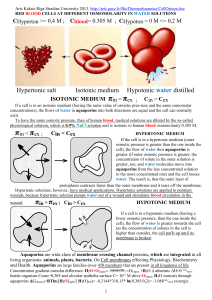
PHYSIOLOGICAL ROLES OF AQUAPORIN-4 IN BRAIN
advertisement

Physiol Rev 93: 1543–1562, 2013 doi:10.1152/physrev.00011.2013 PHYSIOLOGICAL ROLES OF AQUAPORIN-4 IN BRAIN Erlend A. Nagelhus and Ole P. Ottersen Centre for Molecular Medicine Norway, Nordic EMBL Partnership, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway; Letten Centre & Department of Physiology, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway; Oslo University Hospital, Department of Neurology, Oslo, Norway; and Department of Anatomy, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway Nagelhus EA, Ottersen OP. Physiological Roles of Aquaporin-4 in Brain. Physiol Rev 93: 1543–1562, 2013; doi:10.1152/physrev.00011.2013.—Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) is one of the most abundant molecules in the brain and is particularly prevalent in astrocytic membranes at the blood-brain and brain-liquor interfaces. While AQP4 has been implicated in a number of pathophysiological processes, its role in brain physiology has remained elusive. Only recently has evidence accumulated to suggest that AQP4 is involved in such diverse functions as regulation of extracellular space volume, potassium buffering, cerebrospinal fluid circulation, interstitial fluid resorption, waste clearance, neuroinflammation, osmosensation, cell migration, and Ca2⫹ signaling. AQP4 is also required for normal function of the retina, inner ear, and olfactory system. A review will be provided of the physiological roles of AQP4 in brain and of the growing list of data that emphasize the polarized nature of astrocytes. L I. II. III. IV. V. VI. VII. VIII. IX. X. XI. INTRODUCTION STRUCTURE, ISOFORMS, SELECTIVITY POLARIZED DISTRIBUTION REGULATION WATER AND WASTE CLEARANCE EXTRACELLULAR VOLUME DYNAMICS POTASSIUM HOMEOSTASIS NEURONAL EXCITABILITY SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY AND BEHAVIOR SENSORY SYSTEMS CONCLUSIONS 1543 1546 1548 1548 1550 1550 1552 1554 1555 1555 1556 I. INTRODUCTION In 1992, Agre and co-workers (148) discovered that red blood cells contain a membrane protein that confers high water permeability. This protein, later called aquaporin-1 (AQP1), turned out to be a member of a large family of water channel proteins that allow bidirectional transport of water across the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane (77). The phospholipid bilayer shows low water permeability, depending on lipid composition, temperature, and cell type (173). The discovery of the aquaporins marked the end of a longstanding conundrum in biology and paved the way for a molecular understanding of secretion and absorption processes in animals and plants alike. Notably, with the identification of aquaporin-2 (AQP2), it soon became possible to describe in molecular terms how the kidney regulates urine production and thus helps maintain systemic fluid balance (128). In 1994, Agre’s and Verkman’s groups independently reported that the brain expresses a specific aquaporin cDNA in rather high amounts (58, 74). This aquaporin, dubbed mercury-insensitive water channel (MIWC) by Verkman’s group and later renamed AQP4, was immunolocalized to ependymocytes and astrocytes throughout the brain (42, 129) (FIGURE 1). Immunogold cytochemistry revealed that AQP4 was particularly enriched in those astrocytic plasma membrane domains that abut on brain microvessels or on the pial covering of the brain surface (129). AQP4 was also contained in perisynaptic astrocytic processes, but at far lower concentrations. In other words, astrocytes stood out as highly polarized cells, not only with regard to their anatomy, but also in terms of protein expression. The finding that AQP4 is concentrated to perivascular and subpial endfoot membranes helped solve an enigma that had been around for decades: the nature of the conspicuous assemblies of intramembranous particles that cover much of the astrocytic endfoot membranes in freeze fracture replicas (FIGURE 2). These assemblies, originally discovered by Dermietzel (30), were termed orthogonal arrays of particles (OAPs) or square arrays (199, 200). The identity of the component protein remained unknown until it was found that square arrays were absent from endfoot membranes of Aqp4⫺/⫺ animals and that square arrays could be produced in ovary cells following transfection with Aqp4 mRNA (193, 201). More recently, square arrays have been demonstrated also in transfected oocytes (40). The idea that square arrays represent semicrystalline clusters of AQP4 was bolstered by freeze fracture immunogold labeling (151). The very dense expression of AQP4 at the blood-brain interface 0031-9333/13 Copyright © 2013 the American Physiological Society 1543 ERLEND A. NAGELHUS AND OLE P. OTTERSEN Arachnoid AQP4 Artery CSF Pia Endfoot Astrocyte Synapse A AQP4 Endfoot B Capillary Laminin Out Basal lamina Agrin AQP4 α-DG β-DG In NH2 DP -7 1 Actin C PDZ α-Syn SXV COOH Ependyma PDZ α-Syn α-DB D FIGURE 1. Distribution of AQP4 in brain. A: electron micrograph showing distribution of AQP4 immunogold reactivity in cerebellar cortex. Gold particles signaling AQP4 are seen over glial membranes, with highest density over subpial endfoot membranes (double arrowheads). Glial membranes ensheathing synapses (arrowhead) also contain AQP4 but in more modest amounts. Inset displays the principle of immunogold cytochemistry. B: high-magnification micrograph of the blood-brain interface confirms that AQP4 is restricted to glia and has a polarized distribution. The highest density of AQP4 is found along the perivascular glial endfoot membrane (arrow). Labeling obtained by preembedding immunogold cytochemistry. Asterisk denotes vessel lumen. [A and B from Nielsen et al. (129).] C: AQP4 is anchored to the perivascular basal lamina by the dystrophin-associated protein complex (DAPC), consisting of ␣-syntrophin (␣-Syn), ␣-dystrobrevin (␣-DB), the 71-kDa isoform of dystrophin (DP71), -dystroglycan (-DG), and ␣-dystroglycan (␣DG). The COOH-terminal SXV-sequence of AQP4 interacts directly or indirectly with the PDZ domain of ␣-syntrophin. ␣-Dystroglycan is attached to the basal lamina by direct binding to laminin as well as through agrin. O-glycosylation of ␣-dystroglycan is necessary for extracellular matrix ligand binding. D: schematic illustration of AQP4 expression in brain. AQP4 (blue symbols) is expressed in astrocytes and ependymocytes. 1544 Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org Ventricle AQP4 IN BRAIN A Hemipore-1 A Out B Hemipore-2 C C Extracellular side E P N A 1 2 3 4 5 In B W1 6 N P R216 A HE D H2N Out 1 2 A N P P 5 N A + HB In H2N HOOC B N N 4 3 35.3 W W3 + C E 4.6 O=C COOH A 6 O=C D O=C 34.8 W5 13.2 O=C 2.9 O=C 5.9 O=C 11.6 W8 Hourglass Cytoplasmic side D E F AQP4 square array Monomer Tetramer FIGURE 2. AQP4 structure and plasma membrane organization. A: proposed membrane topology based on the hourglass model for aquaporins. AQP4 has six bilayer-spanning domains and five connecting loops (A–E). Loops B and E contain highly conserved Asn-Pro-Ala (NPA) motifs that overlap midway between the leaflets of the bilayer, creating a narrow aqueous pathway (74). B: molecular surface of monomeric AQP4, with carbon in gray, oxygen in red, nitrogen in blue, and sulfate in yellow. The water molecules are shown as red spheres. C: diagram showing AQP4 with eight water molecules (W1–W8). The narrowest constriction of the pore is located close to the extracellular entrance and is ⬃2.8 Å in diameter, i.e., identical to the diameter of a water molecule (196). Arg216 is part of this constriction site. The HE and HB hemipores, shown as rods with their electrostatic dipoles in blue and red, form an electrostatic field that causes water molecules to take opposite orientations in the two half channels. The water molecules form hydrogen bonds with neighboring water molecules or with main chain carbonyl oxygens. The channel does not conduct protons, since the central water molecule forms transient hydrogen bonds with the two amide groups of the Asn residues and thus prevents the water molecules from serving as a proton wire. D: tetrameric organization of AQP4 shown in ribbon diagram with lipids in ball-and-stick representation and the water molecules as red spheres. [B–D from Tani et al. (184). Copyright 2009, with permission from Elsevier.] E: AQP4 tetramers cluster in the plasma membrane as square arrays, also termed orthogonal arrays of particles (OAPs). F: freeze-fracture electron micrograph of OAPs in an astrocyte membrane. [From Wolburg et al. (200). Copyright 2011, with permission from Elsevier.] prompted the hypothesis that this AQP4 pool controls the flux of water between blood and brain. Supporting this idea, Verkman’s group found that postischemic brain edema was much reduced following Aqp4 knockout (99). That this effect was coupled specifically to the endfoot pool of AQP4 was demonstrated in two different models that allowed for a near-selective depletion of perivascular AQP4. Both models were based on the finding that AQP4 is enriched in perivascular endfoot membranes through anchoring to the dystrophin-associated protein complex (DAPC) (43, 116). Va- jda et al. (192) demonstrated reduced edema formation in mdx animals that lack dystrophin. In the second model, Amiry-Moghaddam et al. (4) reported a 50% decrease in edema volume following knockout of the gene for ␣-syntrophin, a dystrophin associated protein shown to be the immediate anchor of AQP4 (116). Recently, reduced edema formation was also reported in a glial-conditional Aqp4 knockout line (55), confirming that the pool of AQP4 that facilitates edema formation resides in astrocytes and not in other cell types, such as endothelial cells. Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org 1545 ERLEND A. NAGELHUS AND OLE P. OTTERSEN The more we have learned about the pathophysiological roles of AQP4, the more obvious has become the void in our understanding of the physiological roles of this protein. The original knockout studies revealed but minor perturbations of normal function, coupled essentially to the kidney (mild urinary concentrating defect) (94), retina (abnormal electroretinogram) (85), and inner ear (partial hearing loss) (86). The contrast between brain and kidney was striking: while the discovery of aquaporins rapidly transformed our concept of kidney function, the identification of AQP4 in brain largely advanced our insight in the realm of pathophysiology (5, 11, 13, 163, 194). The elucidation of physiological roles of AQP4 in brain had to await the development and application of new experimental approaches. II. STRUCTURE, ISOFORMS, SELECTIVITY AQP4 belongs to the aquaporin subfamily that is selectively permeable for water (77). Thus AQP4 stands out from the aquaglyceroporins, which transport glycerol and other molecules in addition to water. The high selectivity for water is determined by three specializations along the channel of the AQP4 monomer (2, 63, 64, 184) (FIGURE 2). First, the pore in each monomer narrows to ⬃2.8 Å, effectively excluding molecules larger than water (196). Second, the pore region contains an arginine residue that serves to block the entrance of protonated water and other cations (184). Third, positively charged dipoles near the midpoint of the channel prevent proton flow and cause the water molecules to reorient (184). Molecular dynamics simulations indicate that the features of the AQP4 pore allow for highly efficient and selective water transport (27, 197). This prediction has been borne out in multiple experimental systems, including frog oocytes (40, 58, 74, 169, 173). A number of AQP4 isoforms have been described (58, 74, 109, 158, 175). The two classical isoforms M1 and M23 are transcribed from two different initiation sites on the same gene. These isoforms show similar water transport capacities when expressed in Xenopus oocytes (74). However, the shorter transcript (M23, with 301 amino acids) differs from the longer transcript (M1, with 323 amino acids) by its ability to form square arrays (24, 46, 177, 179). Moe et al. (109) described six cDNA isoforms of Aqp4, formed by alternative splicing. These were named Aqp4a-f, with Aqp4a corresponding to M1 and Aqp4c corresponding to M23. One of the novel isoforms (AQP4e) contained a distinct NH2-terminal domain and was found to transport water when expressed in Xenopus oocytes (40). The cDNA isoform Aqp4e appears to correspond to Aqp4 Mz which is found in the rat brain but not in brains of mice or humans (158). In rat, AQP4 Mz was immunolocalized to endfoot membranes and found to be integral parts of OAPs (158). Recently, Sorbo et al. (175) isolated a 36-kDa and a 38-kDa 1546 AQP4 isoform from rat brain. The relationship between these two isoforms and the cDNA isoforms previously described remains to be determined. Similar to other aquaporins, AQP4 forms tetramers when assembled in plasma membranes (117, 123) (FIGURE 1D). Each tetramer will have a central pore. There are indications that the central pore could mediate gas transport. Thus transfection of oocytes with Aqp4 mRNA increased membrane permeability for CO2 and NH3 (111). Molecular dynamics simulations suggest that gas transport must occur through the central pore rather than the monomer channels (197). Naturally, gas permeation through AQP4 tetramers would be physiologically relevant only if exceeding permeation through the lipid bilayer that the tetramers are embedded in and displace. Membranes differ considerably when it comes to gas permeability, depending on lipid composition (21, 71, 147). The gas permeability of astrocytic endfoot membranes is not known. Thus it is difficult to predict whether the huge accumulations of square arrays in endfoot membranes provide a net increase or net decrease in gas transport capacity at the blood-brain interface. Adding to the complexity, unstirred layers on cell surfaces may confound measurements of gas transport across cell membranes. Notably, a thick, unstirred layer may show a diffusion resistance that exceeds that of the membrane itself (35). The only in vivo study addressing the role of AQP4 in gas transport is that of Thrane et al. (186). Using NADH fluorescence as a proxy, the latter study recorded oxygen deficit in brain neuropil during cortical spreading depression. Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice showed a more pronounced oxygen deficit in micro-watershed areas than did wild-type controls. The most seminal explanation is that depletion of AQP4 reduces oxygen diffusion from brain microvessels to nerve tissue. Given the close similarities between AQP1 and AQP4, studies on gas transport through AQP1 might inform the current debate on AQP4-mediated gas transport. Molecular dynamics simulations (67, 196) concluded that significant transport of CO2 through AQP1 is to be expected only in membranes with low intrinsic CO2 permeability. Furthermore, the free energy barrier of CO2 permeation was found to be smaller for the central pore than for the monomeric channel (196). This stands in apparent contrast to the finding that HgCl2 prevents CO2 permeation (17), as HgCl2 is known to specifically affect transport through the monomeric channel. It should be noted that Fang et al. (39) found no evidence of CO2 transport through AQP1. In line with earlier studies in AQP1-depleted erythrocytes and AQP1containing liposomes, experiments on lung and kidney were not indicative of any AQP1-mediated CO2 permeation (39). Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org AQP4 IN BRAIN CO2 transport between alveoli and blood was measured from changes in air-space fluid pH in response to addition or removal of HCO3⫺ from the pulmonary artery perfusate. With this approach, Aqp1 knockout animals did not differ from wild-type controls. The central pore of the AQP1 tetramer has been implicated in ion transport (8, 205). Using primary cultures of rat choroid plexus, Boassa et al. (20) observed that AQP1 is associated with a cGMP-gated cationic conductance. They found that this conductance is activated by an endogenous receptor guanylate cyclase for atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), and that it is blocked after targeted knockdown of AQP1 by small interfering RNA (siRNA). The data indicated that tetrameric AQP1 can function as a water channel as well as a gated ion channel. In conclusion, the tetrameric organization of AQP4 opens for the possibility of gas and ion permeation through the central pore, thus complicating the issue of substrate specificity. More work is needed to resolve the nature and permeability of the central pore. The properties of this pore are of particular interest, given the abundance of AQP4 tetramers at the blood-brain interface. Transport of ions, gases, or signaling molecules through these pores may affect local blood flow and directly or indirectly influence exchange of substrates between blood and brain. As noted above, AQP4 tetramers form higher order structures called OAPs or square arrays (FIGURE 1, E AND F). Square arrays are formed primarily by the M23 isoform of AQP4 (40, 46, 169). The extended NH2 terminus of M1 serves to inhibit square array formation. Palmitoylation plays a critical role in this regard, as mutations of cysteine in positions 13 and 17 (the residues normally subject to palmitoylation) render the M1 isoform capable of generating square arrays (179). The Mz isoform does not form square arrays on its own (40), but does so when coexpressed with M23 (158). Also, recent studies indicate that M1 may be incorporated in square arrays, specifically at their peripheries (159). The square arrays in astrocytic endfeet are truly imposing structures when viewed in freeze-fractured replicas. In endfoot membranes, the density of these arrays is typically in the range of 500 – 600/m2 (199). As astrocytic endfeet form a continuous sheath around brain microvessels (101) (FIGURE 3), square arrays represent a substantial fraction of the blood-brain interface. The specific function of square arrays is still a matter of conjecture. As AQP4 channels are assumed to be constitutively open (see sect. IV), their concentration into square arrays should secure a very high capacity for water transport across the endfoot membrane. It is difficult to envisage why such a high capacity should be required for resorption FIGURE 3. The perivascular astroglial sheath provides a complete covering of brain microvessels. A: electron microscopic image of capillary with four endfoot profiles (pve I–IV). The hatched area (enlarged in B) shows endfoot-endfoot overlap. The double arrow in B represents the projection of the overlap, while the black arrow indicates the angle of view in C. C: 3D reconstruction. Endfoot IV is removed to view the remaining endfeet from the inside of the vessel. In the hatched frame, enlarged in D, endfoot I (pve I) is made semitransparent to visualize the underlying endfoot III (pve III). The space between the two rows of arrowheads represents the extent of overlap. E: definition of the intercellular cleft length (IC) and the length of its projection (P). F: a semitransparent 3D reconstruction of a perivascular endfoot (pve I) seen from an abluminal perspective. The footplate is complete and covers about half the circumference of the vessel wall. Elongated mitochondria (green, red, and yellow) enter the endfoot tangentially through the left process (asp) and leave through four processes on the right hand side. Scale bar ⫽ 1 m unless otherwise indicated. [Modified from Mathiisen et al. (101), copyright 2010. This material is reproduced with permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.] Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org 1547 ERLEND A. NAGELHUS AND OLE P. OTTERSEN of extracellular fluid or for facilitating clearance of macromolecules from brain interstitium, two physiological functions attributed to endfoot AQP4 (55, 69, 140). The abundance of AQP4 molecules at the blood-brain interface would be easier to explain if this AQP4 pool helped optimize gas exchange between blood and brain (186) or if it served an adhesive function. As to the latter hypothesis, it is worth pointing out that AQP4 has been described as an “adhennel” since it may do double duty as a channel and an adhesion molecule (36, 63, 65, 184). However, so far the adhesive role of AQP4 has been discussed only in the context of AQP4-AQP4 interactions, i.e., in anatomical settings where two AQP4-containing membranes are opposed to one another (129). This setting is not found at the blood-brain interface where the AQP4-laden endfoot membrane faces the extracellular matrix of the pericapillary basal lamina. It should be noted that transfection of Aqp4 into CHO-K1 and FRT cells failed to increase cell-cell adhesion (214). Also, adhesion between primary astrocytes was insensitive to Aqp4 knockout (214). In conclusion, while the structure-function relationship is well established for AQP4 monomeric channels, the physiological role of the central pore (in AQP4 tetramers) remains to be clarified. There is also a need to elucidate the physiological implications of the higher order structure of AQP4 at the blood-brain interface. None of the physiological functions attributed to the endfoot pool of AQP4 appears to demand the abundance of channel protein represented by the square arrays. III. POLARIZED DISTRIBUTION AQP4 is highly concentrated in astrocytic endfeet (42, 129), attesting to the polarized nature of astrocytes (FIGURE 1). An early quantitative immunogold analysis on retinal macroglia indicated that glial endfeet contain a 10-fold higher density of AQP4 than non-endfoot membranes (112, 114). The endfoot AQP4 pool is concentrated in the adluminal membrane (i.e., the membrane facing the perivascular basal lamina). Unlike lateral membranes of many types of epithelial cell, lateral membranes of astrocytes do not express tight junctions that can hinder diffusion of membrane molecules. Thus the concentration of AQP4 in adluminal endfoot membranes must depend on specific anchoring mechanisms. The first clue that the DAPC could be involved came with studies of mdx mice (44, 90, 202). These mice, which are deficient in dystrophin, showed reduced levels of AQP4 in skeletal muscles. Later, mdx mice were found to exhibit reduced expression of AQP4 also in astrocytic endfeet (43). Dystrophin in muscle and brain is associated with a number of proteins, including ␣-syntrophin (1, 116). Knockout of the gene for ␣-syntrophin caused a loss of AQP4 from endfoot membranes (4, 116), suggesting that ␣-syntrophin could be the immediate anchor 1548 of AQP4. Evidence in support of this was provided by biochemical analyses and coimmunoprecipitation experiments (116). It is now well documented that the entire DAPC is held in place through its attachment to laminin, a principal component of the pericapillary basal lamina (5, 49, 116, 131, 200). This mode of anchoring explains why the density of AQP4 drops as soon as the endfoot plasma membrane is reflected away from the capillary (114, 129). Knockout studies have confirmed that dystrophin with its associated proteins (␣-syntrophin, ␣-dystrobrevin, ␣- and -dystroglycan) play a central role in AQP4 anchoring (28, 37, 89, 116, 134) (FIGURE 1C). The involvement of the DAPC is also compatible with the observation of a reduced perivascular pool of AQP4 in animals with deficient O-glycosylation of ␣-dystroglycan (104, 162). Moreover, the matrix constituent agrin, which interacts with ␣-dystroglycan (47), is necessary for normal AQP4 expression in endfeet (132, 133, 154, 176). However, the anchoring model shown in FIGURE 1C is not alone responsible for the enrichment of AQP4 in endfoot membranes. Dystrophin-deficient mice exhibit a substantial pool of AQP4 in cerebellar astrocytes (125). Also, a residual endfoot pool of AQP4 is found in mice with targeted deletion of the gene for ␣-syntrophin (4, 34, 37). This residual pool is larger in retinal macroglia than in brain astrocytes, pointing to a heterogeneity in anchoring mechanisms (37). It has been proposed that the residual AQP4 pool depends on -syntrophin or another syntrophin isoform other than ␣-syntrophin (149). The clarification of this issue will have to await the development of appropriate knockout lines. Moreover, deletion of the gene for 1-integrin also affects perivascular AQP4 expression (156). IV. REGULATION Regulation by molecular gating mechanisms has been reported for plant aquaporins (59). The spinach plasma membrane aquaporin SoPIP2:1 is a case in point (188). X-ray structure analyses combined with molecular dynamics simulations indicate that SoPIP2:1 is closed when the intracellular loop D caps the channel and occludes the pore. It was suggested that this type of mechanism is conserved among most plasma membrane proteins in plants (196). According to the model proposed, channel closure is initiated by dephosphorylation of two conserved serine residues (Ser115 or Ser 274) or by protonation of a conserved histidine residue. Some problems remain with this model (196). Notably, it has yet to be demonstrated that Ser115 in SoPIP2:1 or a corresponding site in any other plant AQP is subject to phosphorylation. Plants are exposed to severe changes in their environment and need powerful mechanisms for preserving water under drought stress. By comparison, mammals have a well regulated milieu interne. Thus the mechanisms for aquaporin regulation need not be the same. Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org AQP4 IN BRAIN Indeed, despite substantial sequence homologies with plant aquaporins, evidence for bona fide gating of mammalian aquaporins has yet to be provided. AQP4 is endowed with a loop D (like SoPiP2:1) and with a number of phosphorylation consensus sites (208). However, it remains to be demonstrated whether closing of the channel can occur. This does not mean that AQP4 is exempt from short-term regulation: activation or inhibition of AQP4-mediated water flux has been reported in several experimental settings (208). Inhibition of AQP4 has been reported after phosphorylation of Ser180 (57, 102, 110, 209), and activation has been found after phosphorylation of Ser111 (50, 52). The conformational changes responsible for inhibition or activation of AQP4 are not known. Indeed, no changes were found in the structure of AQP4 following a mutation that mimicked phosphorylated Ser180 (107). No indications were found of an obstruction near the cytoplasmic pore entrance. Also, water permeability measurements did not reveal any differences between wild-type and mutant AQP4. A recent paper reported data that indicate a lack of phosphorylation-dependent gating of rat AQP4 (10). Inhibition by metals is an issue of particular relevance to aquaporins, including AQP4 (207, 208). One of the hallmarks of AQP1 and several other aquaporins is their sensitivity to mercury (77). Indeed, when AQP4 was first described, its lack of sensitivity to mercury was noted as an anomaly. Hence, the new protein was dubbed “mercuryinsensitive water channel” (58). Later it was realized that the lack of sensitivity to mercury was not due to absence of a mercury binding site (206). AQP4 does possess such a site, but this is found on an intracellular loop rather than extracellularly (as in AQP1), reflecting differential folding of the two proteins. Hence, when AQP4 molecules are reconstituted in liposomes at random orientation, inhibition is observed by external application of mercury (206). Aquaporins are also subject to regulation at the level of subcellular distribution (77). AQP2 is a classic example (22). Soon after the discovery of this protein, evidence was obtained that translocation of AQP2 is a primary mechanism underlying regulation of water reabsorption in kidney collecting ducts (127). This process is under the control of vasopressin 2 (V2) receptors and key to adjusting urine volume to water ingestion (78). Activation of V2 receptors causes a translocation of AQP2 from intracellular vesicles to the apical plasma membrane, thus allowing for an osmotically driven reabsorption of water from the collecting duct lumen. In perfusion-fixed brains, AQP4 is largely expressed in the astrocyte plasma membrane with no significant intracellular pool (129). Thus there is no evidence that translocation to the plasma membrane is involved in regulating AQP4mediated transport in the intact brain. In contrast, astrocytes in culture display significant pools of AQP4 in intracellular compartments. Several studies have addressed the mechanisms responsible for intracellular trafficking of AQP4 in cultured astrocytes (51, 124, 150, 157) or MDCK cells (98). These data will not be reviewed here. A