Figurative Language Name:__________________________________Period/Days:______________ Alliteration
advertisement

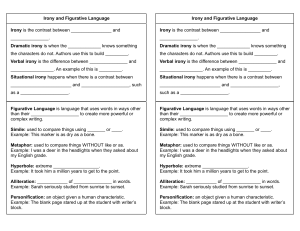
Figurative Language Name:__________________________________Period/Days:______________ Alliteration Allusion Generalization Hyperbole Imagery Irony Metaphor Personification Point of View Satire Simile Theme Tone Figurative Language Name:__________________________________Period/Days:______________ Alliteration The repetition of initial consonant sounds in neighboring words. (She sells seashells) Allusion An implied or indirect reference in literature to a familiar person, place or event. (Referral to Bible stories, songs, historical figures, In Animal Farm, the leader of the animals is a monarchic pig name Napoleon.) Generalizations To make a general overarching conclusion about a people or things. (All movies are boring.) Hyperbole An exaggeration or overstatement (I was so embarrassed I could have died). Imagery A vivid description that produces mental images. The image produced can be an emotion, a sensation, or a visual picture. ("A bed supported on massive pillars of mahogany, hung with curtains of deep red cloth . . ." Jane Eyre The use of a word or phrase to mean the exact opposite of its real meaning; when the outcome is the opposite of what’s expected. (It’s ironic that in Home Alone Kevin was able to thwart two robbers. Viewers would expect the opposite to happen). The comparison of two unlike things in which no words of comparison (like or as) are used (The clouds were cotton puffs floating in the sky.). Irony Metaphor Personification An object or abstract idea given human qualities or human form (Flowers danced about the lawn.). Point of View The way in which an author reveals characters, events and ideas in telling a story; the vantage point from which the story is told. Satire A literary tone used to make fun of a human weakness. (In Gulliver's Travels, Jonathan Swift ridicules the absurd manners and traditions of the British.) Simile A comparison of two unlike things in which a word of comparison (like or as) is used. (I wandered lonely as a cloud.) Theme A topic of discussion or writing; a major idea broad enough to cover the entire scope of a literary work. Tone The attitude of the author toward the audience and characters (serious or humorous).