Alternative Energies (notes L-1) The following are renewable: hydropower, solar, wind,
advertisement

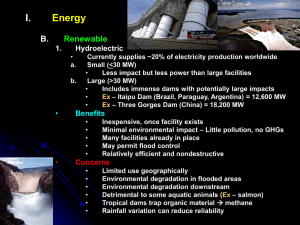
Alternative Energies (notes L-1) - Energies that are not fossil fuels. Most are renewable. The following are renewable: hydropower, solar, wind, geothermal, biomass, hydrogen, tidal, and wave. Research toward alternative energies started in the 70’s due to the oil embargo and are continuing today due to foreign oil dependency and environmental concerns. Only about 5% of today’s energy in the U.S. is renewable. Hydropower – This uses the mechanical power of flowing water to generate electricity. Power depends on the amount of water (flow) and the distance it falls (head). (diagram pg. 450) - Accounts for 6% of electricity in the U.S. - It is the most widely used source of alternative energy in the U.S. - Will not increase in the U.S. because most suitable sites have been used. 1 Impacts - Renewable, nonpolluting, and reliable. - Costly to build and funds to build new dams have not been approved in more than a decade. - Dams disrupt the environment and create different habitats. - Block fish migration (fish lifts) Fish lift video - Dams can fill with sediment becoming useless if not maintained. - Hydropower is on the decline Wind – use of wind to spin turbine to generate electricity. - Researches are looking for ways to store energy and reduce cost. - Fastest growing energy source in the world. (costal Europe) - 3.5% of world’s electricity but could produce up to 30% by 2050 - Electricity is almost as cheap as fossil fuel in areas with strong winds. - Most effective on coasts, mountains, and open plains but now found in many areas - Winds farms exist in PA, West Virginia, and New York and - Impacts - Few environmental impacts (noise, space, damage to bats and birds) - No air pollution - Becoming more available in many areas - No way to store the energy – winds may not be constant, needs a back up system Biomass (biofuels) – The burning of wood, agricultural wastes, sewage, algae, and processed trash. Also includes fuels made from organic matter. - accounts for 10% of the world’s energy – mostly wood - Various methods are used to create fuels that can be used for heating or transportation. (could possibly replace petroleum) - Sugar crops and grains can be converted through fermentation by yeast to produce ethanol. (can be blended with gasoline) Bagasse – residue from crushed sugarcane Biodiesel is a substitute for diesel engines and is made from animal fat or vegetable oils Impacts - Renewable can be quickly made - Storable and easily transported - A lot of land (wildlife habitat) would be used for large scale production of biofuels. - Some air pollution. CO2 - Processing of some organic wastes release hazardous chemicals. - Responsible for forest destruction and soil erosion in rainforests. (burning of wood) A lot of the ethanol we use is coming from South America because it is cheaper. It is destroying tropical grasslands Geothermal – uses the natural heat (dry heat, steam, or hot rock) trapped in the earth to heat homes or produce electricity. (diagram pg. 476) http://www.alternativeenergyanimations.com - power plants must be near the source because too much energy is lost during transportation. - only Hawaii, Nevada, Utah, and California have the potential - Now be offered as a home heating source in our area Impacts – Somewhat renewable – you can overdraw steam - It is limited to certain areas. - Nothing is burned so there is limited air pollution. - Harmful gases can sometime be vented with heat and land surfaces may collapse. Tidal – converts the mechanical energy from ocean tides to electricity. Gravitational effect of the moon - Limited to coastal regions and therefore will never be a major energy source in this country. (Canada, China, and France) Wave – Waves force water up a large tower pushing the air up over a turbine to generate electricity. (Norway) Hydrogen Fuel – the changing of hydrogen gas into a fuel source (gas or liquid) - Makes up most of the universe but not common on earth as a gas - Requires water (methane) and water vapor is the only product given off - The Department of Energy is looking into expanding its use (fuel cell technology) - It would require new equipment and engines (fuel cells) - fuel cell animation - Hydrogen fueled cars have been made. They are still not on the market due to cost and lack of fueling infrastructure (GM – Sequel and Hy-Wire) future car - hydrogen fuel