recent study in oocytes indicates that AQP4 may be internalized following activation of V1 vasopressin receptors (110). The interaction between V1 receptors and AQP4 depended on protein kinase C (PKC) activation and the presence of wild-type Ser180. It remains to show whether activation of V1 receptors has similar effects in vivo. Previous studies have shown that V1 activation facilitates water transport in brain (130) and that V1 antagonists have a protective effect in postischemic brain edema (91). Thus there is still no coherent picture as to how vasopressin is involved in AQP4 regulation in brain. The level of AQP4 in astrocytic endfeet is much depressed following transient ischemia (45, 176). The reduction in AQP4 occurs with no concomitant changes in the level of ␣-syntrophin (45). This suggests that the binding between ␣-syntrophin and the cytoplasmic tail of AQP4 is sensitive to ischemia. Sudden loss of AQP4 occurred in regions of vascular damage and might serve to delimit the influx of water in the postischemic phase (41). In a similar vein, the protective effect of erythropoietin (EPO) against postischemic brain edema might relate to EPO’s ability to depress the plasma membrane pool of AQP4 (183). Loss of AQP4 from endfoot membranes is also found in epilepsy (33, 82), traumatic brain injury (155), and a model of Alzheimer’s disease (203). Generally, the polarized distribution of AQP4 is lost in reactive astrocytes (200). Loss of polarity can be due to reduced AQP4 in endfeet, but commonly also results from increased AQP4 expression in parenchymal membranes (200). Increased expression of AQP4 or Aqp4 mRNA has been found in numerous conditions, including bacterial meningitis (141), inflammation secondary to intraparenchymal injection of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) (187) or lysolecithin (190), subarachnoid hemorrhage (198), intracerebral hemorrhage (182), brain tumors (32, 135, 164), and hydrocephalus (100, 144, 168, 170, 189). It is still not known whether changes in surface expression of AQP4 occur under physiological conditions. In conclusion, while recent years have seen a burgeoning literature on AQP4 regulation, the picture is still far from complete. There is no evidence that mammalian AQP4 is subject to bona fide gating (i.e., switching between a closed and open state). Nor is there any evidence for AQP4 translocation between intra- and extracellular membrane domains of astrocytes under physiological conditions in situ. Numerous studies report up- or downregulation of water permeability following experimental manipulations targeting AQP4 phosphorylation sites. However, it still remains Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org 1549 ERLEND A. NAGELHUS AND OLE P. OTTERSEN to be demonstrated, for any relevant site, that phosphorylation affects AQP4 conformation (196). V. WATER AND WASTE CLEARANCE Brain function is inextricably coupled to efficient control of extracellular volume. Obviously, changes in extracellular volume and tortuosity will affect diffusion and clearance of signal molecules and other solutes (180). It is not only a question of what controls baseline volume. There is also a need to understand the rapid and dynamic changes in extracellular volume that are associated with synaptic transmission. Data have accumulated to suggest that AQP4 is involved in the control of both baseline (FIGURE 4) and dynamic extracellular volume changes (FIGURE 5). Aqp4⫺/⫺ animals show enhanced dextran diffusion in the extracellular space (15). This finding provided the first clue that AQP4 might be involved in the control of extracellular volume, although alternative mechanisms were also discussed. More direct evidence was reported in 2008, when Manley’s group demonstrated an increased extracellular space volume (by 25%) in animals deficient in AQP4 (204). There was no change in tortuosity. Consistent with an enlarged extracellular space, Aqp4⫺/⫺ animals were reported to have increased brain water content, compared with wildtype controls (18, 55). A possible explanation of these findings has been provided (55). Taking advantage of a novel glial-conditional Aqp4 knockout mouse line, evidence was obtained of a delayed resorption of brain water in the first 4 weeks postnatally. Normally, there is a rapid drop in brain water in this phase, from ⬃87 to ⬃79%. Mice lacking glial AQP4 retained more brain water than wild-type animals throughout the observation period (until adult stage, P70). Saline infusion in brains of Aqp4⫺/⫺ animals led to a more rapid increase in intracranial pressure (ICP) than did infusion in wild-type controls (140). This finding was obtained under nonphysiological conditions, but nevertheless is in line with the concept that AQP4 controls brain interstitial water resorption. It is notable that deletion of Aqp4 does not alter blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity, as reported in two of the three Aqp4⫺/⫺ lines that are currently available (34, 167). In the third line, Zhou et al. (215) concluded that Aqp4 deletion did interfere with BBB integrity, although this could not be reproduced in a more recent study of this line (167). Taken together with the large number of studies on edema development (4, 7, 19, 81, 99, 140, 176, 192), the studies on saline infusion and postnatal water resorption suggest that AQP4 can become rate limiting for efflux as well as influx of water across the blood-brain interface. The possibility that interstitial water and waste are cleared by a paravascular route was substantiated by a recent twophoton imaging study visualizing fluorescent tracers through a cranial window of living mice (69). The study 1550 concluded that a significant proportion of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) recycles into the brain along paravascular pathways. Specifically, tracers injected into the subarachnoid space entered the brain along spaces that surround penetrating arteries. The tracers rapidly distributed into the brain parenchyma and eventually accumulated around capillaries and veins, suggesting paravenous drainage pathways. Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice exhibited reduced tracer flow into the brain and delayed clearance of intraparenchymally injected tracers, including tagged amyloid-. Thus AQP4-mediated water flow along vessels may not only be relevant for clearing brain interstitial water, but also interstitial waste and soluble proteins. The possibility must be considered that AQP4 dysfunction or mislocalization (203) might contribute to the accumulation of proteins in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease. VI. EXTRACELLULAR VOLUME DYNAMICS Thirty years ago it was found that the extracellular volume is subject to rapid changes, driven by synaptic activation (31). Specifically, with the use of membrane-impermeant cations, extracellular volume reductions in the range of 5–30% were observed after high-frequency activation of excitatory pathways (180). While the mechanism of these dynamic changes remain to be explained in detail, it is now assumed that they reflect water cotransport coupled to rapid uptake of ions and transmitter in perisynaptic glial cells (95, 96) (FIGURE 5C). Water cotransport has been documented for a number of ions and transmitters, including K⫹, bicarbonate, and glutamate (211). While AQP4 occurs at particularly high densities in astrocytic endfeet, this water channel is also expressed in those delicate astrocytic processes that abut on excitatory synapses (129) (FIGURE 1A). One possibility is that this rather minor pool of AQP4 represents channels that are en route to the endfeet. The hypothesis was put forward that the perisynaptic pool of AQP4 is involved in dynamic control of extracellular space volume. If so, the next question would be whether water flux through AQP4 contributes to or dampens the observed activity-dependent shrinkage of extracellular space. In other words, there was a need to determine whether AQP4 mediates a flux of water out of the extracellular space, or whether it short-circuits the volume change by allowing water reflux to the extracellular compartment. The bidirectional nature of AQP4-mediated water transport opens for either possibility. Modeling studies favored the latter alternative (138). It was concluded that AQP4 would serve as an efflux route for astrocytic water, provided that the Na⫹/K⫹/2Cl⫺ cotransporter 1 (NKCC1) transports water along with the ions. NKCC1 is assumed to be responsible for much of the K⫹ uptake that occurs in astrocytes following synaptic activation (97). Thus the properties of this molecule have a strong impact on synap- Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org AQP4 IN BRAIN B C 82.0 80.0 P1 P8 P15 P70 0.25 0.20 0.15 +/+ Brain [3H]mannitol clearance 2.0 80.0 78.0 Tortuosity (λ) Brain water content (%) -/- AQP4 % of injected radioactivity 76.0 P28 f/f cAqp4-/- 78.0 Volume fraction (α) 84.0 P = 8.4E-06 86.0 P = 0.005 0.30 88.0 0.10 76.0 74.0 72.0 70.0 f/f cAqp4-/- forebrain f/f cAqp4-/- 1.8 1.6 1.4 brainstem 1.2 D Intrastriate injection [3H]Mannitol ECS parameters in neocortex in vivo P = 0.003 Brain water content (%) A Inflow Clearance +/+ -/- Aqp4–/– WT 100 * * 75 50 0 AQP4 1 2 Time (hours) Para-arterial influx Paravenous clearance CSF Glial limitans To cervical lymphatics Glial limitans Bloodstream CSF Interstitial fluid and solute clearance Convective bulk flow Convective bulk flow AQP4 Para-arterial influx Interstitial solutes Water flux Paravenous efflux Solute clearance FIGURE 4. AQP4 regulates interstitial fluid resorption and solute clearance. A, top panel: baseline brain water content of glial-conditional Aqp4 knockout (cAqp4⫺/⫺) mice and litter controls (f/f) at various stages of postnatal development suggests a role for AQP4 in resorption of brain water. At postnatal days P15, P28, and P70, the brain water content was significantly higher in cAqp4⫺/⫺ mice than in litter controls. Bottom panel: brain water content is increased also in adult cAqp4⫺/⫺ mice. [From Haj-Yasein et al. (55), with permission.] B: Aqp4 deletion increases extracellular space (ECS) volume without affecting tortuosity, as measured by real-time iontophoresis with tetramethylammonium. [From Yao et al. (204), with permission.] C: clearance of intraparenchymally injected mannitol is reduced in mice lacking AQP4. D: hypothetical pathway for brain water flow and solute clearance, based on two-photon imaging of intracisternally injected fluorescent tracers and accumulation of intraparenchymally injected radiotracer (see text for explanation). [C and D from Iliff et al. (69). Reprinted with permission from AAAS.] Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org 1551 ERLEND A. NAGELHUS AND OLE P. OTTERSEN A V0 tic function and associated volume changes. Several lines of evidence had suggested that NKCC1, like many other ion transporters, also transports water (211). 10ms 5mV TMA+ The directionality of AQP4-mediated water transport was tested in Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice (FIGURE 5, A AND B). The results were clear: deletion of Aqp4 accentuates the shrinkage that is normally seen after high-frequency synaptic activation (53), in line with the prediction from modeling studies (138). This implies that AQP4 normally serves to counteract the dynamic volume changes, by allowing water reflux from perisynaptic glia. This conclusion is valid even if one takes into account that wild-type and Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice might differ in regard to the baseline extracellular space volume. Wild-type Aqp4–/– % ECS change % ECS change rad B 0 –4 0 –4 –8 –8 –60 0 20 Time (s) 40 60 C Endfoot Pre-synaptic Kir4.1 K+ 2K+ NKCC1 Na+,K+,2Cl– H2O Na+,K+ATPase 3Na+ ADP Glutamate, 3Na+, H+ GluR GLT1 H2O Post-synaptic K+ AQP4 Astrocyte FIGURE 5. AQP4 regulates extracellular space (ECS) volume during neuronal activity. A: schematic drawing of a hippocampal slice showing the localization of the stimulating and extracellular voltage (Vo, green) and ion-sensitive recording (TMA⫹, tetramethylammonium) electrodes. Representative traces from synaptic responses (fEPSP) of wild-type (blue) and Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice are shown. B: deletion of Aqp4 accentuated ECS shrinkage in mouse hippocampal CA1 region during activation of Schaffer collateral/commissural fibers. [A and B are from Haj-Yasein et al. (53), copyright 2012. This material is reproduced with permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.] C: astrocytic channels and transporters relevant for water transport during synaptic activity. Clearance of K⫹ and glutamate from the synaptic cleft imposes a water load on astrocytes and shrinkage of ECS. The data in A indicate that AQP4 helps maintain ECS volume during synaptic activity by facilitating water efflux from astrocytes. Kir4.1, inwardly rectifying potassium channel 4.1; GLT1, glutamate transporter 1 (EAAT2); GluR, ionotropic glutamate receptor; NKCC1, Na⫹/K⫹/2Cl⫺ cotransporter 1. 