Skin Body’s outer covering Integument Body’s largest organ (over 9 pounds)
advertisement
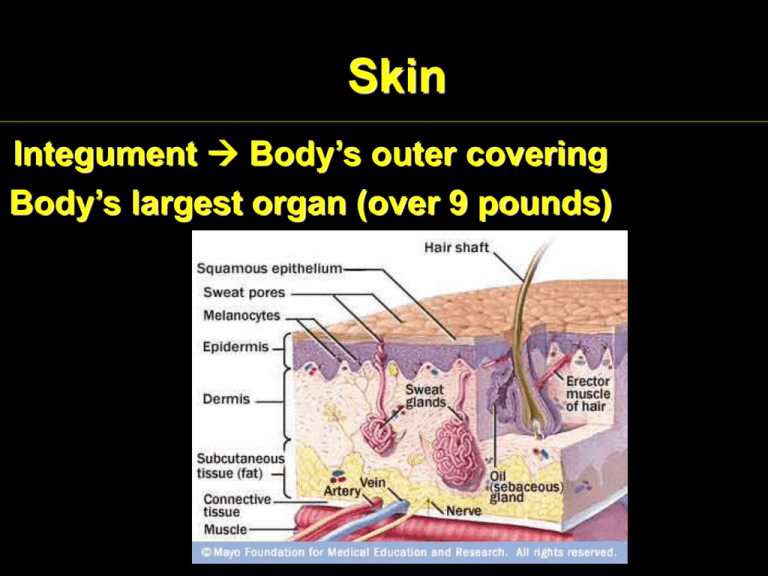
Skin Integument Body’s outer covering Body’s largest organ (over 9 pounds) Skin Functions •Prevents dehydration; infection •Produces Vitamin D •Regulates Body Temperature •Dermis has 10% of body’s blood vessels Blood vessels in dermis Layers of Skin Epidermis •Made of keratinocytes; produce the protein keratin •Outer skin cells are dead & flattened •Deeper layer of epidermis contains melanocytes, contain pigments Layers of the Skin Dermis •Protects internal structures in the body •Made of Dense Irregular Connective Tissue •Some epithelial cells (hair follicles) •Nervous Tissue (receptors) •Blood vessels •Nutrients diffuse through bloodstream through dermis •Glands, fingernails & hair follicles originate in dermal tissue Accessory Organs of the Skin •Hair follicles: rooted in the dermis, extend through epidermis •Arrector Pili muscles give us goose bumps •Pigment: melanin gives our skin its color Accessory Organs of the Skin Merocrine Glands (Sweat Glands) Found in armpits, palms of hands, and forehead Originate in dermis Used to regulate body temperature Accessory Organs of the Skin Sebaceous Glands (Oil Glands) Found everywhere on the body (except on palms and feet) Oil softens hair follicles & kills bacteria In acne, oil glands become infected with bacteria, skin becomes inflamed Accessory Organs of the Skin Apocrine Glands (A Type of Sweat Gland) Glands that connect into the ducts of hair follicles Secreted in response to stress and emotion Odorous secretions Found in armpits and groin Regulation of Body Temperature When body temperature is low •Hypothalamus signals glands on skin to decrease sweat production •If body temperature is still low •Hypothalamus signals muscles of the skin to shiver •This brings blood to surface of skin, warming the body Regulation of Body Temperature If body temperature is high •Hypothalamus signals glands on skin to increase sweat production •That water must be replaced! •If not, heat exhaustion/heat stroke











