Chapter 5 Part 1 – climate
advertisement

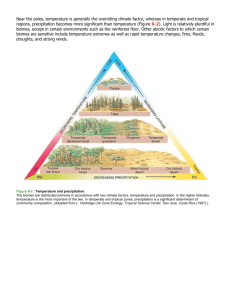
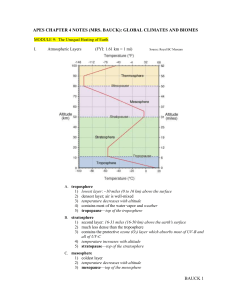
Chapter 5 Part 1 – climate Climate - a region’s general pattern of atmospheric or weather conditions over a long period of time. They are determined by average temperature, average precipitation, latitude and elevation. Four major factors determine global air circulation (convection) 1) Uneven heating of the earth’s surface by the sun - equator heat faster than the poles - variations in elevations (valley vs. mountains) (rain shadow effect – Sierra Nevada’s) - microclimates – cities – heat island effect – heat from concrete and metal in cities 2) Seasonal changes in temperature and precipitation - the tilt of the Earth’s axis causing the various seasons 3) Rotation of the earth on its axis - As cold and warm air move south and north the rotation (Coriolis Effect) deflects the air east and west 4) Properties of air, water, and land - water evaporates and circulates in atmosphere - amount of reflectivity (albedo) of surface light vs. dark - water and land heat differently - sea and land breezes (monsoons in India – low pressure over land brings in moisture for the ocean) Ocean currents affect climates EX. Gulf stream and England Difference in water temperature create currents convection Irregular shaped continents interrupt these currents and cause them to flow clockwise in rough circular patterns. Greenhouse Effect – Greenhouse gases - Terrestrial Biomes – Large geographic regions characterized by similar climate, soil, plants, and animals Why are biomes not uniform but a mosaic of patches? Why do latitudinal patterns exist among the world’s biomes? Biome Reports Create a chart for each of biomes and include the following headings: abiotic characteristics, characteristic plants and animals, plant and animal adaptation. Desert Tropical Grassland Temperate Grassland Tundra Chaparral Tropical Rainforests Deciduous Forest Coniferous Forest Mountains