1552 As water transport through AQP4 is driven by osmotic gradients, the above finding allows inferences to be made with respect to the dynamic osmolarity changes in the perisynaptic space. Specifically, a water reflux from glia must reflect a relative hyperosmolarity in the extracellular space, consequent to synaptic activation. How this happens is not clear. One possibility is that water is cotransported into glia against its concentration gradient. While transport of water against its concentration gradient may occur in some biological systems (211), there is no direct evidence for this in brain neuropil. In fact, the cotransporters known to populate perisynaptic membranes allow for isosmotic or slightly hypertonic water transport. NKCC1 is a case in point: calculations indicate that this cotransporter carries 115 water molecules per ion, while 175 water molecules per ion would be required for the transport to be isosmotic (212). It should also be considered that extracellular hyperosmolarity might be caused by activation of mechanisms responsible for regulatory volume decrease (RVD). This is a phenomenon that has been studied in detail in cultured astrocytes (9, 76). In essence, through RVD, astrocytes that are forced to swell will readjust their volume towards baseline by extrusion of osmolytes followed by osmotically driven water efflux. The time course of RVD as observed in vitro matches the time course of volume changes following synaptic activation in vivo. The recent finding that RVD depends on the presence of the transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4 (TRPV4) allows for experimental testing of this hypothesis (12). VII. POTASSIUM HOMEOSTASIS Early light microscopic (42) and electron microscopic analyses (129) revealed that AQP4 water channels are concentrated in astrocytic endfoot membranes. On the basis of this finding it was hypothesized that AQP4 is coupled to K⫹ clearance (129). Clearance of excess K⫹ is mediated through a number of mechanisms that fall in two major categories: K⫹ spatial Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org AQP4 IN BRAIN buffering and K⫹ uptake (80). A major fraction of K⫹ uptake occurs through the Na⫹/K⫹/2Cl⫺ cotransporter and represents a net movement of osmolytes across the cell membrane (96). In contrast, bona fide K⫹ spatial buffering is osmotically neutral and can be described as a K⫹ current that serves to redistribute K⫹ along the concentration gradient of this ion (137). Potassium siphoning is a special case of K⫹ spatial buffering where K⫹ influx through perisynaptic astrocytic membranes is coupled in series to K⫹ efflux through endfoot membranes (113, 120). Siphoning through the endfoot membrane domain (which typically constitute less than one-tenth of the total expanse of the astrocytic membrane) helps redistribute K⫹ from areas of high synaptic activity to remote liquid compartments (75). Potassium siphoning has been studied in detail in Müller cells (a type of retinal macroglia). These cells display a 10-fold higher K⫹ conductance in endfoot membranes than in membranes facing the neuropil (118, 119). The hypothesis that AQP4 is coupled to K⫹ clearance was first explored in Müller cells. With the use of quantitative immunogold cytochemistry, it was shown that endfoot membranes of these cells were enriched with AQP4 (114) as well as the inwardly rectifying K⫹ channel Kir4.1 (112). Double immunogold labeling at the electron microscopic level pointed to a precise colocalization of the two molecules. Based on its properties and distribution, Kir4.1 is likely to be the prime mediator of K⫹ siphoning in the retina. The concentration of Kir4.1 was ⬃10-fold higher in endfoot membranes than in glial membranes facing neuropil, consistent with the idea that Kir4.1 is responsible for K⫹ influx perisynaptically as well as for K⫹ efflux into the perivascular space and corpus vitreum (112). The reversal potential for K⫹ flux through Kir4.1 is close to the membrane resting potential, allowing for efflux as well as influx depending on the local [K⫹]o (80, 136). Recent studies indicate that Kir4.1 is involved in K⫹ spatial buffering in brain as well as in the retina (23, 54, 79). Glial-conditional deletion of the Kir4.1 gene (Kcnj10) delays K⫹ clearance following high-frequency synaptic activation, without affecting the dynamic changes of extracellular space volume (54). This implies that K⫹ clearance through Kir4.1 is osmotically neutral, as per definition when clearance occurs through spatial buffering rather than through chloride-coupled uptake. Is the precise colocalization of AQP4 with Kir4.1 indicative of a role of AQP4 in K⫹ clearance? While K⫹ is effectively excluded from the water-selective AQP4 pore, AQP4 could affect K⫹ conductance indirectly, by modulating Kir4.1 through molecular interactions or through volume changes resulting in membrane stretch (172). Depletion of ␣-syntrophin, the immediate anchoring molecule for AQP4 in endfoot membranes, results in a loss of AQP4 from these membrane domains (116). Immunogold analyses of these animals indicate that the loss is selective for AQP4 and that the concentration of Kir4.1 is unchanged. Mice lacking ␣-syntrophin were found to display a delayed clearance of K⫹ following high-frequency synaptic activation (6). These experiments were carried out in hippocampal slices. K⫹ measurements were made in the pyramidal cell layer of CA1 during and after activation of the Schaffer collaterals. Delayed K⫹ clearance was also observed following deletion of Aqp4, in two different experimental models. Binder et al. (16) activated neocortical pathways in vivo and found a more protracted removal of K⫹ in Aqp4⫺/⫺ animals than in wild-type controls. Padmawar et al. (139), using a novel K⫹-sensitive dye, showed that depletion of AQP4 resulted in delayed K⫹ clearance following cortical spreading depression. More recent studies indicate that the role of AQP4 in K⫹ clearance is complex. Analyses of hippocampal slices obtained from Aqp4⫺/⫺ animals and subjected to high-frequency synaptic activation revealed a delayed clearance of extracellular K⫹ in the pyramidal cell layer (178), in agreement with the above study of Amiry-Moghaddam et al. (6). In contrast, evidence of a more efficient K⫹ redistribution was found when measurements were made in stratum radiatum (178). To reconcile these data, it was hypothesized that Aqp4 deletion leads to a downregulation of Na⫹-K⫹ATPase activity, and to an upregulation of gap junctional coupling, both of which would affect K⫹ dynamics. Indeed, dye coupling between stratum radiatum astrocytes was increased in Aqp4⫺/⫺ animals. This finding contrasts with those of Nicchia et al. (126), who found reduced cell coupling and downregulation of connexin43 in cultured mouse astrocytes following AQP4 knockdown with small interfering RNA. Adding to the complexity, the effect of Aqp4 deletion on K⫹ buffering in stratum pyramidale was found to depend on the intensity of stimulation, being most pronounced at low stimulation intensities yielding [K⫹]o at 4 mM or below (178). As to the possible mechanisms involved, the observed effects of Aqp4 deletion could be explained if Aqp4 deletion caused a downregulation of Kir4.1. There is no evidence to support this idea. Notably, retinal Müller cells (161) and cortical astrocytes (213) from Aqp4⫺/⫺animals displayed no changes in Kir4.1-mediated currents compared with wild-type controls. While the latter experiments were done under baseline conditions, Soe et al. (172) studied the effects of osmotic stress on Kir4.1 currents in oocytes. In oocytes transfected with mRNA encoding AQP4, these currents were found to increase during swelling and decrease when oocytes were brought to shrink. The authors concluded that Kir4.1 is stretch sensitive and that AQP4 affects Kir4.1 function through facilitation of osmotically induced volume changes. Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org 1553 ERLEND A. NAGELHUS AND OLE P. OTTERSEN Compared with the factors that regulate K⫹ clearance, the mechanisms that govern peak [K⫹]o during high-frequency synaptic stimulation have received little attention. Studies in slices show that peak [K⫹]o is increased following deletion of Aqp4 (unpublished observation) and reduced following depletion of ␣-syntrophin (6). In mice lacking ␣-syntrophin, there is a redistribution of AQP4 from perivascular endfoot membranes to other astrocytic membrane domains, presumably including those astrocytic membranes that face excitatory synapses. Thus available data suggest that an inverse correlation exists between the amount of perisynaptic AQP4 and the magnitude of peak [K⫹]o during synaptic stimulation. This inverse correlation can be easily explained if peak [K⫹]o is a function of the extracellular volume shrinkage that occurs during synaptic stimulation. Obviously, the more pronounced the shrinkage, the smaller is the distribution volume of excess K⫹. One would assume that the activity-dependent shrinkage, shown to be accentuated in Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice (53), would be blunted in animals with an enhanced pool of perisynaptic AQP4 (i.e., in animals showing a mislocalization of AQP4 following deletion of the gene for ␣-syntrophin) (116). Several reports indicate that the rate of K⫹ clearance is positively correlated to the peak concentration of K⫹ (195). This could contribute to the delayed K⫹ clearance observed in animals lacking ␣-syntrophin. A recent modeling study concluded that AQP4 can regulate K⫹ uptake through effects on extracellular volume (73). VIII. NEURONAL EXCITABILITY The evidence pointing to an indirect role of AQP4 in K⫹ homeostasis prompted studies of how removal of AQP4 affects seizure severity and seizure threshold. In the first study of this issue, Amiry-Moghaddam et al. (6) observed an increased seizure severity in mice lacking ␣-syntrophin. These animals lack perivascular AQP4. Seizures were induced by hyperthermia, and seizure severity was assessed according to the Racine scale. In support of this finding, Binder et al. (16) observed that seizures induced by hippocampal stimulation were prolonged in mice lacking AQP4. The latter study also reported that higher stimulation intensities were required to induce seizures in Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice than in wild-type controls. Similarly, an increased seizure threshold following Aqp4 deletion was reported in mice administered the chemoconvulsant pentylenetetrazol (14). At first glance it would seem counterintuitive that increased seizure severity is associated with an increased seizure threshold. However, this can be explained if Aqp4⫺/⫺ animals show an increased extracellular space volume. Several studies report an enlarged extracellular space in mice lacking AQP4 (15, 204), and a recent investigation in mouse indicates that this enlargement reflects a reduced water reabsorption in the first two postnatal weeks (55). An in- 1554 creased extracellular space volume would allow for a more rapid diffusion of excess K⫹, delaying seizure onset and increasing seizure threshold. Knockout strategies may have confounding effects on other proteins than those targeted by the gene deletion. However, the finding of increased seizure severity in mice lacking ␣-syntrophin as well as in Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice strongly suggests that the effect is due to loss of AQP4. Evidence was reported of downregulation of the glutamate transporter EAAT2 (GLT1) in Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice (210), but this result awaits confirmation. The observation of increased seizure severity in animals that had been depleted of perivascular AQP4 (6) prompted the question whether clinical epilepsy is associated with a perturbed AQP4 expression. This issue was addressed in analysis of hippocampi that had been surgically removed from patients suffering from mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE). Hippocampal tissue obtained at surgery can be fixed immediately and allows for a much better ultrastructure preservation than tissue obtained from autopsy material. Hippocampi from MTLE patients showed a pronounced loss of AQP4 from perivascular astrocyte membranes (33), mimicking the loss observed in animals lacking ␣-syntrophin. This loss was restricted to the gliotic part of the hippocampus and was not due to a general downregulation of AQP4. In fact, there was an overall increase in AQP4 expression in the MTLE hippocampi, as judged by quantitative immunoblotting and real time PCR (83). Taken together, the above data indicate that MTLE is associated with changes that specifically affect the perivascular membrane domains of astrocytic endfeet. The most parsimonious explanation would be that the AQP4 loss from these membrane domains was secondary to a disruption of the DAPC known to be responsible for AQP4 anchoring at these sites. A recent and more detailed study of endfoot proteins revealed that MTLE astrocytes lose their perivascular pool of Kir4.1, as well as of syntrophin and dystrophin (60). Again, the changes were restricted to the gliotic areas of the hippocampus. -Dystroglycan was not affected, thus bolstering the hypothesis that there is a mechanism at play that interferes with the integrity of the DAPC. Abnormal proteolytic activities, such as calpain activation, should be explored as possible upstream factors leading to the perturbed expression of astrocytic endfoot proteins in MTLE. A mislocalization of AQP4 and Kir4.1 could be responsible for the loss of water and K⫹ homeostasis in MTLE hippocampi. Diffusion-weighted MR reveals a higher than normal apparent diffusion coefficient pointing to an abnormal water accumulation (68). Loss of perivascular AQP4 would be expected to impede clearance of water to the microcirculation. Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org AQP4 IN BRAIN An important question is whether the mislocalization of endfoot proteins occurs prior to the development of epilepsy or whether the changes observed are a consequence thereof. This issue has been explored in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Rodents that are exposed to kainic acid develop chronic seizures after a well-defined latent phase that is assumed to correspond to the premorbid state of MTLE patients. A loss of AQP4 and ␣-syntrophin from perivascular endfoot membranes was observed already in the latent phase, supporting the idea that these changes could be part of the pathogenic process leading to chronic seizures (3, 82). Genetic analyses support the idea that perturbations of the molecular organization of astrocytic endfoot could play a role in the epileptogenic process. Mice that lack the dystrophin complex due to a mutation in the corresponding gene (mdx mice) show increased seizure severity, but no change is seizure susceptibility (29), mimicking the phenotype of mice lacking ␣-syntrophin (6). Similarly, patients with Beckers muscular dystrophy display an increased propensity for epileptic seizures (191). These patients are known to harbor a mutation in the dystrophin gene. A case control study of a cohort of MTLE patients revealed an association between MTLE and a number of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the genes encoding AQP4 and Kir4.1 (61). However, as none of these polymorphisms could be attributed to the protein coding regions of these genes, the functional implications of these findings remain to be clarified. IX. SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY AND BEHAVIOR As discussed above, while concentrated in endfoot membranes, AQP4 is also expressed in astrocytic membranes abutting on excitatory synapses (129). The question is whether AQP4 is involved in the regulation of basal synaptic transmission. So far the results have been negative. Specifically, deletion of Aqp4 did not affect key parameters of synaptic transmission including excitability (53, 88, 171). Also, paired pulse facilitation, a form of short time plasticity, was not changed in Aqp4⫺/⫺ animals (53, 88, 171). Skucas et al. (171) found that Aqp4 knockout reduced theta burst-induced long-term potentiation (LTP) without any effect on other forms of LTP (171). Theta burst-induced LTP is characterized by a dependence on brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its tyrosine kinase B (TrkB) receptor. It is not clear why this specific form of LTP is AQP4 dependent, although several mechanisms were suggested. One hypothesis is that neurotrophins are dysregulated following deletion of Aqp4. There is a reduced longterm depression (LTD) in Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice, and the LTD can be rescued by the application of BDNF scavengers (171). Cognitive testing of Aqp4⫺/⫺ animals revealed a partial impairment of location specific object memory, while contextual fear conditioning was unchanged. Again, the mech- anisms need to be resolved (171). On the other hand, Li et al. (88) reported that Aqp4 knockout interfered with associated fear memory and high-frequency stimulation induced LTP in the lateral amygdala. The same group also found that Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice exhibited impaired memory consolidation in the Morris water maze and reduced theta burst-induced LTP (38). Taken together, the available data indicate that the effects of Aqp4 deletion on basal synaptic transmission and synaptic plasticity are rather subtle, compared with the rather robust effects on K⫹ and volume homeostasis. X. SENSORY SYSTEMS Already in the first reports on Aqp4 deletion were data provided on sensory systems. Subtle changes were found in electroretinograms (85), and evidence was provided of a partial or complete hearing loss (86). More recently, it was shown that Aqp4 deletion also interferes with olfaction (93). A. Retina In retina, AQP4 is expressed in Müller cells and in the astrocytes that reside in the nerve fiber layer (56, 114). Immunogold analyses show that AQP4 is heterogeneously distributed along the Müller cell plasma membrane, with a 10-fold enrichment in endfoot membrane domains relative to those membrane domains that face neuropil elements (114). The distribution of the inwardly rectifying K⫹ channel Kir4.1 mimics that of AQP4 (112). Only in the microvilli facing the subretinal space do the two channels differ in their subcellular localization. Thus the basal 300 – 400 m of the microvilli contain a high density of Kir4.1 channels but no detectable immunogold signal for AQP4. The finding that the distribution of AQP4 along the Müller cell plasma membrane matched the distribution of Kir4.1 and Kir4.1-mediated K⫹ conductance gave rise to the idea that AQP4 is implicated in K⫹ clearance. As discussed above, while knocking out Aqp4 has no effect on Kir4.1 function under baseline conditions, evidence has been obtained that these two molecules interact during osmotic stress (172). Studies in Aqp4 null mice revealed a significant reduction in the electroretinogram b-wave potentials. These changes were more pronounced in 10-month-old null mice than in 1-month-old mice (85). The null mice did not reveal any overt change in retinal structure. While the b-wave has been used as a measure of K⫹ spatial buffering, the relationship between Müller cell activity and b-wave is disputed (85). Clearly, further studies are needed to unravel the physiological roles of AQP4 in retina. Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org 1555 ERLEND A. NAGELHUS AND OLE P. OTTERSEN B. Inner Ear Similar to the situation in the retina, AQP4 in inner ear is expressed exclusively in nonneuronal cells. The inner ear contains several types of supporting cells. Some of these cell types contain AQP4, while others do not (66, 103, 105, 108, 181). As in the retina, the distribution of AQP4 is consistent with an indirect role in K⫹ clearance. Li and Verkman (86) reported that the auditory brain stem response to a click stimulus shows a higher threshold in Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice than in wild-type mice. The Aqp4 knockout caused a hearing deficit or a complete hearing loss, depending on genetic background. No morphological changes were observed. It was speculated that the hearing deficit was coupled to a loss of osmotic equilibration in epithelial cells in the organ of Corti. That normal hearing depends on AQP4 receives support from a recent study of a patient with a D184E mutation in the AQP4 gene (121). This patient was deaf. When expressed in oocytes, the mutated protein showed reduced water permeability compared with nonmutated AQP4 (121, 174). XI. CONCLUSIONS The 18 years that have elapsed since AQP4 was discovered in the mammalian brain have brought significant advances in our understanding of the mechanisms underlying volume, ion, and water homeostasis in brain. Progress has been particularly rapid over the past few years, with the exploitation of new imaging techniques and experimental approaches. The physiological roles of AQP4 have turned out to be many and diverse. The most robust data are those that point to a role of AQP4 in clearance of interstitial fluid from the CNS. Notably, glial-conditional knockout of Aqp4 delays postnatal resorption of extracellular fluid and leaves the mature brain with a higher than normal water content (55). These recent data tie in with the early finding that intracerebral liquid injections produce a more acute ICP increase in Aqp4⫺/⫺ animals than in wild-type controls (140). Clearance of interstitial fluid may be just one side of the coin, as water passed through the perivascular glial sheath may serve to propel a paracapillary drainage system akin to the lymphatics in peripheral tissues. Attesting to the latter function are the recent data that show delayed clearance of intracerebrally applied amyloid peptides and mannitol in Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice (69). If one assumes that a primary role of AQP4 is that of mediating water transport across the perivascular glial sheath, a number of questions will have to be resolved. First and foremost, the question arises as to what fraction of the surplus water is transported along the capillaries in the arterial or venous direction, and what fraction gains immediate access to the 1556 bloodstream following transendothelial transport. It is notable in this regard that brain endothelial cells are devoid of AQP4 and even lack AQP1, which is an endothelial marker in most peripheral organs (55). In fact, the basic question as to how water passes through brain endothelial cells remains to be addressed in quantitative terms. To the extent that water passes through brain endothelia, it is likely cotransported with glucose or lactate, or with inorganic ions such as K⫹ and Na⫹. The endothelial cells express a multitude of molecules that can contribute to water cotransport, including glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1), monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1), and NKCC1 (211). To elucidate how water is transported across the blood-brain interface, advantage can be taken of the fact that water transport through AQP4 is bidirectional. Intraperitoneal injection of water creates an osmotic driving force for water influx to brain, the route of which can be assessed by two-photon imaging and three-dimensional reconstructions. With the use of this approach, it was found that water first accumulated in pericapillary astrocytes (115). Such cells displayed significant swelling following intraperitoneal injections of distilled water. This is consistent with the idea that water influx occurs through the large pool of AQP4 that resides in the pericapillary endfeet. One important implication of the number of studies on brain edema formation and water resorption is that the perivascular glial sheath may assume a barrier function in conditions of high water flux. Obviously, the barrier is a relative one. Even if the perivascular glial processes form a continuous sheath around brain microvessels (101), these processes are not coupled by tight junctions but by gap junctional complexes that allow water to pass. Also, the plasma membrane is not entirely water impermeant even in the absence of any aquaporin. AQP4 has been implicated in a number of pathophysiological processes that have not been reviewed here. Neuroinflammation is a case in point. In a model of adoptive-transfer experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, inflammation was greatly reduced by deletion of Aqp4 (87). Furthermore, intracerebral injection of LPS produced a stronger neuroinflammatory response in wild-type than in Aqp4 knockout mice (87). There is an extensive literature on the role of AQP4 in neuromyelitis optica (NMO) (25, 26, 62, 70, 84, 106, 145, 146, 152, 153, 160). This literature was recently reviewed (72, 142). In NMO, serum autoantibodies specifically target external epitopes of AQP4 with an apparent preference for OAPs (122). Aqp4⫺/⫺ mice have been reported to show impaired glial scar formation, coupled to reduced migration of reactive astroglia towards the injury site (166). Conversely, transfection with Aqp1 or Aqp4 accelerated cell migration in an in vitro wound healing model (165). Cell migration is coupled to rapid water fluxes at the cell’s leading edge (92, Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org AQP4 IN BRAIN 165), providing a mechanistic link between aquaporin and migratory capacity. Finally, recent data suggest a role for AQP4 in astrocytic calcium signaling (185). In vivo optical imaging in mice subjected to hyposmotic stress suggest that AQP4 not only serves as an influx route for water but also is critical for initiating downstream signaling events in astrocytes. The implication of this finding is that edema might not be as passive a process as formerly believed, but a process that is coupled to release of neuroactive substances that might exacerbate the pathological outcome when an edema develops. Taken together, the data that have been accumulated thus far demonstrate that AQP4 is inextricably coupled to volume control in the brain. AQP4 regulates baseline extracellular space volume and dynamic volume changes following synaptic activation. It is involved in regulatory volume decrease, in edema formation secondary to ischemia or other pathophysiological events, and probably also in waste clearance. In brain, AQP4 stands as a multipurpose aquaporin, quite different from the situation in the kidney where several aquaporins act in concert to regulate water transport. This is not to say that AQP4 is the only aquaporin expressed in brain: AQP1, AQP9, and AQP11 also count as brain aquaporins, but these are quite restricted in their expression (AQP1, AQP9) (143) or without any clear function (AQP11) (48). The fact that AQP4 has a predominant role in brain to the exclusion of other aquaporins must not be taken to imply that this aquaporin alone holds the key to our understanding of how volume is controlled in the central nervous system. While AQP4 is a selective water transporter, a host of membrane molecules mediate water cotransport (95). In fact, for those transporters that are expressed in brain membranes, cotransport of water appears to be the rule rather than the exception. Adding to the complexity, the lipid bilayer shows a water permeability that may vary substantially across membrane domains. There is a need to develop a mathematical model for water transport that adequately takes into account the range of molecules and compartments that interact in volume homeostasis. Such a model is not close at hand. Methodological challenges abound, although some of them can be handled through innovative use of in vivo laser scan microscopy. Efforts are now made to develop drugs that can block water transport through AQP4 in clinical conditions associated with brain edema. The availability of mathematical models will be a prerequisite for safe use of such drugs, should they eventually materialize. Address for reprint requests and other correspondence: O. P. Ottersen, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, Univ. of Oslo, PO Box 1107 Blindern, N-0317 Oslo, Norway (e-mail: o.p. ottersen@medisin.uio.no). GRANTS The work was supported by the Research Council of Norway (NevroNor and FRIMEDBIO Grants), European Commision 7th Framework Programme Grant VPH-DARE@IT project (FP7-ICT-2011–9-601055), and the Letten Foundation. DISCLOSURES No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors. REFERENCES 1. Adams ME, Mueller HA, Froehner SC. In vivo requirement of the alpha-syntrophin PDZ domain for the sarcolemmal localization of nNOS and aquaporin-4. J Cell Biol 155: 113–122, 2001. 2. Agre P, King LS, Yasui M, Guggino WB, Ottersen OP, Fujiyoshi Y, Engel A, Nielsen S. Aquaporin water channels: from atomic structure to clinical medicine. J Physiol 542: 3–16, 2002. 3. Alvestad S, Hammer J, Hoddevik EH, Skare O, Sonnewald U, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP. Mislocalization of AQP4 precedes chronic seizures in the kainate model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 105: 30 – 41, 2013. 4. Amiry-Moghaddam M, Otsuka T, Hurn PD, Traystman RJ, Haug FM, Froehner SC, Adams ME, Neely JD, Agre P, Ottersen OP, Bhardwaj A. An alpha-syntrophin-dependent pool of AQP4 in astroglial end-feet confers bidirectional water flow between blood and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 2106 –2111, 2003. 5. Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP. The molecular basis of water transport in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 4: 991–1001, 2003. 6. Amiry-Moghaddam M, Williamson A, Palomba M, Eid T, de Lanerolle NC, Nagelhus EA, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Agre P, Ottersen OP. Delayed K⫹ clearance associated with aquaporin-4 mislocalization: phenotypic defects in brains of alpha-syntrophinnull mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 13615–13620, 2003. 