian Ma 0 .01 1.6 5 23 35 57 65 146 208 245 290 323 360 408 439 510 540 Hadean erosion Alleghenian Orogeny Passive margin Acadian Orogeny Passive margin Taconic Orogeny Passive margin Quat. = Quaternary Carb. = Carboniferous 4600 Ma Permian Period • No Permian rock preserved in New York. • Assembly of Pangea completed. • Sea floor spreading stops - worldwide regression. • Global climate is arid to seasonally wet. • Massive volcanic eruptions in Siberia. • Permian ends with largest mass extinction ever - up to 95% of all species go extinct over several million years. • Triassic begins with a world depleted in species.