Hydrogen car -GM Check out this web site: http://www1.eere.energy.gov/hydrogenandfuelcells/ Impacts - Pollution free. - Renewable but currently the cheapest way to make it is by using natural gas - cracking - It is too expensive and difficult to store. - It could one day replace gasoline engines and our dependency on foreign oil. - A transition from fossil fuels to hydrogen fuel will take a lot of time and money. Alternative Energies (notes L-1) - Energies that are not fossil fuels. Most are renewable. The following are renewable: _________, __________, _________, __________, _________, ________, ___________, and __________. Research toward alternative energies started in the 70’s due to the oil embargo, and are continuing today due to foreign oil dependency and environmental concerns. About ______of today’s energy in the U.S. is renewable. Hydropower – This uses the mechanical power of flowing water to generate electricity. Power depends on the amount of water (_____) and the distance it falls (______). (diagram pg. 450) - Accounts for 6% of electricity in the U.S. - Will not increase in the U.S. because most suitable sites have been used. Impacts - __________, __________, and ______________. - Costly to build and funds to build new dams have not been approved in more than a decade. - Dams disrupt the environment and create different habitats. - Dams can fill with _________ becoming useless if not maintained. - Hydropower is on the decline Wind – use of wind to spin turbine to generate electricity. - Researches are looking for ways to store energy and reduce cost. - Fastest growing energy source in the world. (costal Europe) - 3.5% of world’s electricity but could produce up to 30% by 2050 - Electricity is almost as cheap as fossil fuel in areas with strong winds. - Most effective on ________, ____________, and ___________, but now found in many areas - No way to store the energy – winds may not be constant, needs a back up system Impacts - Few environmental impacts (noise, space, damage to bats and birds) - No air pollution - Limited globally due to varying winds Biomass – The burning of ______, __________, ___________, _______, and ____________ This also includes fuels made from organic matter. - accounts for 10% of the world’s energy – mostly wood - Various methods are used to create fuels that can be used for heating or transportation. (could possibly replace petroleum) - Sugar crops and grains can be converted through fermentation by yeast to produce __________. (can be blended with gasoline) - ___________ is a substitute for diesel engines and is made from _____________ or ____________. Impacts - Renewable can be quickly made - Storable and easily transported - Some air pollution. - Processing of some organic wastes release hazardous chemicals. - Responsible for forest destruction and soil erosion in rainforests. (burning of wood) Geothermal – uses the natural heat (dry heat, steam, or hot rock) tapped in the earth to heat homes or produce electricity. (diagram pg. 476) - power plants must be near the source because too much energy is lost during transportation. - __________, ________, ________, and ________have the potential . Impacts - It is limited to certain areas as a power plant but is now being offered as a home heating source in our area - Nothing is burned so there is limited air pollution. - Harmful gases can sometime be vented with heat and land surfaces may collapse. Tidal – converts the mechanical energy from ocean tides to electricity. - Limited to coastal regions and therefore will never be a major energy source in this country. (__________, _______, and ________) Wave – Waves force water up a large tower pushing the air up over a turbine to generate electricity. (Norway) Hydrogen Fuel – the changing of hydrogen gas into a fuel source (gas or liquid) - Makes up __________ of the universe and is the lightest element. - Requires water and ___________ is the only product given off when burned - The _______________is looking into expanding its use (fuel cell technology) - It would require new equipment and engines to burn it (fuel cells) - Hydrogen fueled cars have been made. * Check out this web site: HYPERLINK "http://www.eere.energy.gov/hydrogenandfuelcells/" www.eere.energy.gov/hydrogenandfuelcells/ Impacts - Pollution free. - It is too expensive and difficult to store. - It could one day replace gasoline engines and our dependency on foreign oil. - A transition from fossil fuels to hydrogen fuel will take a lot of time and money.