7. Amiry-Moghaddam M, Xue R, Haug FM, Neely JD, Bhardwaj A, Agre P, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Mori S, Ottersen OP. Alpha-syntrophin deletion removes the perivascular but not endothelial pool of aquaporin-4 at the blood-brain barrier and delays the development of brain edema in an experimental model of acute hyponatremia. FASEB J 18: 542–544, 2004. 8. Anthony TL, Brooks HL, Boassa D, Leonov S, Yanochko GM, Regan JW, Yool AJ. Cloned human aquaporin-1 is a cyclic GMP-gated ion channel. Mol Pharmacol 57: 576 –588, 2000. 9. Aschner M. Volume measurements in cultured primary astrocytes. Methods Mol Biol 758: 391– 402, 2011. 10. Assentoft M, Kaptan S, Fenton RA, Hua SZ, de Groot BL, MacAulay N. Phosphorylation of rat aquaporin-4 at Ser is not required for channel gating. Glia 61: 1101–1112, 2013. 11. Badaut J, Ashwal S, Obenaus A. Aquaporins in cerebrovascular disease: a target for treatment of brain edema? Cerebrovasc Dis 31: 521–531, 2011. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS 12. Benfenati V, Caprini M, Dovizio M, Mylonakou MN, Ferroni S, Ottersen OP, AmiryMoghaddam M. An aquaporin-4/transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (AQP4/ TRPV4) complex is essential for cell-volume control in astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108: 2563–2568, 2011. We thank Gunnar F. Lothe, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, University of Oslo, for expert assistance with figures. 13. Binder DK, Nagelhus EA, Ottersen OP. Aquaporin-4 and epilepsy. Glia 60: 1203– 1214, 2012. Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org 1557 ERLEND A. NAGELHUS AND OLE P. OTTERSEN 14. Binder DK, Oshio K, Ma T, Verkman AS, Manley GT. Increased seizure threshold in mice lacking aquaporin-4 water channels. Neuroreport 15: 259 –262, 2004. 15. Binder DK, Papadopoulos MC, Haggie PM, Verkman AS. In vivo measurement of brain extracellular space diffusion by cortical surface photobleaching. J Neurosci 24: 8049 – 8056, 2004. 16. Binder DK, Yao X, Zador Z, Sick TJ, Verkman AS, Manley GT. Increased seizure duration and slowed potassium kinetics in mice lacking aquaporin-4 water channels. Glia 53: 631– 636, 2006. 17. Blank ME, Ehmke H. Aquaporin-1 and HCO3⫺-Cl⫺ transporter-mediated transport of CO2 across the human erythrocyte membrane. J Physiol 550: 419 – 429, 2003. 35. Endeward V, Gros G. Extra- and intracellular unstirred layer effects in measurements of CO2 diffusion across membranes–a novel approach applied to the mass spectrometric 18O technique for red blood cells. J Physiol 587: 1153–1167, 2009. 36. Engel A, Fujiyoshi Y, Gonen T, Walz T. Junction-forming aquaporins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 18: 229 –235, 2008. 37. Enger R, Gundersen GA, Haj-Yasein NN, Eilert-Olsen M, Thoren AE, Vindedal GF, Petersen PH, Skare O, Nedergaard M, Ottersen OP, Nagelhus EA. Molecular scaffolds underpinning macroglial polarization: an analysis of retinal Muller cells and brain astrocytes in mouse. Glia 60: 2018 –2026, 2012. 38. Fan Y, Liu M, Wu X, Wang F, Ding J, Chen J, Hu G. Aquaporin-4 promotes memory consolidation in Morris water maze. Brain Struct Funct 218: 39 –50, 2013. 18. Bloch O, Auguste KI, Manley GT, Verkman AS. Accelerated progression of kaolininduced hydrocephalus in aquaporin-4-deficient mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26: 1527–1537, 2006. 39. Fang X, Yang B, Matthay MA, Verkman AS. Evidence against aquaporin-1-dependent CO2 permeability in lung and kidney. J Physiol 542: 63– 69, 2002. 19. Bloch O, Papadopoulos MC, Manley GT, Verkman AS. Aquaporin-4 gene deletion in mice increases focal edema associated with staphylococcal brain abscess. J Neurochem 95: 254 –262, 2005. 40. Fenton RA, Moeller HB, Zelenina M, Snaebjornsson MT, Holen T, MacAulay N. Differential water permeability and regulation of three aquaporin 4 isoforms. Cell Mol Life Sci 67: 829 – 840, 2010. 20. Boassa D, Stamer WD, Yool AJ. Ion channel function of aquaporin-1 natively expressed in choroid plexus. J Neurosci 26: 7811–7819, 2006. 41. Friedman B, Schachtrup C, Tsai PS, Shih AY, Akassoglou K, Kleinfeld D, Lyden PD. Acute vascular disruption and aquaporin 4 loss after stroke. Stroke 40: 2182–2190, 2009. 21. Boron WF. Sharpey-Schafer lecture: gas channels. Exp Physiol 95: 1107–1130, 2010. 22. Brown D, Bouley R, Paunescu TG, Breton S, Lu HA. New insights into the dynamic regulation of water and acid-base balance by renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 302: C1421–C1433, 2012. 23. Chever O, Djukic B, McCarthy KD, Amzica F. Implication of Kir4.1 channel in excess potassium clearance: an in vivo study on anesthetized glial-conditional Kir4.1 knockout mice. J Neurosci 30: 15769 –15777, 2010. 24. Crane JM, Bennett JL, Verkman AS. Live cell analysis of aquaporin-4 m1/m23 interactions and regulated orthogonal array assembly in glial cells. J Biol Chem 284: 35850 – 35860, 2009. 42. Frigeri A, Gropper MA, Umenishi F, Kawashima M, Brown D, Verkman AS. Localization of MIWC and GLIP water channel homologs in neuromuscular, epithelial and glandular tissues. J Cell Sci 108: 2993–3002, 1995. 43. Frigeri A, Nicchia GP, Nico B, Quondamatteo F, Herken R, Roncali L, Svelto M. Aquaporin-4 deficiency in skeletal muscle and brain of dystrophic mdx mice. FASEB J 15: 90 –98, 2001. 44. Frigeri A, Nicchia GP, Verbavatz JM, Valenti G, Svelto M. Expression of aquaporin-4 in fast-twitch fibers of mammalian skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest 102: 695–703, 1998. 25. Crane JM, Lam C, Rossi A, Gupta T, Bennett JL, Verkman AS. Binding affinity and specificity of neuromyelitis optica autoantibodies to aquaporin-4 M1/M23 isoforms and orthogonal arrays. J Biol Chem 286: 16516 –16524, 2011. 45. Frydenlund DS, Bhardwaj A, Otsuka T, Mylonakou MN, Yasumura T, Davidson KG, Zeynalov E, Skare O, Laake P, Haug FM, Rash JE, Agre P, Ottersen OP, AmiryMoghaddam M. Temporary loss of perivascular aquaporin-4 in neocortex after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 13532– 13536, 2006. 26. Crane JM, Rossi A, Gupta T, Bennett JL, Verkman AS. Orthogonal array formation by human aquaporin-4: examination of neuromyelitis optica-associated aquaporin-4 polymorphisms. J Neuroimmunol 236: 93–98, 2011. 46. Furman CS, Gorelick-Feldman DA, Davidson KG, Yasumura T, Neely JD, Agre P, Rash JE. Aquaporin-4 square array assembly: opposing actions of M1 and M23 isoforms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 13609 –13614, 2003. 27. Cui Y, Bastien DA. Water transport in human aquaporin-4: molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 412: 654 – 659, 2011. 47. Gesemann M, Brancaccio A, Schumacher B, Ruegg MA. Agrin is a high-affinity binding protein of dystroglycan in non-muscle tissue. J Biol Chem 273: 600 – 605, 1998. 28. Dalloz C, Sarig R, Fort P, Yaffe D, Bordais A, Pannicke T, Grosche J, Mornet D, Reichenbach A, Sahel J, Nudel U, Rendon A. Targeted inactivation of dystrophin gene product Dp71: phenotypic impact in mouse retina. Hum Mol Genet 12: 1543–1554, 2003. 48. Gorelick DA, Praetorius J, Tsunenari T, Nielsen S, Agre P. Aquaporin-11: a channel protein lacking apparent transport function expressed in brain. BMC Biochem 7: 14, 2006. 29. De SG, Ibbadu GF, Marra R, Rotiroti D, Loiacono A, Donato Di PE, Russo E. Seizure susceptibility to various convulsant stimuli in dystrophin-deficient mdx mice. Neurosci Res 50: 37– 44, 2004. 49. Guadagno E, Moukhles H. Laminin-induced aggregation of the inwardly rectifying potassium channel, Kir4.1, and the water-permeable channel, AQP4, via a dystroglycan-containing complex in astrocytes. Glia 47: 138 –149, 2004. 30. Dermietzel R. Visualization by freeze-fracturing of regular structures in glial cell membranes. Naturwissenschaften 60: 208, 1973. 50. Gunnarson E, Axehult G, Baturina G, Zelenin S, Zelenina M, Aperia A. Lead induces increased water permeability in astrocytes expressing aquaporin 4. Neuroscience 136: 105–114, 2005. 31. Dietzel I, Heinemann U, Hofmeier G, Lux HD. Transient changes in the size of the extracellular space in the sensorimotor cortex of cats in relation to stimulus-induced changes in potassium concentration. Exp Brain Res 40: 432– 439, 1980. 51. Gunnarson E, Song Y, Kowalewski JM, Brismar H, Brines M, Cerami A, Andersson U, Zelenina M, Aperia A. Erythropoietin modulation of astrocyte water permeability as a component of neuroprotection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 1602–1607, 2009. 32. Dua RK, Devi BI, Yasha TC. Increased expression of Aquaporin-4 and its correlation with contrast enhancement and perilesional edema in brain tumors. Br J Neurosurg 24: 454 – 459, 2010. 52. Gunnarson E, Zelenina M, Axehult G, Song Y, Bondar A, Krieger P, Brismar H, Zelenin S, Aperia A. Identification of a molecular target for glutamate regulation of astrocyte water permeability. Glia 56: 587–596, 2008. 33. Eid T, Lee TS, Thomas MJ, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Bjornsen LP, Spencer DD, Agre P, Ottersen OP, de Lanerolle NC. Loss of perivascular aquaporin-4 may underlie deficient water and K⫹ homeostasis in the human epileptogenic hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 1193–1198, 2005. 53. Haj-Yasein NN, Jensen V, Ostby I, Omholt SW, Voipio J, Kaila K, Ottersen OP, Hvalby O, Nagelhus EA. Aquaporin-4 regulates extracellular space volume dynamics during high-frequency synaptic stimulation: a gene deletion study in mouse hippocampus. Glia 60: 867– 874, 2012. 34. Eilert-Olsen M, Haj-Yasein NN, Vindedal GF, Enger R, Gundersen GA, Hoddevik EH, Petersen PH, Haug FM, Skare O, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Burkhardt JM, Thoren AE, Nagelhus EA. Deletion of aquaporin-4 changes the perivascular glial protein scaffold without disrupting the brain endothelial barrier. Glia 60: 432– 440, 2012. 54. Haj-Yasein NN, Jensen V, Vindedal GF, Gundersen GA, Klungland A, Ottersen OP, Hvalby O, Nagelhus EA. Evidence that compromised K⫹ spatial buffering contributes to the epileptogenic effect of mutations in the human Kir4.1 gene (KCNJ10). Glia 59: 1635–1642, 2011. 1558 Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org AQP4 IN BRAIN 55. Haj-Yasein NN, Vindedal GF, Eilert-Olsen M, Gundersen GA, Skare O, Laake P, Klungland A, Thoren AE, Burkhardt JM, Ottersen OP, Nagelhus EA. Glial-conditional deletion of aquaporin-4 (Aqp4) reduces blood-brain water uptake and confers barrier function on perivascular astrocyte endfeet. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108: 17815–17820, 2011. 75. Karwoski CJ, Lu HK, Newman EA. Spatial buffering of light-evoked potassium increases by retinal Muller (glial) cells. Science 244: 578 –580, 1989. 56. Hamann S, Zeuthen T, La Cour M, Nagelhus EA, Ottersen OP, Agre P, Nielsen S. Aquaporins in complex tissues: distribution of aquaporins 1–5 in human and rat eye. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 274: C1332–C1345, 1998. 77. King LS, Kozono D, Agre P. From structure to disease: the evolving tale of aquaporin biology. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 687– 698, 2004. 76. Kimelberg HK, Nedergaard M. Functions of astrocytes and their potential as therapeutic targets. Neurotherapeutics 7: 338 –353, 2010. 57. Han Z, Wax MB, Patil RV. Regulation of aquaporin-4 water channels by phorbol ester-dependent protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 273: 6001– 6004, 1998. 78. Kishore BK, Mandon B, Oza NB, DiGiovanni SR, Coleman RA, Ostrowski NL, Wade JB, Knepper MA. Rat renal arcade segment expresses vasopressin-regulated water channel and vasopressin V2 receptor. J Clin Invest 97: 2763–2771, 1996. 58. Hasegawa H, Ma T, Skach W, Matthay MA, Verkman AS. Molecular cloning of a mercurial-insensitive water channel expressed in selected water-transporting tissues. J Biol Chem 269: 5497–5500, 1994. 79. Kofuji P, Ceelen P, Zahs KR, Surbeck LW, Lester HA, Newman EA. Genetic inactivation of an inwardly rectifying potassium channel (Kir4.1 subunit) in mice: phenotypic impact in retina. J Neurosci 20: 5733–5740, 2000. 59. Hedfalk K, Tornroth-Horsefield S, Nyblom M, Johanson U, Kjellbom P, Neutze R. Aquaporin gating. Curr Opin Struct Biol 16: 447– 456, 2006. 80. Kofuji P, Newman EA. Potassium buffering in the central nervous system. Neuroscience 129: 1045–1056, 2004. 60. Heuser K, Eid T, Lauritzen F, Thoren AE, Vindedal GF, Tauboll E, Gjerstad L, Spencer DD, Ottersen OP, Nagelhus EA, de Lanerolle NC. Loss of perivascular Kir4.1 potassium channels in the sclerotic hippocampus of patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 71: 814 – 825, 2012. 81. Lee DJ, Amini M, Hamamura MJ, Hsu MS, Seldin MM, Nalcioglu O, Binder DK. Aquaporin-4-dependent edema clearance following status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res 98: 264 –268, 2012. 61. Heuser K, Nagelhus EA, Tauboll E, Indahl U, Berg PR, Lien S, Nakken S, Gjerstad L, Ottersen OP. Variants of the genes encoding AQP4 and Kir4.1 are associated with subgroups of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 88: 55– 64, 2010. 62. Hinson SR, Romero MF, Popescu BF, Lucchinetti CF, Fryer JP, Wolburg H, FallierBecker P, Noell S, Lennon VA. Molecular outcomes of neuromyelitis optica (NMO)IgG binding to aquaporin-4 in astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109: 1245–1250, 2012. 63. Hiroaki Y, Tani K, Kamegawa A, Gyobu N, Nishikawa K, Suzuki H, Walz T, Sasaki S, Mitsuoka K, Kimura K, Mizoguchi A, Fujiyoshi Y. Implications of the aquaporin-4 structure on array formation and cell adhesion. J Mol Biol 355: 628 – 639, 2006. 64. Ho JD, Yeh R, Sandstrom A, Chorny I, Harries WE, Robbins RA, Miercke LJ, Stroud RM. Crystal structure of human aquaporin 4 at 1.8 A and its mechanism of conductance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 7437–7442, 2009. 65. Hofinger S, Yamamoto E, Hirano Y, Zerbetto F, Narumi T, Yasuoka K, Yasui M. Structural features of aquaporin 4 supporting the formation of arrays and junctions in biomembranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1818: 2234 –2243, 2012. 66. Huang D, Chen P, Chen S, Nagura M, Lim DJ, Lin X. Expression patterns of aquaporins in the inner ear: evidence for concerted actions of multiple types of aquaporins to facilitate water transport in the cochlea. Hear Res 165: 85–95, 2002. 67. Hub JS, de Groot BL. Does CO2 permeate through aquaporin-1? Biophys J 91: 842– 848, 2006. 68. Hugg JW, Butterworth EJ, Kuzniecky RI. Diffusion mapping applied to mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: preliminary observations. Neurology 53: 173–176, 1999. 69. Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, Plogg BA, Peng W, Gundersen GA, Benveniste H, Vates GE, Deane R, Goldman SA, Nagelhus EA, Nedergaard M. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid beta. Sci Transl Med 4: 147ra111, 2012. 70. Iorio R, Fryer JP, Hinson SR, Fallier-Becker P, Wolburg H, Pittock SJ, Lennon VA. Astrocytic autoantibody of neuromyelitis optica (NMO-IgG) binds to aquaporin-4 extracellular loops, monomers, tetramers and high order arrays. J Autoimmun 40: 21–27, 2013. 71. Itel F, Al-Samir S, Oberg F, Chami M, Kumar M, Supuran CT, Deen PM, Meier W, Hedfalk K, Gros G, Endeward V. CO2 permeability of cell membranes is regulated by membrane cholesterol and protein gas channels. FASEB J 26: 5182–5191, 2012. 72. Jarius S, Wildemann B. AQP4 antibodies in neuromyelitis optica: diagnostic and pathogenetic relevance. Nat Rev Neurol 6: 383–392, 2010. 73. Jin BJ, Zhang H, Binder DK, Verkman AS. Aquaporin-4-dependent K⫹ and water transport modeled in brain extracellular space following neuroexcitation. J Gen Physiol 141: 119 –132, 2013. 74. Jung JS, Bhat RV, Preston GM, Guggino WB, Baraban JM, Agre P. Molecular characterization of an aquaporin cDNA from brain: candidate osmoreceptor and regulator of water balance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 13052–13056, 1994. 82. Lee DJ, Hsu MS, Seldin MM, Arellano JL, Binder DK. Decreased expression of the glial water channel aquaporin-4 in the intrahippocampal kainic acid model of epileptogenesis. Exp Neurol 235: 246 –255, 2012. 83. Lee TS, Eid T, Mane S, Kim JH, Spencer DD, Ottersen OP, de Lanerolle NC. Aquaporin-4 is increased in the sclerotic hippocampus in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol 108: 493–502, 2004. 84. Lennon VA, Kryzer TJ, Pittock SJ, Verkman AS, Hinson SR. IgG marker of optic-spinal multiple sclerosis binds to the aquaporin-4 water channel. J Exp Med 202: 473– 477, 2005. 85. Li J, Patil RV, Verkman AS. Mildly abnormal retinal function in transgenic mice without Muller cell aquaporin-4 water channels. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43: 573–579, 2002. 86. Li J, Verkman AS. Impaired hearing in mice lacking aquaporin-4 water channels. J Biol Chem 276: 31233–31237, 2001. 87. Li L, Zhang H, Varrin-Doyer M, Zamvil SS, Verkman AS. Proinflammatory role of aquaporin-4 in autoimmune neuroinflammation. FASEB J 25: 1556 –1566, 2011. 88. Li YK, Wang F, Wang W, Luo Y, Wu PF, Xiao JL, Hu ZL, Jin Y, Hu G, Chen JG. Aquaporin-4 deficiency impairs synaptic plasticity and associative fear memory in the lateral amygdala: involvement of downregulation of glutamate transporter-1 expression. Neuropsychopharmacology 37: 1867–1878, 2012. 89. Lien CF, Mohanta SK, Frontczak-Baniewicz M, Swinny JD, Zablocka B, Gorecki DC. Absence of glial alpha-dystrobrevin causes abnormalities of the blood-brain barrier and progressive brain edema. J Biol Chem 287: 41374 – 41385, 2012. 90. Liu JW, Wakayama Y, Inoue M, Shibuya S, Kojima H, Jimi T, Oniki H. Immunocytochemical studies of aquaporin 4 in the skeletal muscle of mdx mouse. J Neurol Sci 164: 24 –28, 1999. 91. Liu X, Nakayama S, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP, Bhardwaj A. Argininevasopressin V1 but not V2 receptor antagonism modulates infarct volume, brain water content, and aquaporin-4 expression following experimental stroke. Neurocrit Care 12: 124 –131, 2010. 92. Loitto VM, Forslund T, Sundqvist T, Magnusson KE, Gustafsson M. Neutrophil leukocyte motility requires directed water influx. J Leukoc Biol 71: 212–222, 2002. 93. Lu DC, Zhang H, Zador Z, Verkman AS. Impaired olfaction in mice lacking aquaporin-4 water channels. FASEB J 22: 3216 –3223, 2008. 94. Ma T, Yang B, Gillespie A, Carlson EJ, Epstein CJ, Verkman AS. Generation and phenotype of a transgenic knockout mouse lacking the mercurial-insensitive water channel aquaporin-4. J Clin Invest 100: 957–962, 1997. 95. MacAulay N, Zeuthen T. Water transport between CNS compartments: contributions of aquaporins and cotransporters. Neuroscience 168: 941–956, 2010. 96. MacAulay N, Zeuthen T. Glial K⫹ clearance and cell swelling: key roles for cotransporters and pumps. Neurochem Res 37: 2299 –2309, 2012. Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org 1559 ERLEND A. NAGELHUS AND OLE P. OTTERSEN 97. MacVicar BA, Feighan D, Brown A, Ransom B. Intrinsic optical signals in the rat optic nerve: role for K⫹ uptake via NKCC1 and swelling of astrocytes. Glia 37: 114 –123, 2002. 98. Madrid R, Le MS, Barrault MB, Janvier K, Benichou S, Merot J. Polarized trafficking and surface expression of the AQP4 water channel are coordinated by serial and regulated interactions with different clathrin-adaptor complexes. EMBO J 20: 7008 –7021, 2001. 99. Manley GT, Fujimura M, Ma T, Noshita N, Filiz F, Bollen AW, Chan P, Verkman AS. Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat Med 6: 159 –163, 2000. 100. Mao X, Enno TL, Del Bigio MR. Aquaporin 4 changes in rat brain with severe hydrocephalus. Eur J Neurosci 23: 2929 –2936, 2006. 101. Mathiisen TM, Lehre KP, Danbolt NC, Ottersen OP. The perivascular astroglial sheath provides a complete covering of the brain microvessels: an electron microscopic 3D reconstruction. Glia 58: 1094 –1103, 2010. 102. McCoy ES, Haas BR, Sontheimer H. Water permeability through aquaporin-4 is regulated by protein kinase C and becomes rate-limiting for glioma invasion. Neuroscience 168: 971–981, 2010. 103. Mhatre AN, Stern RE, Li J, Lalwani AK. Aquaporin 4 expression in the mammalian inner ear and its role in hearing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 297: 987–996, 2002. 104. Michele DE, Barresi R, Kanagawa M, Saito F, Cohn RD, Satz JS, Dollar J, Nishino I, Kelley RI, Somer H, Straub V, Mathews KD, Moore SA, Campbell KP. Post-translational disruption of dystroglycan-ligand interactions in congenital muscular dystrophies. Nature 418: 417– 422, 2002. 105. Minami S, Kobayashi H, Yamashita A, Yanagita T, Uezono Y, Yokoo H, Shiraishi S, Saitoh T, Asada Y, Komune S, Wada A. Selective expression of aquaporin 1, 4 and 5 in the rat middle ear. Hear Res 158: 51–56, 2001. 106. Misu T, Fujihara K, Kakita A, Konno H, Nakamura M, Watanabe S, Takahashi T, Nakashima I, Takahashi H, Itoyama Y. Loss of aquaporin 4 in lesions of neuromyelitis optica: distinction from multiple sclerosis. Brain 130: 1224 –1234, 2007. 107. Mitsuma T, Tani K, Hiroaki Y, Kamegawa A, Suzuki H, Hibino H, Kurachi Y, Fujiyoshi Y. Influence of the cytoplasmic domains of aquaporin-4 on water conduction and array formation. J Mol Biol 402: 669 – 681, 2010. 108. Miyabe Y, Kikuchi T, Kobayashi T. Comparative immunohistochemical localizations of aquaporin-1 and aquaporin-4 in the cochleae of three different species of rodents. Tohoku J Exp Med 196: 247–257, 2002. 109. Moe SE, Sorbo JG, Sogaard R, Zeuthen T, Ottersen OP, Holen T. New isoforms of rat Aquaporin-4. Genomics 91: 367–377, 2008. 110. Moeller HB, Fenton RA, Zeuthen T, MacAulay N. Vasopressin-dependent short-term regulation of aquaporin 4 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuroscience 164: 1674 – 1684, 2009. 111. Musa-Aziz R, Chen LM, Pelletier MF, Boron WF. Relative CO2/NH3 selectivities of AQP1, AQP4, AQP5, AmtB, and RhAG. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 5406 –5411, 2009. 112. Nagelhus EA, Horio Y, Inanobe A, Fujita A, Haug FM, Nielsen S, Kurachi Y, Ottersen OP. Immunogold evidence suggests that coupling of K⫹ siphoning and water transport in rat retinal Muller cells is mediated by a coenrichment of Kir4.1 and AQP4 in specific membrane domains. Glia 26: 47–54, 1999. 113. Nagelhus EA, Mathiisen TM, Ottersen OP. Aquaporin-4 in the central nervous system: cellular and subcellular distribution and coexpression with Kir4.1. Neuroscience 129: 905–913, 2004. 114. Nagelhus EA, Veruki ML, Torp R, Haug FM, Laake JH, Nielsen S, Agre P, Ottersen OP. Aquaporin-4 water channel protein in the rat retina and optic nerve: polarized expression in Muller cells and fibrous astrocytes. J Neurosci 18: 2506 –2519, 1998. 115. Nase G, Helm PJ, Enger R, Ottersen OP. Water entry into astrocytes during brain edema formation. Glia 56: 895–902, 2008. 116. Neely JD, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP, Froehner SC, Agre P, Adams ME. Syntrophin-dependent expression and localization of Aquaporin-4 water channel protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 14108 –14113, 2001. 117. Neely JD, Christensen BM, Nielsen S, Agre P. Heterotetrameric composition of aquaporin-4 water channels. Biochemistry 38: 11156 –11163, 1999. 1560 118. Newman EA. Regional specialization of retinal glial cell membrane. Nature 309: 155– 157, 1984. 119. Newman EA. Distribution of potassium conductance in mammalian Muller (glial) cells: a comparative study. J Neurosci 7: 2423–2432, 1987. 120. Newman EA, Frambach DA, Odette LL. Control of extracellular potassium levels by retinal glial cell K⫹ siphoning. Science 225: 1174 –1175, 1984. 121. Nicchia GP, Ficarella R, Rossi A, Giangreco I, Nicolotti O, Carotti A, Pisani F, Estivill X, Gasparini P, Svelto M, Frigeri A. D184E mutation in aquaporin-4 gene impairs water permeability and links to deafness. Neuroscience 197: 80 – 88, 2011. 122. Nicchia GP, Mastrototaro M, Rossi A, Pisani F, Tortorella C, Ruggieri M, Lia A, Trojano M, Frigeri A, Svelto M. Aquaporin-4 orthogonal arrays of particles are the target for neuromyelitis optica autoantibodies. Glia 57: 1363–1373, 2009. 123. Nicchia GP, Rossi A, Mola MG, Pisani F, Stigliano C, Basco D, Mastrototaro M, Svelto M, Frigeri A. Higher order structure of aquaporin-4. Neuroscience 168: 903–914, 2010. 124. Nicchia GP, Rossi A, Mola MG, Procino G, Frigeri A, Svelto M. Actin cytoskeleton remodeling governs aquaporin-4 localization in astrocytes. Glia 56: 1755–1766, 2008. 125. Nicchia GP, Rossi A, Nudel U, Svelto M, Frigeri A. Dystrophin-dependent and -independent AQP4 pools are expressed in the mouse brain. Glia 56: 869 – 876, 2008. 126. Nicchia GP, Srinivas M, Li W, Brosnan CF, Frigeri A, Spray DC. New possible roles for aquaporin-4 in astrocytes: cell cytoskeleton and functional relationship with connexin43. FASEB J 19: 1674 –1676, 2005. 127. Nielsen S, Chou CL, Marples D, Christensen EI, Kishore BK, Knepper MA. Vasopressin increases water permeability of kidney collecting duct by inducing translocation of aquaporin-CD water channels to plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 1013– 1017, 1995. 128. Nielsen S, Frokiaer J, Marples D, Kwon TH, Agre P, Knepper MA. Aquaporins in the kidney: From molecules to medicine. Physiol Rev 82: 205–244, 2002. 129. Nielsen S, Nagelhus EA, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Bourque C, Agre P, Ottersen OP. Specialized membrane domains for water transport in glial cells: high-resolution immunogold cytochemistry of aquaporin-4 in rat brain. J Neurosci 17: 171–180, 1997. 130. Niermann H, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Holthoff K, Witte OW, Ottersen OP. A novel role of vasopressin in the brain: modulation of activity-dependent water flux in the neocortex. J Neurosci 21: 3045–3051, 2001. 131. Noel G, Tham DK, Moukhles H. Interdependence of laminin-mediated clustering of lipid rafts and the dystrophin complex in astrocytes. J Biol Chem 284: 19694 –19704, 2009. 132. Noell S, Fallier-Becker P, Beyer C, Kroger S, Mack AF, Wolburg H. Effects of agrin on the expression and distribution of the water channel protein aquaporin-4 and volume regulation in cultured astrocytes. Eur J Neurosci 26: 2109 –2118, 2007. 133. Noell S, Fallier-Becker P, Deutsch U, Mack AF, Wolburg H. Agrin defines polarized distribution of orthogonal arrays of particles in astrocytes. Cell Tissue Res 337: 185– 195, 2009. 134. Noell S, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Mack AF, Beedle AM, Satz JS, Campbell KP, Wolburg H, Fallier-Becker P. Evidence for a role of dystroglycan regulating the membrane architecture of astroglial endfeet. Eur J Neurosci 33: 2179 –2186, 2011. 135. Noell S, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Mack AF, Ritz R, Tatagiba M, Beschorner R, Wolburg H, Fallier-Becker P. Dynamics of expression patterns of AQP4, dystroglycan, agrin and matrix metalloproteinases in human glioblastoma. Cell Tissue Res 347: 429 – 441, 2012. 136. Olsen ML, Sontheimer H. Functional implications for Kir4.1 channels in glial biology: from K⫹ buffering to cell differentiation. J Neurochem 107: 589 – 601, 2008. 137. Orkand RK, Nicholls JG, Kuffler SW. Effect of nerve impulses on the membrane potential of glial cells in the central nervous system of amphibia. J Neurophysiol 29: 788 – 806, 1966. 138. Ostby I, Oyehaug L, Einevoll GT, Nagelhus EA, Plahte E, Zeuthen T, Lloyd CM, Ottersen OP, Omholt SW. Astrocytic mechanisms explaining neural-activity-induced shrinkage of extraneuronal space. PLoS Comput Biol 5: e1000272, 2009. Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org AQP4 IN BRAIN 139. Padmawar P, Yao X, Bloch O, Manley GT, Verkman AS. K⫹ waves in brain cortex visualized using a long-wavelength K⫹-sensing fluorescent indicator. Nat Methods 2: 825– 827, 2005. 160. Rossi A, Ratelade J, Papadopoulos MC, Bennett JL, Verkman AS. Neuromyelitis optica IgG does not alter aquaporin-4 water permeability, plasma membrane M1/M23 isoform content, or supramolecular assembly. Glia 60: 2027–2039, 2012. 140. Papadopoulos MC, Manley GT, Krishna S, Verkman AS. Aquaporin-4 facilitates reabsorption of excess fluid in vasogenic brain edema. FASEB J 18: 1291–1293, 2004. 161. Ruiz-Ederra J, Zhang H, Verkman AS. Evidence against functional interaction between aquaporin-4 water channels and Kir4.1 potassium channels in retinal Muller cells. J Biol Chem 282: 21866 –21872, 2007. 141. Papadopoulos MC, Verkman AS. Aquaporin-4 gene disruption in mice reduces brain swelling and mortality in pneumococcal meningitis. J Biol Chem 280: 13906 –13912, 2005. 142. Papadopoulos MC, Verkman AS. Aquaporin 4 and neuromyelitis optica. Lancet Neurol 11: 535–544, 2012. 143. Papadopoulos MC, Verkman AS. Aquaporin water channels in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 14: 265–277, 2013. 144. Paul L, Madan M, Rammling M, Chigurupati S, Chan SL, Pattisapu JV. Expression of aquaporin 1 and 4 in a congenital hydrocephalus rat model. Neurosurgery 68: 462– 473, 2011. 145. Phuan PW, Ratelade J, Rossi A, Tradtrantip L, Verkman AS. Complement-dependent cytotoxicity in neuromyelitis optica requires aquaporin-4 protein assembly in orthogonal arrays. J Biol Chem 287: 13829 –13839, 2012. 146. Pittock SJ, Weinshenker BG, Lucchinetti CF, Wingerchuk DM, Corboy JR, Lennon VA. Neuromyelitis optica brain lesions localized at sites of high aquaporin 4 expression. Arch Neurol 63: 964 –968, 2006. 147. Prasad GV, Coury LA, Finn F, Zeidel ML. Reconstituted aquaporin 1 water channels transport CO2 across membranes. J Biol Chem 273: 33123–33126, 1998. 162. Rurak J, Noel G, Lui L, Joshi B, Moukhles H. Distribution of potassium ion and water permeable channels at perivascular glia in brain and retina of the Large(myd) mouse. J Neurochem 103: 1940 –1953, 2007. 163. Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC. Aquaporin-4 in brain and spinal cord oedema. Neuroscience 168: 1036 –1046, 2010. 164. Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Davies DC, Krishna S, Bell BA. Aquaporin-4 expression is increased in oedematous human brain tumours. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72: 262–265, 2002. 165. Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Hara-Chikuma M, Verkman AS. Impairment of angiogenesis and cell migration by targeted aquaporin-1 gene disruption. Nature 434: 786 – 792, 2005. 166. Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Watanabe H, Yan D, Manley GT, Verkman AS. Involvement of aquaporin-4 in astroglial cell migration and glial scar formation. J Cell Sci 118: 5691–5698, 2005. 167. Saadoun S, Tait MJ, Reza A, Davies DC, Bell BA, Verkman AS, Papadopoulos MC. AQP4 gene deletion in mice does not alter blood-brain barrier integrity or brain morphology. Neuroscience 161: 764 –772, 2009. 148. Preston GM, Carroll TP, Guggino WB, Agre P. Appearance of water channels in Xenopus oocytes expressing red-cell Chip28 protein. Science 256: 385–387, 1992. 168. Shen XQ, Miyajima M, Ogino I, Arai H. Expression of the water-channel protein aquaporin 4 in the H-Tx rat: possible compensatory role in spontaneously arrested hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 105: 459 – 464, 2006. 149. Puwarawuttipanit W, Bragg AD, Frydenlund DS, Mylonakou MN, Nagelhus EA, Peters MF, Kotchabhakdi N, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Haug FM, Ottersen OP, AmiryMoghaddam M. Differential effect of alpha-syntrophin knockout on aquaporin-4 and Kir41 expression in retinal macroglial cells in mice. Neuroscience 137: 165–175, 2006. 169. Silberstein C, Bouley R, Huang Y, Fang P, Pastor-Soler N, Brown D, Van Hoek AN. Membrane organization and function of M1 and M23 isoforms of aquaporin-4 in epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287: F501–F511, 2004. 150. Rao KV, Jayakumar AR, Reddy PV, Tong X, Curtis KM, Norenberg MD. Aquaporin-4 in manganese-treated cultured astrocytes. Glia 58: 1490 –1499, 2010. 170. Skjolding AD, Rowland IJ, Sogaard LV, Praetorius J, Penkowa M, Juhler M. Hydrocephalus induces dynamic spatiotemporal regulation of aquaporin-4 expression in the rat brain. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res 7: 20, 2010. 151. Rash JE, Yasumura T, Hudson CS, Agre P, Nielsen S. Direct immunogold labeling of aquaporin-4 in square arrays of astrocyte and ependymocyte plasma membranes in rat brain and spinal cord. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 11981–11986, 1998. 152. Ratelade J, Bennett JL, Verkman AS. Evidence against cellular internalization in vivo of NMO-IgG, aquaporin-4, and excitatory amino acid transporter 2 in neuromyelitis optica. J Biol Chem 286: 45156 – 45164, 2011. 171. Skucas VA, Mathews IB, Yang J, Cheng Q, Treister A, Duffy AM, Verkman AS, Hempstead BL, Wood MA, Binder DK, Scharfman HE. Impairment of select forms of spatial memory and neurotrophin-dependent synaptic plasticity by deletion of glial aquaporin-4. J Neurosci 31: 6392– 6397, 2011. 172. Soe R, MacAulay N, Klaerke DA. Modulation of Kir4.1 Kir-Kir5.1 channels by small changes in cell volume. Neurosci Lett 457: 80 – 84, 2009. 153. Ratelade J, Zhang H, Saadoun S, Bennett JL, Papadopoulos MC, Verkman AS. Neuromyelitis optica IgG and natural killer cells produce NMO lesions in mice without myelin loss. Acta Neuropathol 123: 861– 872, 2012. 173. Solenov E, Watanabe H, Manley GT, Verkman AS. Sevenfold-reduced osmotic water permeability in primary astrocyte cultures from AQP-4-deficient mice, measured by a fluorescence quenching method. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286: C426 –C432, 2004. 154. Rauch SM, Huen K, Miller MC, Chaudry H, Lau M, Sanes JR, Johanson CE, Stopa EG, Burgess RW. Changes in brain beta-amyloid deposition and aquaporin 4 levels in response to altered agrin expression in mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 70: 1124 – 1137, 2011. 174. Sorani MD, Zador Z, Hurowitz E, Yan D, Giacomini KM, Manley GT. Novel variants in human Aquaporin-4 reduce cellular water permeability. Hum Mol Genet 17: 2379 – 2389, 2008. 155. Ren Z, Iliff JJ, Yang L, Yang J, Chen X, Chen MJ, Giese RN, Wang B, Shi X, Nedergaard M. “Hit & Run” model of closed-skull traumatic brain injury (TBI) reveals complex patterns of post-traumatic AQP4 dysregulation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33: 834 – 845, 2013. 156. Robel S, Mori T, Zoubaa S, Schlegel J, Sirko S, Faissner A, Goebbels S, Dimou L, Gotz M. Conditional deletion of beta1-integrin in astroglia causes partial reactive gliosis. Glia 57: 1630 –1647, 2009. 157. Rossi A, Baumgart F, Van Hoek AN, Verkman AS. Post-Golgi supramolecular assembly of aquaporin-4 in orthogonal arrays. Traffic 13: 43–53, 2012. 158. Rossi A, Crane JM, Verkman AS. Aquaporin-4 Mz isoform: brain expression, supramolecular assembly and neuromyelitis optica antibody binding. Glia 59: 1056 –1063, 2011. 159. Rossi A, Moritz TJ, Ratelade J, Verkman AS. Super-resolution imaging of aquaporin-4 orthogonal arrays of particles in cell membranes. J Cell Sci 125: 4405– 4412, 2012. 175. Sorbo JG, Fleckenstein B, Ottersen OP, Holen T. Small-scale purification and mass spectrometry analysis reveal a third aquaporin-4 protein isoform of 36 kDa in rat brain. J Neurosci Methods 211: 31–39, 2012. 176. Steiner E, Enzmann GU, Lin S, Ghavampour S, Hannocks MJ, Zuber B, Ruegg MA, Sorokin L, Engelhardt B. Loss of astrocyte polarization upon transient focal brain ischemia as a possible mechanism to counteract early edema formation. Glia 60: 1646 –1659, 2012. 177. Strand L, Moe SE, Solbu TT, Vaadal M, Holen T. Roles of aquaporin-4 isoforms and amino acids in square array assembly. Biochemistry 48: 5785–5793, 2009. 178. Strohschein S, Huttmann K, Gabriel S, Binder DK, Heinemann U, Steinhauser C. Impact of aquaporin-4 channels on K⫹ buffering and gap junction coupling in the hippocampus. Glia 59: 973–980, 2011. 179. Suzuki H, Nishikawa K, Hiroaki Y, Fujiyoshi Y. Formation of aquaporin-4 arrays is inhibited by palmitoylation of N-terminal cysteine residues. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778: 1181–1189, 2008. Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org 1561 ERLEND A. NAGELHUS AND OLE P. OTTERSEN 180. Sykova E, Nicholson C. Diffusion in brain extracellular space. Physiol Rev 88: 1277– 1340, 2008. 196. Walz T, Fujiyoshi Y, Engel A. The AQP structure and functional implications. Handb Exp Pharmacol 31–56, 2009. 181. Takumi Y, Nagelhus EA, Eidet J, Matsubara A, Usami S, Shinkawa H, Nielsen S, Ottersen OP. Select types of supporting cell in the inner ear express aquaporin-4 water channel protein. Eur J Neurosci 10: 3584 –3595, 1998. 197. Wang Y, Tajkhorshid E. Nitric oxide conduction by the brain aquaporin AQP4. Proteins 78: 661– 670, 2010. 182. Tang Y, Wu P, Su J, Xiang J, Cai D, Dong Q. Effects of Aquaporin-4 on edema formation following intracerebral hemorrhage. Exp Neurol 223: 485– 495, 2010. 183. Tang Z, Sun X, Huo G, Xie Y, Shi Q, Chen S, Wang X, Liao Z. Protective effects of erythropoietin on astrocytic swelling after oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation: mediation through AQP4 expression and MAPK pathway. Neuropharmacology 67C: 8 –15, 2012. 184. Tani K, Mitsuma T, Hiroaki Y, Kamegawa A, Nishikawa K, Tanimura Y, Fujiyoshi Y. Mechanism of aquaporin-4’s fast and highly selective water conduction and proton exclusion. J Mol Biol 389: 694 –706, 2009. 185. Thrane AS, Rappold PM, Fujita T, Torres A, Bekar LK, Takano T, Peng W, Wang F, Thrane VR, Enger R, Haj-Yasein NN, Skare O, Holen T, Klungland A, Ottersen OP, Nedergaard M, Nagelhus EA. Critical role of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) in astrocytic Ca2⫹ signaling events elicited by cerebral edema. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108: 846 – 851, 2011. 186. Thrane AS, Takano T, Thrane VR, Wang F, Peng W, Ottersen OP, Nedergaard M, Nagelhus EA. In vivo NADH fluorescence imaging indicates effect of aquaporin-4 deletion on oxygen microdistribution in cortical spreading depression J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33: 996 –999, 2013. 187. Tomas-Camardiel M, Venero JL, Herrera AJ, de Pablos RM, Pintor-Toro JA, Machado A, Cano J. Blood-brain barrier disruption highly induces aquaporin-4 mRNA and protein in perivascular and parenchymal astrocytes: protective effect by estradiol treatment in ovariectomized animals. J Neurosci Res 80: 235–246, 2005. 188. Tornroth-Horsefield S, Wang Y, Hedfalk K, Johanson U, Karlsson M, Tajkhorshid E, Neutze R, Kjellbom P. Structural mechanism of plant aquaporin gating. Nature 439: 688 – 694, 2006. 189. Tourdias T, Dragonu I, Fushimi Y, Deloire MS, Boiziau C, Brochet B, Moonen C, Petry KG, Dousset V. Aquaporin 4 correlates with apparent diffusion coefficient and hydrocephalus severity in the rat brain: a combined MRI-histological study. Neuroimage 47: 659 – 666, 2009. 198. Wang Z, Meng CJ, Shen XM, Shu Z, Ma C, Zhu GQ, Liu HX, He WC, Sun XB, Huo L, Zhang J, Chen G. Potential contribution of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, aquaporin-4, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 to blood-brain barrier disruption and brain edema after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Mol Neurosci 48: 273–280, 2012. 199. Wolburg H. Orthogonal arrays of intramembranous particles: a review with special reference to astrocytes. J Hirnforsch 36: 239 –258, 1995. 200. Wolburg H, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Fallier-Becker P, Noell S, Mack AF. Structure and functions of aquaporin-4-based orthogonal arrays of particles. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 287: 1– 41, 2011. 201. Yang B, Brown D, Verkman AS. The mercurial insensitive water channel (AQP-4) forms orthogonal arrays in stably transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem 271: 4577– 4580, 1996. 202. Yang B, Verbavatz JM, Song Y, Vetrivel L, Manley G, Kao WM, Ma T, Verkman AS. Skeletal muscle function and water permeability in aquaporin-4 deficient mice. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 278: C1108 –C1115, 2000. 203. Yang J, Lunde LK, Nuntagij P, Oguchi T, Camassa LM, Nilsson LN, Lannfelt L, Xu Y, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP, Torp R. Loss of astrocyte polarization in the tg-ArcSwe mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 27: 711–722, 2011. 204. Yao X, Hrabetova S, Nicholson C, Manley GT. Aquaporin-4-deficient mice have increased extracellular space without tortuosity change. J Neurosci 28: 5460 –5464, 2008. 205. Yu J, Yool AJ, Schulten K, Tajkhorshid E. Mechanism of gating and ion conductivity of a possible tetrameric pore in aquaporin-1. Structure 14: 1411–1423, 2006. 206. Yukutake Y, Tsuji S, Hirano Y, Adachi T, Takahashi T, Fujihara K, Agre P, Yasui M, Suematsu M. Mercury chloride decreases the water permeability of aquaporin-4reconstituted proteoliposomes. Biol Cell 100: 355–363, 2008. 207. Yukutake Y, Yasui M. Regulation of water permeability through aquaporin-4. Neuroscience 168: 885– 891, 2010. 208. Zelenina M. Regulation of brain aquaporins. Neurochem Int 57: 468 – 488, 2010. 190. Tourdias T, Mori N, Dragonu I, Cassagno N, Boiziau C, Aussudre J, Brochet B, Moonen C, Petry KG, Dousset V. Differential aquaporin 4 expression during edema build-up and resolution phases of brain inflammation. J Neuroinflammation 8: 143, 2011. 209. Zelenina M, Zelenin S, Bondar AA, Brismar H, Aperia A. Water permeability of aquaporin-4 is decreased by protein kinase C and dopamine. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283: F309 –F318, 2002. 191. Tsao CY, Mendell JR. Coexisting muscular dystrophies and epilepsy in children. J Child Neurol 21: 148 –150, 2006. 210. Zeng XN, Sun XL, Gao L, Fan Y, Ding JH, Hu G. Aquaporin-4 deficiency downregulates glutamate uptake and GLT-1 expression in astrocytes. Mol Cell Neurosci 34: 34 –39, 2007. 192. Vajda Z, Pedersen M, Fuchtbauer EM, Wertz K, Stodkilde-Jorgensen H, Sulyok E, Doczi T, Neely JD, Agre P, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S. Delayed onset of brain edema and mislocalization of aquaporin-4 in dystrophin-null transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 13131–13136, 2002. 193. Verbavatz JM, Ma T, Gobin R, Verkman AS. Absence of orthogonal arrays in kidney, brain and muscle from transgenic knockout mice lacking water channel aquaporin-4. J Cell Sci 110: 2855–2860, 1997. 194. Verkman AS. Aquaporins in clinical medicine. Annu Rev Med 63: 303–316, 2012. 195. Wallraff A, Kohling R, Heinemann U, Theis M, Willecke K, Steinhauser C. The impact of astrocytic gap junctional coupling on potassium buffering in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 26: 5438 –5447, 2006. 1562 211. Zeuthen T. Water-transporting proteins. J Membr Biol 234: 57–73, 2010. 212. Zeuthen T, MacAulay N. Cotransport of water by Na⫹-K⫹-2Cl⫺ cotransporters expressed in Xenopus oocytes: NKCC1 versus NKCC2. J Physiol 590: 1139 –1154, 2012. 213. Zhang H, Verkman AS. Aquaporin-4 independent Kir 4.1 K⫹ channel function in brain glial cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 37: 1–10, 2008. 214. Zhang H, Verkman AS. Evidence against involvement of aquaporin-4 in cell-cell adhesion. J Mol Biol 382: 1136 –1143, 2008. 215. Zhou J, Kong H, Hua X, Xiao M, Ding J, Hu G. Altered blood-brain barrier integrity in adult aquaporin-4 knockout mice. Neuroreport 19: 1–5, 2008. Physiol Rev • VOL 93 • OCTOBER 2013 • www.prv.org